Tolvaptan
Synonym(s):N-[4-[(7-Chloro-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-5-hydroxy-1H-1-benzazepin-1-yl)carbonyl]-3-methylphenyl]-2-methylbenzamide;OPC 41061
- CAS NO.:150683-30-0
- Empirical Formula: C26H25ClN2O3
- Molecular Weight: 448.94
- MDL number: MFCD09838782
- EINECS: 691-537-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
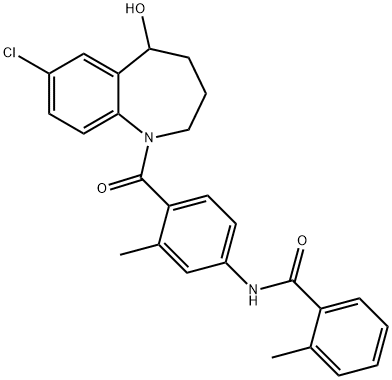
What is Tolvaptan?
Absorption
Tmax, Healthy subjects: 2 - 4 hours; Cmax, Healthy subjects, 30 mg: 374 ng/mL; Cmax, Healthy subjects, 90 mg: 418 ng/mL; Cmax, heart failure patients, 30 mg: 460 ng/mL; Cmax, heart failure patients, 90 mg: 723 ng/mL; AUC(0-24 hours), 60 mg: 3.71 μg·h/mL; AUC(∞), 60 mg: 4.55 μg·h/mL; The pharmacokinetic properties of tolvaptan are stereospecific, with a steady-state ratio of the S-(-) to the R-(+) enantiomer of about 3. The absolute bioavailability of tolvaptan is unknown. At least 40% of the dose is absorbed as tolvaptan or metabolites. Food does not impact the bioavailability of tolvaptan.
Toxicity
The oral LD50 of tolvaptan in rats and dogs is >2000 mg/kg. Most common adverse reactions (≥5% placebo) are thirst, dry mouth, asthenia, constipation, pollakiuria or polyuria, and hyperglycemia.
Description
The potent antidiuretic hormone AVP orchestrates the regulation of free water absorption, body fluid osmolality, cell contraction, blood volume, and blood pressure through stimulation of three G-proteincoupled receptor subtypes:V1-vascular types a and b, V2-renal, and V3-pituitary. Increased AVP secretion is the trademark of several pathophysiological disorders, including heart failure, impaired renal function, liver cirrhosis, and SIADH. As a consequence, these patients experience excess water retention or inadequate free-water excretion, which results in the dilution of sodium concentrations, frequently manifesting as clinical hyponatremia (serum sodium concentration <135 mmol/L). This electrolyte imbalance increases mortality rates by 60-fold. Selective antagonism of the AVP V2receptor promotes water excretion without perturbing electrolyte balance making it an appealing target for preventing disease progression. Following the introduction of the dual AVP V1a/V2 receptor antagonist conivaptan, tolvaptan has recently been launched as a nonpeptide, selective V2 receptor antagonist with potent aquaretic attributes for the treatment of hypervolemic and euvolemic hyponatremia (serum sodium concentration of <125 mmol/L or less distinct hyponatremia that is symptomatic and has resisted correction with fluid restriction). As a more potent and selective V2 receptor antagonist, tolvaptan is a follow-up to mozavaptan, which possesses weak V1 receptor antagonism and was approved for the treatment of SIADH in Japan. .
Description
Tolvaptan is a nonpeptide vasopressin V2 receptor antagonist (IC50 = 3 nM for rat receptor) and a diuretic agent. It is selective for V2 over V1 receptors (IC50 = 0.58 μM). Tolvaptan increases urine volume by 3-fold in rats when administered at a dose of 0.54 mg/kg. It also reduces left ventricular end-systolic volumes and improves left ventricular ejection fraction in a rat model of myocardial infarction. Formulations containing tolvaptan have been used to treat hyponatremia.
