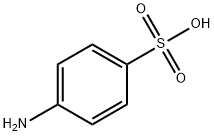
4-Aminophenylarsonic acid
Synonym(s):p-Arsanilic acid;4-Aminobenzenearsonic acid;4-Aminophenylarsonic acid;4-Arsanilic acid
- CAS NO.:98-50-0
- Empirical Formula: C6H8AsNO3
- Molecular Weight: 217.05
- MDL number: MFCD00007819
- EINECS: 202-674-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:52
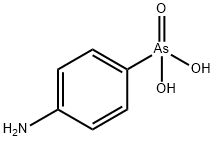
What is 4-Aminophenylarsonic acid?
Chemical properties
off-white fine crystalline powder
Chemical properties
p-Arsanilic acid is an off-white powder. It is slightly soluble in cold water. It is incompatible with oxidizing agents; on hazardous decomposition, p-arsanilic acid produces nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, nitrogen gas, and oxides of arsenic.
Originator
Arsanilic acid,Fleming Laboratories, Inc.
The Uses of 4-Aminophenylarsonic acid
4-Aminophenylarsonic acid is an organoarsenic compound. 4-Aminophenylarsonic acid is a highly toxic contaminant and can be found in plants growing in contaminated soil. 4-Aminophenylarsonic acid was used as an additive in animal feed. It has also been used in treating dysentery in swine as well as having potential chemotherapeutic activity.
The Uses of 4-Aminophenylarsonic acid
Arsanilic acid reacts essentially analogously to phenylarsonic acid. According to Chandelle, in the presence of relatively large amounts of accompanying ions the determination of zirconium gives more accurate results with this reagent than with phenylarsonic acid. This statement has not yet been confirmed. Nevertheless, the reagent is much more widely used than any other arsonic acid derivative.
The Uses of 4-Aminophenylarsonic acid
manufacture of medicinal arsenicals.
Definition
ChEBI: Arsanilic acid is an organoarsonic acid. It is a conjugate acid of an arsanilate(1-).
Manufacturing Process
342.0 g (2 mol) of 83% arsenic acid were added during 75 min to a rapidly
stirred mixture of 372.5 g (4 mol) aniline and 111.0 g chlorobenzene while
the temperature of the mixture was kept at 147°-150°C. After the addition of
arsenic acid was complete the mixture was stirred for an additional 8 h while
being maintained at 149°-153°C. Water was continuously removed by
distillation, and the organic phase of the distillate was continuously recycled back into the reaction mixture. At the end of that time a total of 121.0 g of
water, containing the condensation of aniline and arsenic acid has been
removed. The mixture was then allowed to cool to 110°C. 562.0 g (2.81 mol)
of 20% sodium hydroxide were added over a 2 h period while water,
chlorobenzene and excess aniline were distilled off at a temperature of from
102°-113°C. The distillation was continued for an additional 2 h while the
volume of the mixture was kept at about 700 ml by the addition of water.
The mixture was then diluted with water to a volume of 1400 ml and allowed
to cool to 23°C. At this point, 52.0 g of by-product material, which was
predominantly tri-(p-aminophenyl)-arsineoxide, were filtered out. The pH of
the filtrate was then brought from 8.7 to 5.1 by the addition of 1.8 mol of
hydrochloric acid while the volume of the mixture was increased to 2,200 ml
by the addition of water. The mixture was stirred for 5 h at room temperature
and again filtered. 108.0 g of by-product material comprising predominantly
di-(p-aminophenyl)-arsinic acid was filtered off at this point.
The pH of the filtrate was lowered to 4.5 by the addition of 0.2 mole of
hydrochloric acid, and an additional 5.0 g of by-products, the composition of
which was not determined, was filtered off. The filtrate was then brought to a
pH of 3.2 by addition of 0.6 mole of hydrochloric acid, and 128.0 g (29.5%
based upon arsenic acid) of arsanilic acid were recovered as a precipitate.
The arsanilic acid filtrate was combined with the by-products filtered off during
each of the three filtration steps. 2.8 mol of hydrochloric acid were added to
the combined arsanilic acid filtrate and the mixture was heated at 80°C for 5
days. Arsanilic acid was then precipitated from the remaining hydrolyzed
mixture in the manner described for the primary reaction product, and an
additional 120.0 g (27.5% based on arsenic acid) were recovered. The filtrate
contained 14.0 g (3.2%) of arsanilic acid which could be recovered at least
partially in subsequent processing. Thus it can be seen from this example that
an arsanilic acid yield of 59% was obtained.
Therapeutic Function
Antibacterial
Hazard
Toxic.
Health Hazard
Occupational workers exposed to p-arsanilic acid develop poisoning. The symptoms include, but are not limited to, eye and skin irritation, chemical conjunctivitis and corneal damage, hyperpigmentation of the skin and, perkeratoses of plantar and palmar surfaces, primary irritation and sensitization, digestive tract irritation, gastrointestinal hypermotility, diarrhea, hepatitis, hepatocellular necrosis, central nervous system depression, cardiac disturbances, and liver and kidney damage. The target organs include the kidneys, central nervous system, liver, and cardiovascular system. After a prolonged period of exposure to arsenic compounds, including arsenical dust, workers are known to develop shortness of breath, nausea, chest pains, garlic odor, and impairment of peripheral circulation. The toxicological properties of p-arsanilic acid have not been fully investigated.
Safety Profile
Poison by intravenous and intraperitoneal routes. Moderately toxic by ingestion. Flammable, decomposes with heat to yield flammable vapors. When heated to decomposition or on contact with acid or acid fumes it emits highly toxic fumes of As and NO,. See also ARSENIC COMPOUNDS and ANILINE.
storage
p-Arsanilic acid should be kept stored in a tightly closed container in a cool, dry, wellventilated area. It should be kept away from incompatible materials, dust generation, excess heat, and strong oxidants.
Purification Methods
Crystallise it from water or ethanol/ether. POISONOUS. [Beilstein 16 I 466.]
Precautions
Occupational workers should wash thoroughly after using p-arsanilic acid. Any contaminated clothing should be washed before reuse. Work areas should have adequate ventilation and minimum dust generation and accumulation. Workers should avoid any kind of contact of p-arsanilic acid with the eyes, skin, clothing, ingestion or inhalation.
Properties of 4-Aminophenylarsonic acid
| Melting point: | ≥300 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 528.5±52.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.9571 |
| solubility | Sparingly soluble in water, soluble in concentrated mineral acids, alkali
carbonate solutions, alcohol and diethyl ether. Practically insoluble in
acetone, benzene and chloroform. |
| form | solid |
| pka | pK1: ca 2;pK2: 4.02;pK3: 8.62 (25°C) |
| color | Needles from aq solns |
| Water Solubility | SLIGHTLY SOLUBLE IN COLD WATER |
| Merck | 14,792 |
| BRN | 1102334 |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 98-50-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | p-Aminobenzenearsonic acid (98-50-0) |
Safety information for 4-Aminophenylarsonic acid
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P273:Avoid release to the environment. |
Computed Descriptors for 4-Aminophenylarsonic acid
| InChIKey | XKNKHVGWJDPIRJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
4-Aminophenylarsonic acid manufacturer
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 p-Arsanilic acid 98%View Details
p-Arsanilic acid 98%View Details -
 4-Aminophenylarsonic Acid CAS 98-50-0View Details
4-Aminophenylarsonic Acid CAS 98-50-0View Details
98-50-0 -
 p-Arsanilic acid CAS 98-50-0View Details
p-Arsanilic acid CAS 98-50-0View Details
98-50-0 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1