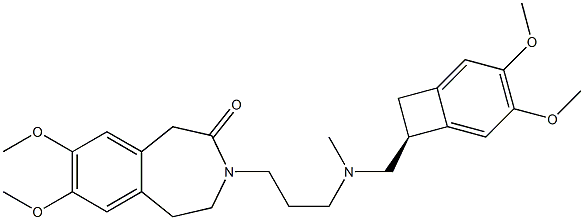
Ivabradine
- CAS NO.:155974-00-8
- Empirical Formula: C27H36N2O5
- Molecular Weight: 468.59
- MDL number: MFCD04975447
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-10-28 16:00:23
What is Ivabradine?
Absorption
It is recommended to take ivabradine with food to reduce variability in systemic exposure. Administration with food slows absorption by 1 hour, but increases systemic absorption by 20-30%. Ivabradine's oral bioavailability is about 40%.
Toxicity
Ivabradine may cause fetal toxicity when administered to pregnant women. Animal studies in pregnant rats have shown embryo-fetal toxicity and cardiac teratogenic effects. Effective contraception in women is recommended while using ivabradine.
Description
Ivabradine is a first selective and specific If inhibitor that was approved by EMEA in November for symptomatic treatment of chronic stable angina pectoris in patients with normal sinus rhythm. This is the first agent to lower heart rate by inhibiting the cardiac pacemaker If current. The compound was discovered and developed by Servier and is currently being marketed in Ireland.
Background
Ivabradine is a novel heart rate lowering medicine for the symptomatic management of stable angina pectoralis and symptomatic chronic heart failure. Ivabradine, brand name Corlanor, was approved by the FDA in April 2015 for the treatment of chronic heart failure in patients with an ejection fraction of ≤35%, in sinus rhythm with resting heart rate ≥70 beats per minute, who are not on beta-blockers due to contraindications or already receiving maximum beta-blocker dose. Recently a new indication was added to treat symptomatic heart failure from dilated cardiomyopathy for patients 6 months or more in age. Ivabradine acts by selectively inhibiting the "funny" channel pacemaker current (If) in the sinoatrial node in a dose-dependent fashion, resulting in a lower heart rate and thus more blood to flow to the myocardium. Although non-dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers and beta blockers also effectively lower heart rate, they exhibit adverse events due to their negative ionotropic effects. Therefore, as ivabradine is designed as a "pure" heart rate-lowering drug by selectively acting on the If channels, it may offer a more favorable side effect profile due to its lower likelihood of causing serious adverse effects.
Indications
Ivabradine is indicated by the FDA to reduce the risk of hospitalization for worsening heart failure in adult patients with stable, symptomatic chronic heart failure with left ventricular ejection fraction ≤35%, who are in sinus rhythm with resting heart rate ≥70 beats per minute and either are on maximally tolerated doses of beta-blockers or have a contraindication to beta-blocker use. It is also indicated for treatment of stable symptomatic heart failure as a result of dilated cardiomyopathy for pediatric patients 6 months of age or more.
Definition
ChEBI: A member of the class of benzazepines that is 7,8-dimethoxy-1,3,4,5-tetrahydro-3-benzazepin-2-one in which the amide hydrogen is replaced by a [{[(7S)-3,4-dimethoxybicyclo[4.2.0]octa-1,3,5-trien-7-yl]methyl}(methyl)amino]propyl} group. Use (as its hydrochloride salt) to treat patients with angina who have intolerance to beta blockers and/or heart failure.
Pharmacokinetics
The funny channels (If) open during repolarization and close during depolarization, making ivabradine's activity dependent on heart rate or the closing and opening of the channels. Therefore ivabradine exhibits use-dependence and is more pharmacologically active at higher heart rates. Ivabradine exhibits a linear dose-dependent heart-rate lowering activity (bradycardic effect) until a maximum dose of 30-40mg. At higher doses, the concentration of ivabradine tends to plateau, reducing risk of serious sinus bradycardia. It has been shown that the metabolite of ivabradine lowers heart rate as well, contributing to ivabradine's overall effect.
