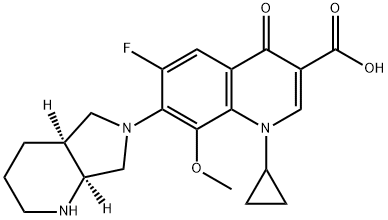
Moxifloxacin
- CAS NO.:151096-09-2
- Empirical Formula: C21H24FN3O4
- Molecular Weight: 401.43
- MDL number: MFCD04117996
- EINECS: 604-773-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 11:34:44
What is Moxifloxacin?
Absorption
Well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Absolute oral bioavailability is approximately 90%. Food has little effect on absorption.
Toxicity
Symptoms of overdose include CNS and gastrointestinal effects such as decreased activity, somnolence, tremor, convulsions, vomiting, and diarrhea. The minimal lethal intravenous dose in mice and rats is 100 mg/kg.
Originator
Avelox,Bayer
The Uses of Moxifloxacin
Moxifloxacin is an antibiotic for the treatment of bacterial infections like bacterial sinusitis, acute bacterial exacerbations of chronic bronchitis, and community-acquired pneumonia.
Background
Moxifloxacin is a synthetic fluoroquinolone antibiotic agent. Bayer AG developed the drug (initially called BAY 12-8039) and it is marketed worldwide (as the hydrochloride) under the brand name Avelox (in some countries also Avalox) for oral treatment.
Indications
For the treatment of sinus and lung infections such as sinusitis, pneumonia, and secondary infections in chronic bronchitis. Also for the treatment of bacterial conjunctivitis (pinkeye).
Definition
ChEBI: A quinolone that consits of 4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid bearing a cyclopropyl substituent at position 1, a fluoro substitiuent at position 6, a (4aS,7aS)-octahydro-6H-pyrrolo[3,4-b /ital>]pyridin-6-yl group at position 7 and a methoxy substituent at position 8. A member of the fluoroquinolone class of antibacterial agents.
Therapeutic Function
Antibacterial
Antimicrobial activity
It displays good activity in vitro against Enterobacteriaceae and fastidious Gram-negative bacilli such as H. influenzae and Mor. catarrhalis, as well as against Grampositive cocci including Str. pneumoniae, but is poorly active against Enterococcus spp. Activity against non-fermentative Gramnegative bacilli is species dependent: Acinetobacter spp. (MIC 0.006–2.0 mg/L) and Sten. maltophilia (MIC 0.5–2.0 mg/L) are partially susceptible in vitro, but it has poor activity against Ps. aeruginosa and other non-fermenting Gram-negative rods. It displays good in-vitro activity against Ch. pneumoniae, C. trachomatis, mycoplasmas (including M. pneumoniae), L. pneumophila and B. fragilis. Although highly active against M. tuberculosis, it is less active against the M. avium complex, M. intracellulare, M. chelonei and M. fortuitum.
Pharmaceutical Applications
fluoroquinolone substituted with an 8-methoxy group and a 7-diazabicyclononyl moiety, formulated as the hydrochloride for oral or intravenous use.
Biological Activity
moxifloxacin is an orally bio-available, broad spectrum bacterial gyrase-inhibiting fluoroquinolone antibiotic [1].moxifloxacin at 50 μg/ml has been reported to induce a significant reduction of viable cells. a remarkable anti-proliferative activity of moxifloxacin has been proved in the concentrations between 50 and 1500 μg/ml. moreover, moxifloxacin could lead to signs of cellular damage which were seen like binucleation in a dose-dependent manner [2].rats intravenously injected with moxifloxacin at 100 mg/kg have shown the increase of serum glucose and serum epinephrine concentrations as well as the release of histamine. however, moxifloxacin at 75 mg/kg did not show any effects on serum epinephrine, glucose or histamine concentrations increase [3].
Pharmacokinetics
Moxifloxacin is a quinolone/fluoroquinolone antibiotic. Moxifloxacin can be used to treat infections caused by the following bacteria: Aerobic Gram-positive microorganisms: Corynebacterium species, Micrococcus luteus, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Staphylococcus haemolyticus, Staphylococcus hominis, Staphylococcus warneri, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Streptococcus viridans group. Aerobic Gram-negative microorganisms: Acinetobacter lwoffii, Haemophilus influenzae, and Haemophilus parainfluenzae. Other microorganisms: Chlamydia trachomatis. Moxifloxacin is bactericidal and its mode of action depends on blocking of bacterial DNA replication by binding itself to an enzyme called DNA gyrase, which allows the untwisting required to replicate one DNA double helix into two. Notably the drug has 100 times higher affinity for bacterial DNA gyrase than for mammalian. Moxifloxacin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that is active against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
Pharmacokinetics
absorption and distribution
By the oral route, drug uptake is rapid, with moderate variability. As with all quinolones iron and antacids significantly reduce the bioavailability. No significant drug interactions with theophylline, itraconazole, probenecid or oral contraceptives have been found. In escalating dose studies (50–80 mg doses), Cmax and AUC values increased proportionally to the dose.
It is widely distributed throughout the body and into many tissues in concentrations exceeding those in plasma. Around 50–80% of plasma concentrations penetrate into CSF if the meninges are inflamed. The apparent plasma half-life is 15.6 h.
Metabolism and excretion
Biliary elimination and metabolism are the main elimination pathways. About 19.3% of the administered dose is eliminated in the urine, with a bioavailability of 86.2%. Urinary excretion is via glomerular filtration and tubular reabsorption. Two main metabolites are recovered: M1 (a sulfocompound) and M2 (a glucuronide). M1 is mainly eliminated in feces (34.4%) and only 2.5% in urine: M2 is eliminated in urine (13.8%).
