Valdecoxib
Synonym(s):4-(5-Methyl-3-phenyl-4-isoxazolyl)benzenesulfonamide
- CAS NO.:181695-72-7
- Empirical Formula: C16H14N2O3S
- Molecular Weight: 314.36
- MDL number: MFCD00950568
- EINECS: 803-082-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-15 14:23:52
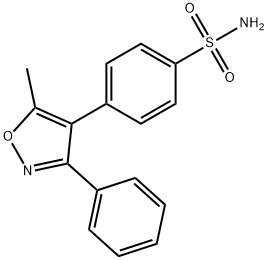
What is Valdecoxib?
Absorption
Oral bioavailability is 83%.
Toxicity
Symptoms following acute NSAID overdoses are usually limited to lethargy, drowsiness, nausea, vomiting, and epigastric pain, which are generally reversible with supportive care. Gastrointestinal bleeding can occur. Hypertension, acute renal failure, respiratory depression and coma may occur, but are rare.
Description
Valdecoxib is a second-generation COX-2 inhibitor, developed as a follow-up to celecoxib for the oral once-daily treatment of osteoarthritis, adult rheumatoid arthritis and menstrual pain. Valdecoxib is approximately 28,000-fold more selective against human recombinant COX-2 than human recombinant COX-1. In an ex viva human whole blood assay, the I&O values against COX-2 and COX-1 were respectively 0.89 PM and 25.4 FM. In animal models, valdecoxib possesses excellent oral activity as an antiinflammatory. In rats, valdecoxib potently inhibited carrageenan footpad edema and adjuvant-induced arthritis.
Chemical properties
Valdecoxib is a white crystalline powder that is relatively insoluble in water (10 μg/mL) at 25°C and pH 7.0, soluble in methanol and ethanol, and freely soluble in organic solvents and alkaline (pH=12) aqueous solutions.
Originator
Pharmacia (Searle) (USA)
The Uses of Valdecoxib
Valdecoxib is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that exhibits anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic properties in animal models. It is a potent and selective inhibitor of prostaglandin synthesis primarily through inhibition of COX-2. Valdecoxib is used to relieve some symptoms caused by arthritis (rheumatism), such as inflammation, swelling, stiffness, and joint pain.
Background
Valdecoxib was removed from the Canadian, U.S., and E.U. markets in 2005 due to concerns about a possible increased risk of heart attack and stroke.
Indications
For the treatment of osteoarthritis and dysmenorrhoea
Definition
ChEBI: Valdecoxib is a member of the class of isoxazoles that is isoxazole which is substituted at positions 3, 4 and 5 by phenyl, p-sulfamoylphenyl and methyl groups, respectively. A selective cyclooxygenase 2-inhibitor, it used as a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) for the treatment of arthritis from 2001 until 2005, when it was withdrawn following concerns of an associated increased risk of heart attack and stroke. It has a role as a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug, a cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitor, a non-narcotic analgesic, an antirheumatic drug and an antipyretic. It is a member of isoxazoles and a sulfonamide.
Preparation
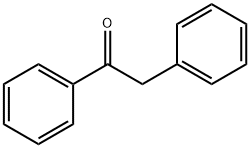
The step for the synthesis of valdecoxib: Deoxybenzoin is converted to the corresponding oxime by treatment with hydroxylamine under basic conditions with sodium acetate in aqueous ethanol or in toluene in presence of potassium hydroxide in absolute ethanol. The treatment of the oxime under nitrogen with two equivalents of butyllithium in tetrahydrofuran is followed by cyclization in ethyl acetate or acetic anhydride to the isoxazoline derivative. Finally, treatment of the isoxazoline with cold chlorosulfuric acid followed by reaction of the intermediate with aqueous ammonia afforded valdecoxib.
brand name
Bextra (Searle).
General Description
Valdecoxib (VCX) is a diaryl substituted isoxazole compound. It comprises of sulfonyl propanamide and is a metabolite of parecoxib.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Valdecoxib is reported to elicit anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic functionality. It acts as a substrate for the liver enzyme cytochrome P450 2C9(CYP2C9) and cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4).
Pharmacokinetics
Valdecoxib, a selective cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitor, is classified as a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). Valdecoxib is used for its anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antipyretic activities in the management of osteoarthritis (OA) and for the treatment of dysmenorrhea or acute pain. Unlike celecoxib, valdecoxib lacks a sulfonamide chain and does not require CYP450 enzymes for metabolism.
