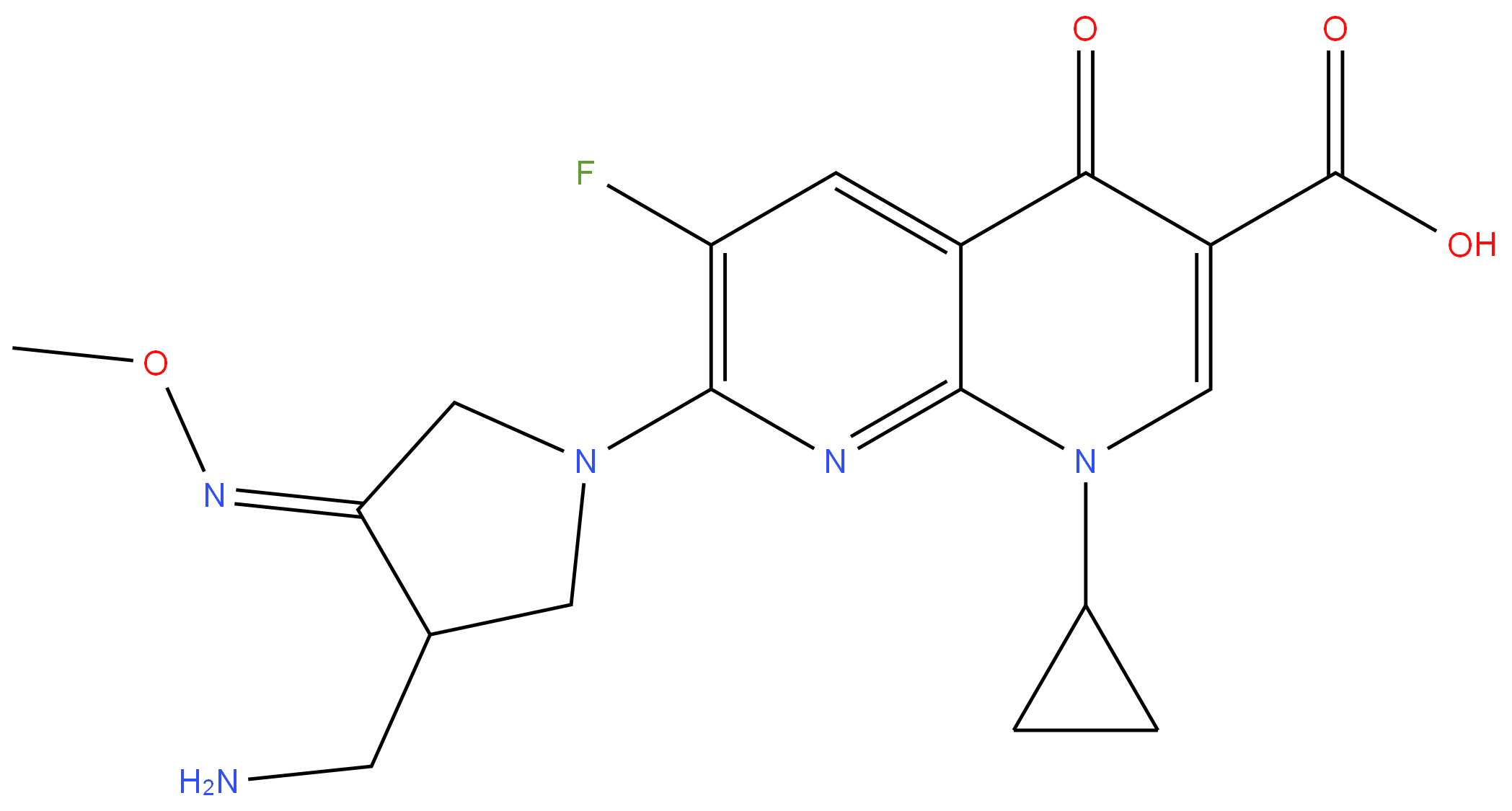
Gemifioxacin
- CAS NO.:175463-14-6
- Empirical Formula: C18H20FN5O4
- Molecular Weight: 389.38
- MDL number: MFCD07779399
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2023-05-15 10:43:23
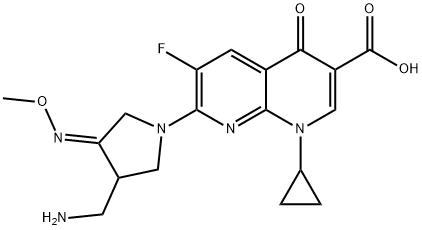
What is Gemifioxacin?
