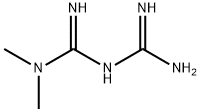
1,3-Dimethylurea
Synonym(s):1,3-Dimethylurea;DMU;N,N′-Dimethylurea
- CAS NO.:96-31-1
- Empirical Formula: C3H8N2O
- Molecular Weight: 88.11
- MDL number: MFCD00008286
- EINECS: 202-498-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
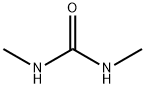
What is 1,3-Dimethylurea ?
Chemical properties
white crystals
The Uses of 1,3-Dimethylurea
N,N′-Dimethylurea can be used:
- As a starting material to synthesize N,N′-dimethyl-6-amino uracil.
- In combination with β-cyclodextrin derivatives, to form low melting mixtures (LMMs), which can be used as solvents for hydroformylation and Tsuji-Trost reactions.
- To synthesize N,N′-disubstituted-4-aryl-3,4-dihydropyrimidinones via Biginelli condensation under solvent-free conditions.
Definition
ChEBI: A member of the class of ureas that is urea substituted by methyl groups at positions 1 and 3.
General Description
Colorless crystals.
Air & Water Reactions
Water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
1,3-Dimethylurea is an amide. Amides/imides react with azo and diazo compounds to generate toxic gases. Flammable gases are formed by the reaction of organic amides/imides with strong reducing agents. Amides are very weak bases (weaker than water). Imides are less basic yet and in fact react with strong bases to form salts. That is, they can react as acids. Mixing amides with dehydrating agents such as P2O5 or SOCl2 generates the corresponding nitrile. The combustion of these compounds generates mixed oxides of nitrogen (NOx).
Health Hazard
ACUTE/CHRONIC HAZARDS: When heated to decomposition 1,3-Dimethylurea emits toxic fumes.
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for 1,3-Dimethylurea are not available; 1,3-Dimethylurea is probably combustible.
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by intraperitoneal route. Experimental teratogenic and reproductive effects. Human mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx
Purification Methods
Crystallise the urea from acetone/diethyl ether by cooling in an ice bath. Also crystallise it from EtOH and dry it at 50o/5mm for 24hours [Bloemendahl & Somsen J Am Chem Soc 107 3426 1985]. [Beilstein 4 IV 207.]
Properties of 1,3-Dimethylurea
| Melting point: | 101-104 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 268-270 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 1.142 |
| vapor pressure | 6 hPa (115 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.4715 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 157 °C |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | H2O: 0.1 g/mL, clear, colorless |
| pka | 14.57±0.46(Predicted) |
| form | Crystals |
| color | White |
| PH | 9.0-9.5 (100g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| Water Solubility | 765 g/L (21.5 ºC) |
| BRN | 1740672 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 96-31-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Urea, N,N'-dimethyl-(96-31-1) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 1,3-Dimethylurea (96-31-1) |
Safety information for 1,3-Dimethylurea
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H373:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P314:Get medical advice/attention if you feel unwell. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for 1,3-Dimethylurea
| InChIKey | MGJKQDOBUOMPEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
1,3-Dimethylurea manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
New Products
(R)-1-Boc-3-hydroxypyrrolidine Methyl (R)-1-Boc-4,4-difluoropyrrolidine-2-carboxylate 2,2-Difluoropropylamine hydrochloride tert-butyl 3-bromoazetidine-1-carboxylate DIFLUOROACETIC ANHYDRIDE 2,2-Difluoropropionic acid Diallylamine, 99% Calcium hydroxide, 95% Aluminum oxide, basic 2-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 97% L-tert-Leucine,97% N-Hydroxy-2-methylpropanimidamide 4-(3,4-Dichlorophenyl)-3,4-Dihydro-N-Methyl-1-(2H)-Naphthalenimine (Schiff Base) 2-AMINO-3,5-DIBROMO BENZALDEHYDE [ADBA] L-Glutamic Acid Dimethyl Ester Hcl 10-Methoxy-5H-dibenz[b,f]azepine 5-Cyanophthalide N, N-Carbonyldiimidazole (CDI) Dibenzoyl Peroxide Titanium Dioxide 2-(Methylthio) Benzonitrile Sodium Acetate Anhydrous Allopurinol 1,5-DibromopentaneRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 96-31-1 N,N-Dimethylurea 98%View Details
96-31-1 N,N-Dimethylurea 98%View Details
96-31-1 -
 1, 3-Dimethylurea, 98% CAS 96-31-1View Details
1, 3-Dimethylurea, 98% CAS 96-31-1View Details
96-31-1 -
 N,N-Dimethylurea (1,3-Dimethylurea) extrapure CAS 96-31-1View Details
N,N-Dimethylurea (1,3-Dimethylurea) extrapure CAS 96-31-1View Details
96-31-1 -
 N,N-Dimethylurea CAS 96-31-1View Details
N,N-Dimethylurea CAS 96-31-1View Details
96-31-1 -
 Dimethylurea. CAS 96-31-1View Details
Dimethylurea. CAS 96-31-1View Details
96-31-1 -
 1,3-Dimethylurea CAS 96-31-1View Details
1,3-Dimethylurea CAS 96-31-1View Details
96-31-1 -
 N,N-Dimethylurea CAS 96-31-1View Details
N,N-Dimethylurea CAS 96-31-1View Details
96-31-1 -
 N,N-DIMETHYLUREA For Synthesis CAS 96-31-1View Details
N,N-DIMETHYLUREA For Synthesis CAS 96-31-1View Details
96-31-1
