Trimethyl borate
Synonym(s):Boric acid trimethyl ester;Methyl borate;Trimethyl borate
- CAS NO.:121-43-7
- Empirical Formula: C3H9BO3
- Molecular Weight: 103.91
- MDL number: MFCD00008346
- EINECS: 204-468-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
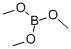
What is Trimethyl borate?
Chemical properties
Water-white moisture-sensitive liquid, fumes in the air. It forms an azeotrope with methanol with an azeotrope of 55°C. Miscible with ether, methanol, hexane, tetrahydrofuran; It is stable in anhydrous state and decomposes into methanol and boric acid in presence of water.
The Uses of Trimethyl borate
Trimethyl borate is a useful reagent in organic synthesis. It is involved in the production of resins, waxes and paints and acts as a methylation agent. As a boron source, it is used to prepare flame retardants, anti-oxidants and corrosion inhibitors. It reacts with Grignard reagents followed by hydrolysis to prepare boronic acid. It is also used as a precursor of borate esters, which finds application in the Suzuki coupling reaction. It is used as neutron detector gas in the presence of a scintillation counter; as a promoter of diborane reactions.
What are the applications of Application
Trimethyl borate is the main precursor to sodium borohydride (sc-215866A)
Definition
ChEBI: Trimethyl borate is a member of the class of borate esters obtained by the formal condensation of three equivalents of methanol with boric acid.
What are the applications of Application
Trimethyl borate reacts with a Grignard reagent or organolithium compounds to yield dimethyl boronates, which upon subsequent aqueous acid treatment afford corresponding boronic acids. The resultant boronic acids or esters are useful intermediates in various cross-coupling reactions such as Suzuki coupling and Chan-Lam coupling. It is also used in the preparation of sodium borohydride.
Preparation
The preparation method of trimethyl borate
1. The direct reaction between boric acid and methanol is as follows:
3CH30H+H3B03→B (OCH3) 3+3H20
Usually the trimethyl borate formed in the reaction forms an azeotrope with excess methanol and is distilled out together, and then the trimethyl borate is obtained by separating the azeotrope.
2. The direct reaction between boron oxide and methanol is as follows:
B203+6CH30H→2B (OCH3) 3+3H20
3. Borax, methanol and sulfuric acid are directly reacted, and the reaction formula is :
Na2B4O7.1OH2O+12CH30H+2H2S04→4B (OCH3)3+2NaHS04+17H20
Reactions
Trimethyl borate B(OCH3)3 is a popular borate ester used in organic synthesis.
borate esters are prepared from alkylation of trimethyl borate:
ArMgBr + B(OCH3 )3 → MgBrOCH3 + ArB(OCH3 )2
ArB(OCH3 )2 + 2H2O → ArB(OH)2 + 2 HOCH3
General Description
Trimethyl borate appears as a water-white liquid. Denser than water. Vapors heavier than air. Used as a solvent and fungicide for fruit.
Air & Water Reactions
Highly flammable. Rapidly decomposes in water.
Reactivity Profile
Borates, such as Trimethyl borate, behave similarly to esters in that they react with acids to liberate heat along with alcohols and acids. Strong oxidizing acids may cause a vigorous reaction that is sufficiently exothermic to ignite the reaction products. Heat is also generated by the interaction of esters with caustic solutions. Flammable hydrogen is generated by mixing esters/borates with alkali metals and hydrides.
Health Hazard
May cause toxic effects if inhaled or absorbed through skin. Inhalation or contact with material may irritate or burn skin and eyes. Fire will produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Vapors may cause dizziness or suffocation. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may cause pollution.
Fire Hazard
HIGHLY FLAMMABLE: Will be easily ignited by heat, sparks or flames. Vapors may form explosive mixtures with air. Vapors may travel to source of ignition and flash back. Most vapors are heavier than air. They will spread along ground and collect in low or confined areas (sewers, basements, tanks). Vapor explosion hazard indoors, outdoors or in sewers. Runoff to sewer may create fire or explosion hazard. Containers may explode when heated. Many liquids are lighter than water.
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by ingestion, skin contact, and intraperitoneal routes. An eye irritant. A very dangerous fire hazard when exposed to heat, flame, or oxidizers. Moderately explosive when exposed to flame. Will react with water or steam to produce toxic and flammable vapors. To fight fire, use dry chemical, CO2, spray, foam. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes. See also ESTERS and BORON COMPOUNDS.
