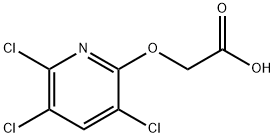
2,4,5-Trichlorophenoxyacetic acid
Synonym(s):2,4,5-T;2,4,5-Trichlorophenoxyacetic acid;Trioxone
- CAS NO.:93-76-5
- Empirical Formula: C8H5Cl3O3
- Molecular Weight: 255.48
- MDL number: MFCD00004301
- EINECS: 202-273-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:30
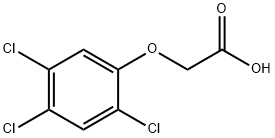
What is 2,4,5-Trichlorophenoxyacetic acid?
Chemical properties
white to light tan odourless solid
Chemical properties
2,4,5-T Acid is an odorless, colorless to tan crystalline solid.
Physical properties
Colorless to pale brown, odorless crystals. Odor threshold from water is 2.92 mg/kg (quoted, Keith and Walters, 1992). Metallic taste.
The Uses of 2,4,5-Trichlorophenoxyacetic acid
It is suitable for plant cell culture tested. Post-emergence herbicide.
The Uses of 2,4,5-Trichlorophenoxyacetic acid
Plant hormone; defoliant; herbicide used to control undesirable brush and woody plants.
The Uses of 2,4,5-Trichlorophenoxyacetic acid
2,4,5-T was formerly used as a herbicide. Itis currently not used, following a ban by theEPA.
Definition
ChEBI: A chlorophenoxyacetic acid that is phenoxyacetic acid in which the ring hydrogens at postions 2, 4 and 5 are substituted by chlorines.
General Description
Light tan solid (melting point 153°C). Insoluble in water. Contact may irritate the skin.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
2,4,5-Trichlorophenoxyacetic acid is a weak acid. Reacts with organic and inorganic bases to form water-soluble salts and with alcohols to form esters. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents and strong bases. Can corrode metals, especially if moist. May harm painted surfaces .
Health Hazard
Overexposure to dust by inhalation or ingestion may cause fatigue, nausea, vomiting, lowered blood pressure, convulsions, coma. Dust may irritate eyes and skin.
Health Hazard
The toxicity of 2,4,5-T is very similar tothat of 2,4-D. The symptoms are irritationof skin, acne-like rash, somnolence, gastritis,fatty liver degeneration, and ataxia.
LD50 value, oral (rats): 300 mg/kg
Oral administration of this compound inhamsters and mice produced fetotoxicity,as well as developmental toxic effects onthe central nervous system, eyes, ear, andprostate.
Fire Hazard
Special Hazards of Combustion Products: Toxic hydrogen chloride and phosgene gases may be formed.
Potential Exposure
Those engaged in the manufacture, formulation, and application of this herbicide used to control woody and herbaceous weeds. The EPA has issued a rebuttable presumption against registration of 2,4,5-T for pesticide uses, however. The Viet Nam war era defoliant, Agent Orange, was a mixture of 2,4,5-T and 2,4-D.
Carcinogenicity
2,4,5-T was not mutagenic in bacterial assays, and it did not induce aneuploidy or somatic mutation in vitro. In vivo it did not cause micronuclei in mice or dominant lethal mutations in mice or rats.
Environmental Fate
Biological. 2,4,5-T degraded in anaerobic sludge by reductive dechlorination to 2,4,5-
trichlorophenol, 3,4-dichlorophenol and 4-chlorophenol (Mikesell and Boyd, 1985). An anaerobic methanogenic consortium, growing on 3-chlorobenzoate, metabolized 2,4,5-T to
(2,5-dichlorophenoxy)acetic acid at a rate of 1.02 × 10–7 M/hr. The half-life was reported to
be 2 days at 37°C (Su?ita et al., 1984). Under aerobic conditions, 2,4,5-T degraded to 2,4,5-
trichlorophenol and 3,5-dichlorocatechol which may further degrade to 4-chlorocatechol or
cis,cis-2,4-dichloromuconic acid, 2-chloro-4-carboxymethylenebut-2-enolide, chlorosuccinic
acid and succinic acid (Byast and Hance, 1975). The cometabolic oxidation of 2,4,5-T by
Brevibacterium sp. yielded a product tentatively identified as 3,5-dichlorocatechol (Horvath,
1970). The cometabolism of this compound by Achromobacter sp. gave 3,5-dichloro-2-
hydroxymuconic semialdehyde (Horvath, 1970a). Rosenberg and Alexander (1980) reported
that 2,4,5-trichlorophenol, the principal degradation product of 2,4,5-T by microbes, was
further metabolized to 3,5-dichlorocatechol, 4-chlorocatechol, succinate, cis,cis-2,4-dichlo-
romuconate, 2-chloro-4-(carboxymethylene)but-2-enolide and chlorosuccinate.