Chemical properties
White Solid
Originator
Otsuka Pharmaceutical (US)
The Uses of Tolvaptan
Tolvaptan (OPC-41061) is a selective, competitive arginine vasopressin receptor 2 antagonist with an IC50 of 1.28μM for the inhibition of AVP-induced platelet aggregation. Tolvaptan (OPC-41061) is used to treat hyponatremia (low blood sodium levels) assoc
The Uses of Tolvaptan
Labelled Tolvaptan s, and the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH).
The Uses of Tolvaptan
It is a selective, competitive arginine vasopressin V2 receptor antagonist f inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH).
What are the applications of Application
Tolvaptan is a selective vasopressin receptor 2 antagonist
Indications
Treatment of symptomatic and resistant to fluid restriction euvolemic or hypervolemic hyponatremia associated with congestive heart failure, SIADH, and cirrhosis.
Background
Tolvaptan is used to treat low blood sodium levels (hyponatremia) associated with various conditions like congestive heart failure, cirrhosis, and syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormones (SIADH). FDA approved on May 19, 2009.
Definition
ChEBI: Tolvaptan is a benzazepine derivative incorporating a benzenedicarboxamide function whch is a selective vasopressin V2 receptor antagonist used to treat euvolemic and hypervolemic hyponatremia. It is also used in the treatment of rapidly progressing autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease to slow the rate of cyst development and renal insufficiency. Tolvaptan is a racemate consisting of a 1:1 mixture of 5R and 5S stereomers. It has a role as a vasopressin receptor antagonist. It is a benzazepine and a benzenedicarboxamide.
brand name
Samsca
Biochem/physiol Actions
Tolvaptan (OPC 41061) is a potent, orally active non-peptide vasopressin V2 selective antagonist. IC50 = 3 nM at the rat V2 receptor; 29 times more selective for the V2 than for V1a. Tolvaptan has also been shown to inhibit the development of polycystic kidney disease in several animal models.
Pharmacokinetics
Urine volume and fluid intake increase in a dose dependent manner which results in overall negative fluid balance in patients taking tolvaptan. Increases in serum sodium and osmolality can be observed 4-8 hours post-administration and is maintained for 24 hours. The magnitude of serum sodium and osmolality change increases with escalating doses. Furthermore, a decrease in urine osmolality and increase in free water clearance can be observed 4 hours after post-administration of tolvaptan. The affinity for V2 receptors is 29x greater than that of V1a receptors and does not have any appreciable affinity for V2 receptors.
Clinical Use
Tolvaptan, also known as OPC-41061, is a selective, competitive arginine vasopressin receptor 2 antagonist used to treat hyponatremia (low blood sodium levels) associated with congestive heart failure, cirrhosis, and the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH). Otsuka Pharmaceutical licensed tolvaptan under the trade name Samsca after the FDA approved the drug in May 2009. Tolvaptan has also shown efficacy against polycystic kidney disease. In a 2004 trial, tolvaptan administered with traditional diuretics was noted to increase excretion of excess fluids and improve blood sodium levels in patients with heart failure without producing side effects such as hypotension (low blood pressure) or hypokalemia (decreased blood levels of potassium). The drug also exhibited no adverse effect on kidney function.
Side Effects
The most common adverse events were thirst, dry mouth, asthenia, constipation, pollakiuria or polyuria, and hyperglycemia. The recommended starting dose is 15 mg daily with a daily 15-mg adjustment to a maximum of 60 mg daily to raise serum sodium concentration. Initiation should be in a hospital setting where serum sodium and volume status may be monitored since too rapid correction of hyponatremia (>12 mEq/L/24 h) can cause osmotic demyelination resulting in dysarthria, mutism, dysphagia, lethargy, spastic quadriparesis, seizures, coma, and death. In addition to avoiding concomitant use of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors, tolvaptan is contraindicated in settings of urgent need to raise serum sodium acutely, in patients with an inability to sense or appropriately respond to thirst, in hypovolemic hyponatremia conditions, and in anuric patients.