Pharmacokinetics
Valdecoxib is freely soluble in alkaline aqueous solutions. At recommended doses, the mean oral bioavailability for valdecoxib is 83%, and the time to peak concentration is approximately 3 hours. Time to peak plasma concentration was delayed by 1 to 2 hours when administered with a high-fat meal. Protein binding is very high at 98%. Valdecoxib exhibits linear pharmacokinetics over the usual clinical dose range. Valdecoxib is extensively metabolized in humans. The primary metabolite for valdecoxib involved CYP2C9 hydroxylation of the 5-Me group, which was further metabolized to the inactive carboxylate, and N-hydroxylation at the sulfonamide moiety. Oxidative breakdown of the N-hydroxy sulfonamide function group led to the formation of the corresponding sulfinic acid and sulfonic acid metabolites. The O-and N-glucuronides were the major urinary metabolites. Only 3% of the administered dose was recovered in urine as unchanged valdecoxib.
Clinical Use
Valdecoxib is approved for the relief of the signs and symptoms of osteoarthritis and adult rheumatoid arthritis and for the treatment of primary dysmenorrhea. Valdecoxib is contraindicated for the treatment of postoperative pain immediately following coronary artery bypass graft surgery.
Synthesis
Deoxybenzoin is converted to
the corresponding oxime by treatment with
hydroxylamine under basic conditions with
sodium acetate in aqueous ethanol or in toluene
in presence of potassium hydroxide in absolute
ethanol. The treatment of the oxime under nitrogen
with two equivalents of butyllithium in tetrahydrofuran
is followed by cyclization in ethyl
acetate or acetic anhydride to the isoxazoline
derivative. Finally, treatment of the isoxazoline
with cold chlorosulfuric acid followed by reaction
of the intermediate with aqueous ammonia
affords the desired product .
Metabolism
Hepatic (involves CYP3A4 and 2C9)
Storage
Store at RT
Clinical claims and research
Valdecoxib is a substrate of CYP3A4 but no metabolism interference was seen with commonly used synthetic narcotics, alfentanil and fentanyl. Clinical studies have shown that valdecoxib is as effective as naproxen in treating osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and dysmenornhoea. The efficacy of valdecoxib was also demonstrated in managing postoperative pain (oral and orthopedic surgery) with effective analgesia and time to rescue medication superior to those obtained with rofecoxib. Several clinical trials showed that valdecoxib has a better upper gastrointestinal safety profile compared to naproxen, ibuprofen or diclofenac and does not affect platelet function. Less abdominal pain, dyspepsia and constipation were observed with valdecoxib than with naproxen. Valdecoxib is contraindicated in patients with a history of allergic reactions to sulfonamides due to reported anaphylactic and skin reactions.
Mode of action
Valdecoxib is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that exhibits anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic properties in animal models. The mechanism of action is believed to be due to inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis primarily through inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2). At therapeutic plasma concentrations in humans valdecoxib does not inhibit cyclooxygenase-1 (COX-1).
References
[1] talley j j, brown d l, carter j s, et al. 4-[5-methyl-3-phenylisoxazol-4-yl]-benzenesulfonamide, valdecoxib: a potent and selective inhibitor of cox-2. journal of medicinal chemistry, 2000, 43(5): 775-777.
[2] nussmeier n a, whelton a a, brown m t, et al. complications of the cox-2 inhibitors parecoxib and valdecoxib after cardiac surgery. new england journal of medicine, 2005, 352(11): 1081-1091.
Properties of Valdecoxib
| Melting point: | 162-164°C |
| Boiling point: | 481.2±55.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.303±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | room temp |
| solubility | DMSO: >25mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| pka | 9.83±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | white to off-white |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C16H14N2O3S/c1-11-15(12-7-9-14(10-8-12)22(17,19)20)16(18-21-11)13-5-3-2-4-6-13/h2-10H,1H3,(H2,17,19,20) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 181695-72-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Valdecoxib
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H373:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Valdecoxib
| InChIKey | LNPDTQAFDNKSHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | C1(S(N)(=O)=O)=CC=C(C2=C(C)ON=C2C2=CC=CC=C2)C=C1 |
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 VALDECOXIB 99%View Details
VALDECOXIB 99%View Details -
 181695-72-7 98%View Details
181695-72-7 98%View Details
181695-72-7 -
 Valdecoxib 98%View Details
Valdecoxib 98%View Details
181695-72-7 -
 Valdecoxib 98% (HPLC) CAS 181695-72-7View Details
Valdecoxib 98% (HPLC) CAS 181695-72-7View Details
181695-72-7 -
 Valdecoxib 95% CAS 181695-72-7View Details
Valdecoxib 95% CAS 181695-72-7View Details
181695-72-7 -
 Valdecoxib CAS 181695-72-7View Details
Valdecoxib CAS 181695-72-7View Details
181695-72-7 -
 Valdecoxib CAS 181695-72-7View Details
Valdecoxib CAS 181695-72-7View Details
181695-72-7 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0
