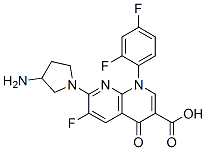
TROVAFLOXACIN
- CAS NO.:147059-72-1
- Empirical Formula: C20H15F3N4O3
- Molecular Weight: 416.36
- MDL number: MFCD00871697
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2023-09-20 16:43:00
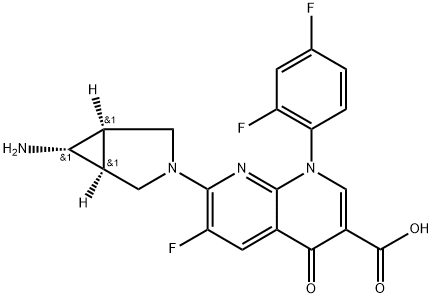
What is TROVAFLOXACIN?
Absorption
Well-absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract after oral administration and does not depend on concomitant food intake. The absolute bioavailability is approximately 88%.
Toxicity
Symptoms of overdose include convulsions, decreased activity, diarrhea, sleepiness, tremors, and/or vomiting.
Originator
Trovan,Pfizer,USA
The Uses of TROVAFLOXACIN
Trovafloxacin is a fluroquinolone antibiotic, recently identified as an inhibitor of pannexin-1 (Panx1) channels. Trovafloxacin attenuates neuroinflammation and improves outcome after traumatic brain injury in mice.
The Uses of TROVAFLOXACIN
Antibacterial.
Indications
For treatment of infections caused by susceptible strains of the designated microorganisms in uncomplicated urethral gonorrhea in males and endocervical and rectal gonorrhea in females caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae as well as non gonoccocal urethritis and cervicitis due to Chlamydia trachomatis.
Background
Trovafloxacin is a broad spectrum antibiotic that has been commonly marketed under the brand name Trovan by Pfizer. It exerts its antibacterial activity by inhibiting the uncoiling of supercoiled DNA in various bacteria by blocking the activity of DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV. It was shown to be more effective against Gram-positive bacteria than Gram-negative bacteria when compared to previous fluoroquinolones. Due to its hepatotoxic potential, trovafloxacin was withdrawn from the market.
Definition
ChEBI: A 1,8-naphthyridine derivative that is 4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic acid bearing additional 2,4-difluorophenyl, fluoro and 6-amino-3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hex-3-yl substituents at positions 1, 6 and 7 respectively. A broad-spectrum antibiot c that was withdrawn from the market due to risk of liver failure.
Manufacturing Process
N-Benzylmaleimide (500 g, 2.67 mole), 90% bromonitromethane (831 g, 5.34
mole), powdered molecular sieves 200 mesh (2020 g) and toluene (12 dm3)
were stirred under nitrogen at -10°C. 1,2-Dimethyl-1,4,5,6-
tetrahydropyrimidine (616 g, 5.49 mole) was added slowly over about 3 h
maintaining the reaction temperature at <-8°C throughout the addition. After
completion of the addition, the reaction mixture was stirred for 1.5 h at 25°C,
filtered under a nitrogen atmosphere in a sealed pressure filter to remove
sieves and resulting tar, and the sieves were washed with toluene (2 L). The
combined filtrates were washed with 2 N dilute hydrochloric acid (3 times 750
cm3), treated with carbon (50 g) at 70°C, 1 h filtered, concentrated, and
triturated with 2-propanol (about 4 dm3) to obtain crystals of the (1α,5α,6α)-
3-N-benzyl-6-nitro-2,4-dioxo-3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexane (223 g, 34%) melting
point 116°-118°C.
Tetrahydrofuran (350 cm3), sodium borohydride (14.1 g) and (1α,5α,6α)-3-N_x0002_benzyl-6-nitro-2,4-dioxo-3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexane (35.0 g, mmol) obtained
above were stirred under nitrogen for 0.25 h and then treated dropwise with
boron trifluoride-THF complex containing 21.5% BF3 (44.9 cm3) so that the
exotherm was controlled to <40°C. After addition was completed, the reaction
mixture was stirred for 3 h at 40°C, quenched slowly with water/THF 1:1 (70
cm3) to avoid excessive foaming, and stirred for 0.5 h at 50°C to ensure that
the quench of unreacted diborane generated in situ was completed. The
quench formed a salt slurry which was filtered and washed with THF (140
cm3); the combined filtrate was partially concentrated, diluted with water (350
cm3) and further concentrated to remove most of the THF, and extracted with
ethyl acetate (140 cm3). The resulting ethyl acetate solution was concentrated
to afford the (1α,5α,6α)-3-N-benzyl-6-nitro-3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexane as a
clear oil (30.6 g, 97%).