Synthesis
Tolvaptan may be prepared in 11 steps starting from 5chloro- 2-nitrobenzoic acid. Following esterification, reduction of the nitro moiety with tin(II) chloride, subsequent protection (tosylation) and alkylation of the resulting aniline, and a Dieckmann cyclization with potassium tert-butoxide generate the benzazepinone core that is ultimately decarboxylated by heating with hydrochloric acid in acetic acid. After deprotection of the amine group, condensation with 2methyl- 4-nitrobenzoyl chloride affords another nitro handle that is reduced with tin(II) chloride. This aniline is coupled with 2-methylbenzoyl chloride to give the penultimate intermediate. In the final step, reduction of the ketone functionality with sodium borohydride provides racemic tolvaptan that is formulated into 15- and 30-mg tablets for oral administration.
Metabolism
Metabolism exclusively by CYP3A4 enzyme in the liver. Metabolites are inactive.
storage
Store at +4°C
References
[1] miyazaki t, fujiki h, yamamura y, et al. tolvaptan, an orally active vasopressin v2-receptor antagonist-pharmacology and
Properties of Tolvaptan
| Melting point: | 219-222°C |
| Boiling point: | 594.4±50.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.311±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO: ≥15mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| pka | 13.00±0.70(Predicted) |
| color | white to tan |
Safety information for Tolvaptan
Computed Descriptors for Tolvaptan
| InChIKey | GYHCTFXIZSNGJT-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | C(NC1=CC=C(C(N2C3=CC=C(Cl)C=C3C(O)CCC2)=O)C(C)=C1)(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1C |
Tolvaptan manufacturer
SETV ASRV LLP
New Products
Methyl (R)-1-Boc-4,4-difluoropyrrolidine-2-carboxylate 2,2-Difluoropropylamine hydrochloride tert-butyl 3-bromoazetidine-1-carboxylate (R)-1-Boc-3-hydroxypyrrolidine DIFLUOROACETIC ANHYDRIDE 2,2-Difluoropropionic acid Diallylamine, 99% Calcium hydroxide, 95% Aluminum oxide, basic 2-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 97% L-tert-Leucine,97% N-Hydroxy-2-methylpropanimidamide 4-(3,4-Dichlorophenyl)-3,4-Dihydro-N-Methyl-1-(2H)-Naphthalenimine (Schiff Base) 2-AMINO-3,5-DIBROMO BENZALDEHYDE [ADBA] L-Glutamic Acid Dimethyl Ester Hcl 10-Methoxy-5H-dibenz[b,f]azepine 5-Cyanophthalide N, N-Carbonyldiimidazole (CDI) Dibenzoyl Peroxide Titanium Dioxide 2-(Methylthio) Benzonitrile Sodium Acetate Anhydrous Allopurinol 1,5-DibromopentaneRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Tolvaptan 97%View Details
Tolvaptan 97%View Details -
 150683-30-0 99%View Details
150683-30-0 99%View Details
150683-30-0 -
 Tolvaptan 95% CAS 150683-30-0View Details
Tolvaptan 95% CAS 150683-30-0View Details
150683-30-0 -
 Tolvaptan 150683-30-0 98%View Details
Tolvaptan 150683-30-0 98%View Details
150683-30-0 -
 150683-30-0 Tolvaptan 95-99%View Details
150683-30-0 Tolvaptan 95-99%View Details
150683-30-0 -
 Tolvaptan 98%View Details
Tolvaptan 98%View Details
150683-30-0 -
 Tolvaptan 96% CAS 150683-30-0View Details
Tolvaptan 96% CAS 150683-30-0View Details
150683-30-0 -
 Tolvaptan CAS 150683-30-0View Details
Tolvaptan CAS 150683-30-0View Details
150683-30-0