Absorption
Rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. The absolute bioavailability averages approximately 71%.
Description
LG Life Sciences (formerly LG Chemical) has developed gemifloxacin (SB-265805, LB-20304a), a fluoronaphthyridone active against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, including methicillin-resistant staphylococci, as a treatment for bacterial infection. By December 2002, the drug had been approved in Korea.
The Uses of Gemifioxacin
Acyl Glucuronide - Gemifloxacin is a derivative of Gemifloxacin (G336000); a third generation fluorinated quinolone antibacterial.
Background
Gemifloxacin is a quinolone antibacterial agent with a broad-spectrum activity that is used in the treatment of acute bacterial exacerbation of chronic bronchitis and mild-to-moderate pneumonia. It is available in oral formulations. Gemifloxacin acts by inhibiting DNA synthesis through the inhibition of both DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV, which are essential for bacterial growth.
Indications
For the treatment of bacterial infection caused by susceptible strains such as S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae, H. parainfluenzae, or M. catarrhalis, S. pneumoniae (including multi-drug resistant strains [MDRSP]), M. pneumoniae, C. pneumoniae, or K. pneumoniae.
Definition
ChEBI: A 1,4-dihydro-1,8-naphthyridine with a carboxy group at the 3-position, an oxo sustituent at the 4-position, a fluoro substituent at the 5-position and a substituted pyrrolin-1-yl group at the 7-position.
Antimicrobial activity
The broad antibacterial spectrum embraces most Gram-positive cocci (including high potency against Str. pneumoniae) and Gram-negative bacilli. It possesses a high affinity for pneumococcal topoisomerase IV. Activity against Gram-negative respiratory tract pathogens such as H. influenzae, Mor. catarrhalis, Ch. pneumoniae, L. pneumophila and Mycoplasma pneumonia is good. It is relatively inactive against Ps. aeruginosa and Enterococcus spp. Activity against Enterobacteriaceae is similar to that of moxifloxacin but it is less potent against anaerobes. Gemifloxacin is inactive against M. tuberculosis. Activity against Nocardia asteroides (MIC 0.5–1 mg/L) is better than that of other quinolones other than the investigational compound nemonoxacin .
Multistep resistance studies suggest that it is less likely than other quinolones to select for quinolone-resistant Str. pneumoniae strains. Because it inhibits both DNA gyrase and DNA topoisomerase IV enzyme systems at therapeutically relevant drug levels in Str. pneumoniae, single mutations in parC or gyrA result in only a small increase in the MIC. In Str. pneumoniae gyrA mutations arise at a lower rate (1.6 × 10?11) than mutations in parC. It seems to be unaffected clinically by quinolone efflux mechanisms in Str. pneumoniae. Low rates of resistance selection have also been reported in H. influenzae.
Pharmaceutical Applications
A fluoronaphthyridone derivative with a dual substituted pyrrolidine moiety at the C-7 position. It is formulated as the mesylate.
Pharmacokinetics
Gemifloxacin is a quinolone/fluoroquinolone antibiotic. Gemifloxacin is bactericidal and its mode of action depends on blocking of bacterial DNA replication by binding itself to an enzyme called DNA gyrase, which allows the untwisting required to replicate one DNA double helix into two. Notably the drug has 100 times higher affinity for bacterial DNA gyrase than for mammalian. Gemifloxacin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that is active against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
Pharmacokinetics
absorption and distribution
In oral escalating dose studies (single doses of 20–800 mg), Cmax ranged from 0.12 to 4.33 mg/L after an average of 1 h. Antacids significantly reduce the systemic availability and protein binding is relatively high. Excellent concentrations are achieved in serum as well as various tissues such as bronchial mucosa, epithelial lining fluid and alveolar macrophages. Absolute bioavailability of the 320 mg oral tablet is around 71%. Pharmacokinetics are not significantly altered when administered with a high fat meal.