Soil. 2,4,5-Trichlorophenol and 2,4,5-trichloroanisole were the primary degradation
products formed when 2,4,5-T was incubated in soil at 25°C under aerobic conditions.
The half-life under these conditions was 14 days (McCall et al., 1981a). When
The half-lives of 2,4,5-T in soil incubated in the laboratory under aerobic conditions
ranged from 14 to 64 days with an average of 33 days (Altom and Stritzke, 1973; Foster
and McKercher, 1973; Yoshida and Castro, 1975). In field soils, the disappearance
Groundwater . According to the U.S. EPA (1986) 2,4,5-T has a high potential to leach
to groundwater .
Photolytic. When 2,4,5-T (10–4 M) in oxygenated water containing titanium dioxide
(2 g/L) suspension was irradiated by sunlight (λ ≥340 nm), 2,4,5-trichlorophenol, 2,4,5-
trichlorophenyl formate and nine chlorinated aromatic hydrocarbons formed a
Solubility in water
Soluble in ethanol (548.2 mg/L), ether (243.2 mg/L), heptane (400 mg/L), xylenes (6.8 g/L), methanol (496 g/L), toluene (7.32 g/L) (quoted, Keith and Walters, 1992).
Shipping
UN2811 Toxic solids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required. UN3345 Phenoxyacetic acid derivative pesticide, solid, toxic, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials.
Purification Methods
Crystallise this herbicide from *benzene. [Beilstein 6 III 721.] (CANCER SUSPECT)
Incompatibilities
The aqueous solution is a weak acid. Incompatible with sulfuric acid, bases, ammonia, aliphatic amines; alkanolamines, isocyanates, alkylene oxides; epichlorohydrin; strong oxidizers, such as chlorine, bromine, fluorine, and strong bases.
Waste Disposal
Two disposal procedures have been discussed for 2,4,5-T: (1) Mix with excesssodium carbonate, add water and let stand for 24 hours before flushing down the drain with excess water; and (2) pour onto vermiculite and incinerate with wood, paper, and waste alcohol. In accordance with 40CFR165, follow recommendations for the disposal of pesticides and pesticide containers. Must be disposed properly by following package label directions or by contacting your local or federal environmental control agency, or by contacting your regional EPA office. Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform with EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal.
Properties of 2,4,5-Trichlorophenoxyacetic acid
| Melting point: | 154-158 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 361.82°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.6048 (rough estimate) |
| vapor pressure | 6.46 at 25 °C (Lewis, 1989) |
| refractive index | 1.4700 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 2 °C |
| storage temp. | 0-6°C |
| solubility | Soluble in ethanol (548.2 mg/L), ether (243.2 mg/L), heptane (400 mg/L), xylenes (6.8 g/L),
methanol (496 g/L), toluene (7.32 g/L) (quoted, Keith and Walters, 1992). |
| form | crystalline |
| pka | 2.80 and 2.83 at 25 °C (ionic strength <0.01 M, Jafvert et al., 1990) 2.88 (Nelson and Faust, 1969) |
| color | off-white to yellow |
| Water Solubility | 238mg/L(20 ºC) |
| Merck | 13,9111 |
| Henry's Law Constant | 4.87 at 25 °C (approximate - calculated from water solubility and vapor pressure) |
| Exposure limits | NIOSH REL: TWA 10 mg/m3, IDLH 250 mg/m3; OSHA PEL: TWA
10 mg/m3; ACGIH TLV: TWA 10 mg/m3. |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong bases, strong oxidizing agents, alkali metals, amines, alcohols. Reacts with many common metals. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 93-76-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Acetic acid, 2,4,5-trichlorophenoxy-(93-76-5) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 2,4,5-T (93-76-5) |
Safety information for 2,4,5-Trichlorophenoxyacetic acid
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H301:Acute toxicity,oral H312:Acute toxicity,dermal H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for 2,4,5-Trichlorophenoxyacetic acid
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 2-(2,4,5-Trichlorophenoxy)acetic acid 93-76-5 99%View Details
2-(2,4,5-Trichlorophenoxy)acetic acid 93-76-5 99%View Details
93-76-5 -
 Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
110-86-1 -
 Guanine , 99%View Details
Guanine , 99%View Details
73-40-5 -
 Piperazine Spot supply, best priceView Details
Piperazine Spot supply, best priceView Details
110-85-0 -
 Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
84-74-2 -
 Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
288-32-4 -
 Octadecyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate 98% (GC)View Details
Octadecyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate 98% (GC)View Details
2082-79-3 -
 Thiourea 99% ARView Details
Thiourea 99% ARView Details
62-56-6