Synthesis
The convergent synthesis
of ivabradine was accomplished by coupling the key
benzocylclobutanyl amine 73 with oxadioxalane 76 in an in
situ deprotection and amination as shown in Scheme 13.
For the synthesis of the key amine 73, cyano group of compound
69 is reduced with borane-THF to give amine 70 in
90% yield, which was reacted with ethyl chloroformate to
give carbamate 71 in 80% yield. Complete reduction of the
carbamate was accomplished by refluxing with LAH in THF
to give racemic methyl amine 72 in 92% yield, which was
then resolved by crystallizing with N-acetyl ¨CL-glutamic acid to give chiral salt 73. Prior to the next step, the amine is
converted to the hydrochloride salt.
The coupling partner 76 to make ivabradine was prepared
from the azepinone 74 by first reacting with bromoethyldioxalane
to give 75. The olefin in 75 was reduced by hydrogenating
with palladium/carbon catalyst at 55??C to give 76.
To the same pot, the amine 73 was added and hydrogenated
to give reductive amination product ivabradine hydrochloride
(X) in very good yields.

Metabolism
Ivabradine is extensively metabolized by oxidation in the gut and liver by cytochrome P450 3A4 enzyme. Its active metabolite, N-desmethylated derivative, is also metabolized by CYP 3A4. Ivabradine's affinity for CYP 3A4 is low, making it unlikely to affect the metabolism of other drugs; however potent inhibitors or inducers of CYP 3A4 may affect ivabradine's plasma concentration and pharmacodynamic effects and should not be co-administered.
Properties of Ivabradine
| Boiling point: | 626.9±55.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.146±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| pka | 8.77±0.50(Predicted) |
Safety information for Ivabradine
Computed Descriptors for Ivabradine
Ivabradine manufacturer
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
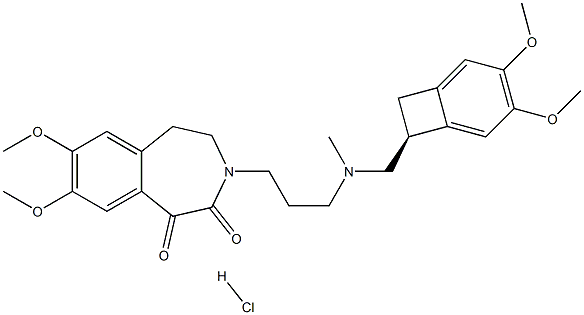
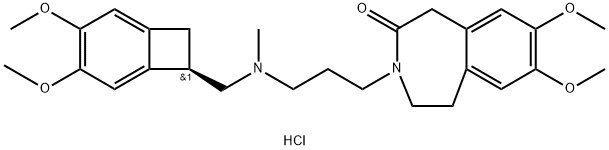
![3-[3-[[[(7S)-3,4-DiMethoxybicyclo[4.2.0]octa-1,3,5-trien-7-yl]Methyl]MethylaMino]propyl]-1,3-dihydro-7,8-diMethoxy-H-3-benzazepin-2-one](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/1086026-31-4.gif)
![C-(3,4-DIMETHOXY-BICYCLO[4.2.0]OCTA-1(6),2,4-TRIEN-7-YL)-METHYLAMINE](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/73344-75-9.gif)
You may like
-
 IVABRADINE 98%View Details
IVABRADINE 98%View Details -
 155974-00-8 98%View Details
155974-00-8 98%View Details
155974-00-8 -
 Ivabradine 98%View Details
Ivabradine 98%View Details
155974-00-8 -
 Ivabradine 155974-00-8 99%View Details
Ivabradine 155974-00-8 99%View Details
155974-00-8 -
 Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
110-86-1 -
 Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
84-74-2 -
 Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
288-32-4 -
 Thiourea 99% ARView Details
Thiourea 99% ARView Details
62-56-6
