PHENYLARSONIC ACID
- CAS NO.:98-05-5
- Empirical Formula: C6H7AsO3
- Molecular Weight: 202.04
- MDL number: MFCD00002097
- EINECS: 202-631-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:32
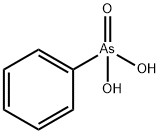
What is PHENYLARSONIC ACID?
Description
Benzenearsonic acid is a colorless, crystallinepowder. Molecular weight = 202.05; Specific gravity(H2O:1)= 1.76; Freezing/Melting point=160℃ (decomposes). Hazard Identification (based on NFPA-704 MRating System): Health 4, Flammability 1, Reactivity 0.Soluble in water.
Chemical properties
white to slightly yellow crystalline powder
Chemical properties
Benzenearsonic acid is a colorless, crystalline powder.
The Uses of PHENYLARSONIC ACID
Arsonic acids (arsonic acid, phenylarsonic acid, p-hydroxyphenylarsonic acid,
arsanilic acid) react with the tetravalent metals of group IV of the periodic
system to give water-insoluble complexes of composition MA2 . The composition
of the precipitates is not exactly stoichiometric, and hence the precipitates are not
suitable for direct gravimetric analysis. Instead, the precipitates are transformed
by ignition to the corresponding metal oxides and weighed as such. The main
advantage of the application of these reagents is the possibility offered of the
selective determination of zirconium(IV), hafnium(IV) and titanium(IV) in the
presence of many other metals, such as zinc, manganese, nickel, cobalt, aluminium,
copper, calcium, magnesium and chromium. In practice they are utilized most
frequently for the determination of zirconium.
In strong mineral acidic media phenylarsonic acid forms water-insoluble precipitates
with zirconium and hafnium only. In highly concentrated acetic acid
solution the thorium phenylarsonate complex is also precipitated, which makes
possible the separation of thorium from rare earth metals.
The procedure gives satisfactory results in the presence of alkaline earth metals,
iron, aluminium, manganese, cobalt, nickel, copper, zinc and bismuth.
The Uses of PHENYLARSONIC ACID
Reagent for tin.
Definition
ChEBI: Phenylarsonic acid is an organoarsonic acid and a member of arsonic acids. It is a conjugate acid of a phenylarsonate(1-).
General Description
Colorless solid. Used as an analytical reagent for tin.
Reactivity Profile
PHENYLARSONIC ACID emits poisonous fumes of arsenic when heated to decomposition. [EPA, 1998].
Health Hazard
PHENYLARSONIC ACID is a deadly poison. (Non-Specific -- Arsenic Compounds) Chronic exposure to arsenic compounds can cause dermatitis and digestive disorders. Renal damage may develop.
Fire Hazard
PHENYLARSONIC ACID emits poisonous fumes of arsenic when heated to decomposition.
Safety Profile
A deadly poison by ingestion andintravenous routes. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of As.
Potential Exposure
This material is used as an analytical reagent for tin.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Speed in removing material from skinis of extreme importance. Shampoo hair promptly if contaminated. Seek medical attention immediately. If thischemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure, beginrescue breathing (using universal precautions, includingresuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and inducevomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.Note to physician: For severe poisoning BAL [British AntiLewisite, dimercaprol, dithiopropanol (C3H8OS2)] has beenused to treat toxic symptoms of certain heavy metals poisoning—including arsenic. Although BAL is reported tohave a large margin of safety, caution must be exercisedbecause toxic effects may be caused by excessive dosage.Most can be prevented by premedication with 1-ephedrinesulfate (CAS: 134-72-5). For milder poisoning penicillamine (not penicillin) has been used, both with mixed success. Side effects occur with such treatment and it is nevera substitute for controlling exposure. It can only be doneunder strict medical care
storage
Color Code—Blue: Health Hazard/Poison: Storein a secure poison location. Store in tightly closed containers in a cool, well-ventilated area.
Shipping
UN3280 Organoarsenic compound, liquid, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1—Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required. Potential Inhalation Hazard (Special Provision 5).
Purification Methods
Crystallise it from H2O (3mL/g) between 90o and 0o. Alternatively dissolve 600g of the acid in 500mL of boiling H2O, add 20g of Norite, filter hot, cool, filter off the crystals and dry them. On heating at ~154-160o it is converted to the anhydride. [Bullard & Dickery Org Synth Coll Vol II 494 1943, for the 4-nitro derivative see Ruddy & Starkey Org Synth Coll Vol III 665 1955, Beilstein 16 H 868, 16 I 448, 16 II 457, 16 III 1057, 16 IV 1183.]
Properties of PHENYLARSONIC ACID
| Melting point: | 160 °C |
| Boiling point: | 66 °C(Press: 1 Torr) |
| Density | 1,76 g/cm3 |
| solubility | 3.2% in water and 15.5% in ethanol. |
| form | Powder |
| pka | pK2: 8.48(+1) (22°C) |
| Specific Gravity | 1.76 |
| color | white |
| Water Solubility | 31.6g/L(28 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,1067 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 98-05-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Benzenearsonic acid (98-05-5) |
Safety information for PHENYLARSONIC ACID
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H301:Acute toxicity,oral H331:Acute toxicity,inhalation H400:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, acute hazard H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P304+P340:IF INHALED: Remove victim to fresh air and Keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing. P405:Store locked up. |
Computed Descriptors for PHENYLARSONIC ACID
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 98-05-5 Phenylarsonic acid, 99% 99%View Details
98-05-5 Phenylarsonic acid, 99% 99%View Details
98-05-5 -
 Phenylarsonic acid CAS 98-05-5View Details
Phenylarsonic acid CAS 98-05-5View Details
98-05-5 -
 Phenyl arsonic acid, GR 99% CAS 98-05-5View Details
Phenyl arsonic acid, GR 99% CAS 98-05-5View Details
98-05-5 -
 Phenylarsonic Acid CAS 98-05-5View Details
Phenylarsonic Acid CAS 98-05-5View Details
98-05-5 -
 Phenylarsonic acid CAS 98-05-5View Details
Phenylarsonic acid CAS 98-05-5View Details
98-05-5 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8