(1α,5α,6α)-3-N-Benzyl-6-nitro-3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexane (30.9 g, 142 mmol)
obtained above, 2-propanol (310 cm3), water (30 cm3), and 10% Pd on
carbon, 50% water content (12.3 g) were hydrogenated at 50 psi and 50°C
for 18-24 h in a Parr shaker. The Pd catalyst was filtered off, and the resulting
pale yellow filtrate was azeotropically distilled at constant volume to remove
water. The resulting solution was treated with triethylamine (46 g, 456 mmol)
and heated to reflux. Benzaldehyde (15.0 g, 141 mmol) was added dropwise
over 15 min. The reaction mixture was heated at reflux for 4 h to form
(1α,5α,6α)-6-benzylidenylamino-3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexane in situ. The
resulting orange solution was cooled to 40°-50°C, and ethyl 7-chloro-1-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic acid
(42.45 g, 111 mmol; see United Kingdom Patent Publication No. GB
2,191,776) and triethylamine (13.1 g, 130 mmol) were added. The resulting
slurry was heated at reflux for 16-18 h, cooled to 20°C and stirred for 5 h.
The slurry was filtered, and the compound was isolated as a white solid
(75.5% yield based on (1α,5α,6α)-3-N-benzyl-6-nitro-2,4-dioxo-3-
azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexane; 96.6% based on ethyl 7-chloro-1-(2,4-
difluorophenyl)-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic
acid). The ethyl (1α,5α,6α)-7-(6-benzylidenylamino-3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hex-
3yl)-1-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-1,8-naphthyridine-3-
carboxylate was recrystallized from acetonitrile, melting point 148°-155°C
decomp.
Tetrahydrofuran (250 cm3), ethyl (1α,5α,6α)-7-(6-benzylidenylamino-3-
azabicyclo[3.1.0]hex-3-yl)-1-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-
1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylate (25.05 g, 47 mmol) obtained above, and
water (250 cm3) were treated with 97% methanesulfonic acid (13.3 g, 138
mmol) and heated to reflux for 24 h. The resulting solution was cooled to
45°C, treated with activated carbon (2.5 g) for 1 h and filtered. The resulting
filtrate was concentrated under vacuum to approximately 25% of its original
volume to provide a white crystal slurry, cooled to 15°-25°C, granulated for 4
h and filtered to yield the trovafloxacin methanesulfonate salt (mesylate)
(16.86 g, 70.0%). Melting point 253°-256°C decomp.
brand name
Trovan (Pfizer).
Therapeutic Function
Antibacterial
Pharmacokinetics
Trovafloxacin is a broad spectrum antibiotic that inhibits DNA supercoiling in various bacteria by blocking the activity of DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV. It is not used widely due to the risk of hepatotoxicity. It tends to have better gram-positive bacterial coverage and less gram-negative coverage than the previous fluoroquinolones. Mechanism of action of fluoroquinolones including trovafloxacin is different from that of penicillins, cephalosporins, aminoglycosides, macrolides, and tetracyclines. Therefore fluoroquinolones may be active against pathogens that are resistant to these antibiotics. There is no cross-resistance between trovafloxacin and the mentioned classes of antibiotics. The overall results obtained from in vitro synergy studies, testing combinations of trovafloxacin with beta-lactams and aminoglycosides, indicate that synergy is strain specific and not commonly encountered. This agrees with results obtained previously with other fluoroquinolones. Resistance to trovafloxacin in vitro develops slowly via multiple-step mutation in a manner similar to other fluoroquinolones. Resistance to trovafloxacin in vitro occurs at a general frequency of between 1x10-7 to 10-10. Although cross-resistance has been observed between trovafloxacin and some other fluoroquinolones, some microorganisms resistant to other fluoroquinolones may be susceptible to trovafloxacin.
Metabolism
Metabolism Trovafloxacin is metabolized by conjugation (the role of cytochrome P450 oxidative metabolism of trovafloxacin is minimal). The major metabolites include the ester glucuronide, which appears in the urine (13% of the administered dose); and the N -acetyl metabolite, which appears in the feces and serum (9% and 2.5% of the administered dose, respectively). Other minor metabolites include diacid, hydroxycarboxylic acid, and sulfamate, which have been identified in both the feces and the urine in small amounts (< 4% of the administered dose).
Properties of TROVAFLOXACIN
| Melting point: | >195oC (dec.) |
| Boiling point: | 630.5±55.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.612±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | -20°C Freezer, Under inert atmosphere |
| solubility | Acetonitrile (Slightly), DMSO (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 5.80±0.70(Predicted) |
| color | Pale Beige to Light Beige |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 147059-72-1 |
Safety information for TROVAFLOXACIN
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for TROVAFLOXACIN
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Trovafloxacin 95% CAS 147059-72-1View Details
Trovafloxacin 95% CAS 147059-72-1View Details
147059-72-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8