Metabolism and excretion
The apparent elimination half-life ranges from 6 to 9 h, and 26–40% of administered doses are eliminated in urine. It is metabolized to a limited extent in the liver. Cytochrome P450 enzymes do not play an important role in metabolism, and the metabolic activity of these enzymes is unaffected. Around 65% of the parent compound and its metabolites are eliminated in the feces and the remainder in the urine. The mean renal clearance after repeated doses of 320 mg is about 11.6 L/h, indicating active renal secretion. The mean apparent elimination half-life at steady state following administration of 320 mg to healthy subjects was approximately 7 h. No dosage adjustment is recommended in patients with mild, moderate or severe hepatic impairment. Clearance is reduced and plasma elimination is prolonged in patients with renal insufficiency, leading to an average increase in AUC values of c. 70%. Hemodialysis removes approximately 20–30% of an oral dose from plasma.
Clinical Use
Community-acquired pneumonia in adults
Acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis in adults
Side Effects
The most commonly reported side effects are diarrhea (3.6%), rash (2.8%) and nausea (2.7%). No evidence has emerged of a clinically significant prolongation in QTc interval. The phototoxicity potential is low and similar to that seen with ciprofloxacin. The overall incidence of drugrelated rash is 2.8%. The rash is most commonly mild, macropapular (occasionally urticarial), predominantly selflimiting, and mainly occurs in women under 40 years and in postmenopausal women on hormone replacement therapy after ≥10 days.
Synthesis
Oral gemifloxacin was
approved by the FDA in April 2003. Two key intermediates,
3-aminomethyl-4-methoxyiminopyrrolidine (105) and 7-
chloro-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-1,8-naphthyridine-
3-carboxylic acid (108) were involved in the synthesis
of gemifloxacin (XII). Michael addition of glycine ethyl
ester hydrochloride (98) to acrylonitrile (99) in the presence
of KOH furnished cyanoester 100 in 48% yield. Protection
of the amino group and Dieckmann cyclization were
accomplished in a one-pot process to furnish 4-cyano-1-(N-tbutoxycarbonyl)-
pyrrolidine-3-one (101) in almost
quantitative yield. The conversion of ketone 101 to alcohol
102 was achieved via three reaction sequences in a one-pot
process in 83% yield. The hydroxy group was oxidized to
ketone 103 with pyridine-sulfur trioxide complex in DMSO.
Treatment of ketone 103 with methoxyamine in the presence
of NaHCO3 provided methyloxime 104 in 88% yield.
Deprotection of the Boc groups in 104 by TFA afforded
pyrrolidine 105 in 84% yield. Quinolone acid 108 was
employed in the synthesis of ciprofloxacin and can be
readily prepared according to literature methods. A
four step sequence/one-pot process is depicted in
Scheme 12. Nicotinoyl acetate 106 was converted to
enaminoester 107 by reaction with ethyl orthoformate and
acetic anhydride, followed by reaction with the cyclopropyl
amine. 1,8-Naphthyridine 108 was obtained through baseassisted
cyclization, followed by acid hydrolysis of the ester
function via a one-pot process in 52% overall yield. The
coupling reaction of quinolone 108 with pyrrolidine 105 was
carried out in CH3CN-H2O in the presence of benzaldehyde
and triethylamine. The benzaldehyde served as an important
reagent to protect the primary amine selectively and therefore
the desired gemifloxacin derivative 109 was obtained in high
yield and purity, otherwise a 10% by-product was observed. The deprotection and salt formation reactions were
carried out in one step by treatment of 109 with
methanesulfonic acid at 40-45oC in water. The gemifloxacin
mesylate (XII) was collected by filtration upon cooling in
95% yield.

Metabolism
Gemifloxacin is metabolized to a limited extent by the liver. All metabolites formed are minor (<10% of the administered oral dose); the principal ones are N-acetyl gemifloxacin, the E-isomer of gemifloxacin and the carbamyl glucuronide of gemifloxacin.
Properties of Gemifioxacin
| Melting point: | 235-237° |
| Boiling point: | 638.9±65.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1?+-.0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| pka | 6.02±0.70(Predicted) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 175463-14-6 |
Safety information for Gemifioxacin
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Gemifioxacin
Gemifioxacin manufacturer
Humble Healthcare Limited
Aspen Biopharma Labs Pvt Ltd
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
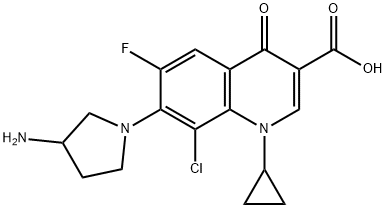
 175463-14-6 Gemifloxacin 99%View Details
175463-14-6 Gemifloxacin 99%View Details
175463-14-6 -
 Gemifloxacin 98%View Details
Gemifloxacin 98%View Details
175463-14-6 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8