Clinical Use
Acute bacterial exacerbations of chronic bronchitis and community
acquired pneumonia
Acute bacterial sinusitis
Treatment of complicated skin and soft-tissue infections caused by methicillin-susceptible Staph. aureus and Gram-negative rods (i.v. formulation)
Treatment of complicated intra-abdominal infections (i.v. formulation)
Side Effects
Adverse events are similar to those for other fluoroquinolones. Phototoxicity rates are not significantly above placebo levels. Gastrointestinal side effects are the most common, particularly nausea, diarrhea, abdominal pain and vomiting. Dizziness and headache may occur as well as allergic reactions. Attention has been drawn to a potential to cause lifethreatening hepatotoxicity. Moxifloxacin has the potential to prolong the QTc interval in some patients but the clinical significance of this phenomenon is unclear.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Aminophylline and theophylline: possibly increased
risk of convulsions.
Analgesics: increased risk of convulsions with
NSAIDs.
Anti-arrhythmics: increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias with amiodarone, disopyramide and
procainamide - avoid Antibacterials: increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias with parenteral erythromycin - avoid;
increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias with
delamanid and telithromycin.
Anticoagulants: anticoagulant effect enhanced.
Antidepressants: increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias with tricyclics, citalopram, escitalopram
and venlafaxine - avoid.
Antihistamines: increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias with mizolastine - avoid.
Antimalarials: increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias with chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine,
mefloquine or quinine - avoid; avoid with
artemether with lumefantrine and piperaquine with
artenimol.
Antipsychotics: increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias with benperidol, droperidol, haloperidol,
phenothiazines, pimozide or zuclopenthixol - avoid.
Antivirals: increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias
with saquinavir - avoid.
Atomoxetine: increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias - avoid.
Beta-blockers: increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias with sotalol - avoid.
Ciclosporin: some reports of increased
nephrotoxicity.
Cytotoxics: increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias with arsenic trioxide, bosutinib,
ceritinib, panobinostat and vandetanib, avoid with
panobinostat and vandetanib.
Pentamidine: increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias - avoid.
Metabolism
Approximately 52% or oral or intravenous dose is metabolized via glucuronide and sulphate conjugation. The cytochrome P450 system is not involved in metabolism. The sulphate conjugate accounts for 38% of the dose, and the glucuronide conjugate accounts for 14% of the dose.
Metabolism
Metabolised mainly via sulphate and glucuronide conjugation, and is excreted in the urine and the faeces as unchanged drug and as metabolites, the sulphate conjugate mainly in the faeces and the glucuronide exclusively in the urine.
References
[1] iatropoulos mj1, jeffrey am, enzmann hg, von keutz e, schlueter g, williams gm. assessment of chronic toxicity and carcinogenicity in an accelerated cancer bioassay in rats of moxifloxacin, a quinolone antibiotic. exp toxicol pathol. 2001 oct;53(5):345-57.
[2] sobolewska b1, hofmann j, spitzer ms, bartz-schmidt ku, szurman p, yoeruek e. antiproliferative and cytotoxic properties of moxifloxacin on rat retinal ganglion cells. curr eye res. 2013 jun;38(6):662-9.
[3] ishiwata y1, takahashi y, nagata m, yasuhara m. effects of moxifloxacin on serum glucose concentrations in rats. biol pharm bull. 2013;36(4):686-90.
Properties of Moxifloxacin
| Melting point: | 203-208 C |
| Boiling point: | 636.4±55.0 °C(Predicted) |
| alpha | 23D -193° |
| Density | 1.408±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C(protect from light) |
| solubility | Acetonitrile (Slightly), DMSO (Slightly, Heated, Sonicated), Methanol (Slightly) |
| pka | 6.43±0.50(Predicted) |
| form | Solid |
| color | Off-White to Light Yellow |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 151096-09-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 3-Quinolinecarboxylic acid, 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-8-methoxy-7-[(4aS,7aS)-octahydro-6H-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridin-6-yl]-4-oxo- (151096-09-2) |
Safety information for Moxifloxacin
Computed Descriptors for Moxifloxacin
Moxifloxacin manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 151096-09-2 MOXIFLOXACIN 57.15% DC GRANULES 98%View Details
151096-09-2 MOXIFLOXACIN 57.15% DC GRANULES 98%View Details
151096-09-2 -
 Moxifloxacin 98%View Details
Moxifloxacin 98%View Details
151096-09-2 -
 Moxifloxacin 99%View Details
Moxifloxacin 99%View Details
151096-09-2 -
 Moxifloxacin 98% CAS 151096-09-2View Details
Moxifloxacin 98% CAS 151096-09-2View Details
151096-09-2 -
 Moxifloxacin for system suitability CAS 151096-09-2View Details
Moxifloxacin for system suitability CAS 151096-09-2View Details
151096-09-2 -
 Moxifloxacin for peak identification B CAS 151096-09-2View Details
Moxifloxacin for peak identification B CAS 151096-09-2View Details
151096-09-2 -
 Moxifloxacin for peak identification A CAS 151096-09-2View Details
Moxifloxacin for peak identification A CAS 151096-09-2View Details
151096-09-2 -
 Moxifloxacin 0.5 Eye Drops, 10 mlView Details
Moxifloxacin 0.5 Eye Drops, 10 mlView Details
151096-09-2