Purification Methods
Carefully fractionate the borate through a gauze-packed column. Re-distil and collect it in weighed glass vials and seal them. Keep it away from moisture. It undergoes alkyl exchange with alcohols and forms azeotropes, e.g. with MeOH the azeotrope consists of 70% (MeO)3B and 30% MeOH with b 52-54o/760mm, d 0.87. [Charnley et al. J Chem Soc 2288 1952, Gerrard & Lappert Chem Ind (London) 53 1952, Schlesinger et al. J Am Chem Soc 75 213 1953.] It has also been dried with Na and then distilled. [Beilstein 1 IV 1269.]
Properties of Trimethyl borate
| Melting point: | -34 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 68-69 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 0.932 g/mL at 20 °C (lit.) |
| vapor density | 3.59 (vs air) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 8 °F |
| storage temp. | Store at <= 20°C. |
| solubility | Miscible with tetrahydrofuran, ether, isoporpylamine, hexane and methanol. |
| form | Liquid |
| color | Colorless |
| Specific Gravity | 0.915 |
| Water Solubility | reacts |
| Sensitive | Moisture Sensitive |
| Hydrolytic Sensitivity | 7: reacts slowly with moisture/water |
| Merck | 14,9712 |
| BRN | 1697939 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 200 ppm; STEL 250 ppm (Skin) OSHA: TWA 200 ppm(260 mg/m3) NIOSH: IDLH 6000 ppm; TWA 200 ppm(260 mg/m3); STEL 250 ppm(325 mg/m3) |
| Dielectric constant | 8.2(20℃) |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with oxidizing agents. Decomposes slowly in the presence of moisture, rapidly in water. Flammable. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 121-43-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Boric acid, trimethyl ester(121-43-7) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Boric acid (H3BO3), trimethyl ester (121-43-7) |
Safety information for Trimethyl borate
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H225:Flammable liquids H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H370:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Trimethyl borate
| InChIKey | WRECIMRULFAWHA-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Trimethyl borate manufacturer
AKASH PHARMA EXPORTS
New Products
3-Iodophenylacetic acid 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 3-(hexyloxy)-4-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,2,5-thiadiazole 2-Hexyn-1-ol Dibenzo-18-crown-6 Nickel(II) perchlorate hexahydrate, 98% 4-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 95% 3-Bromo-4-fluoroaniline, 97% Sodium tetraborate decahydrate, 98% Palladium(II) acetate, trimer, Pd 99% 4-Bromo-2-chlorotoluene, 97% N N Dimethylformamide Dimethyl Acetal (Dmf Dma) 2,3-Dichloro Benzoyl Cyanide [Side Chain] Bis(2-Chloroethyl) Amine Hydrochloride L-Glutamic Acid Diethyl Ester Hydrochloride 5-(Difluoromethoxy)-2-Mercaptobenzimidazole 1-Ethyl-3-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-Carbodiimide Hydrochloride [EDC Hcl] 1,4-Napthoquinone Bromoiodomethane Sodium Bicarbonate Methylene Dichloride (MDC) Ethyl Acetate Indole-3-Carbinol (I3C)Related products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Trimethyl Borate 99%View Details
Trimethyl Borate 99%View Details -
 Trimethyl borate CAS 121-43-7View Details
Trimethyl borate CAS 121-43-7View Details
121-43-7 -
 Trimethyl borate CAS 121-43-7View Details
Trimethyl borate CAS 121-43-7View Details
121-43-7 -
 Trimethyl borate CAS 121-43-7View Details
Trimethyl borate CAS 121-43-7View Details
121-43-7 -
 Trimethyl borate CAS 121-43-7View Details
Trimethyl borate CAS 121-43-7View Details
121-43-7 -
 Trimethyl borate CAS 121-43-7View Details
Trimethyl borate CAS 121-43-7View Details
121-43-7 -
 Trimethyl borate 95% CAS 121-43-7View Details
Trimethyl borate 95% CAS 121-43-7View Details
121-43-7 -
 Trimethyl borate CAS 121-43-7View Details
Trimethyl borate CAS 121-43-7View Details
121-43-7
