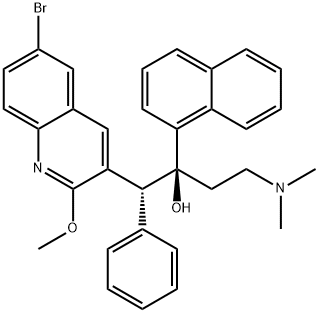
TMC-207
- CAS NO.:843663-66-1
- Empirical Formula: C32H31BrN2O2
- Molecular Weight: 555.5
- MDL number: MFCD22628872
- EINECS: 1308068-626-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-26 08:49:36
What is TMC-207?
Absorption
After the recommended dosing regimen of bedaquiline (400 mg for 2 weeks followed by 200 mg three times per week for 22 weeks), the Cmax and AUC24h were calculated to be 1.659 μg/ml and 25.863 μg.h/ml respectively.
After a single oral dose administration of bedaquiline, maximum plasma concentrations (Cmax) are typically achieved at approximately 5 hours post-dose. Cmax and the area under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC) increased proportionally up to 700 mg (1.75 times the 400 mg loading dose).
Administration of bedaquiline with a standard meal containing approximately 22 grams of fat (558 total Kcal) increased the relative bioavailability by approximately 2-fold compared to administration under fasted conditions. Bedaquiline should be taken with food to enhance its oral bioavailability.
Toxicity
There is no experience with the treatment of acute overdose with SIRTURO. Take general measures to support basic vital functions including monitoring of vital signs and ECG (QT interval) in case of deliberate or accidental overdose. It is advisable to contact a poison control center to obtain the latest recommendations for the management of an overdose. Since bedaquiline is highly protein-bound, dialysis is not likely to significantly remove bedaquiline from plasma.
Bedaquiline was not carcinogenic in rats up to the maximum tolerated dose of 10 mg/kg/day. Exposures at this dose in rats (AUCs) were within 1-fold to 2-fold of those observed in adult patients in the clinical trials.
No mutagenic or clastogenic effects were detected in the in vitro non-mammalian reverse mutation (Ames) test, in vitro mammalian (mouse lymphoma) forward mutation assay, and an in vivo mouse bone marrow micronucleus assay.
SIRTURO did not affect fertility when evaluated in male and female rats at approximately twice the clinical exposure based on AUC comparisons. There was no effect of maternal treatment on sexual maturation, mating performance, or fertility in the F1 generation exposed to bedaquiline in utero at approximately twice the human exposure.
Description
In December 2012, the US FDA approved bedaquiline as part of combination therapy for the treatment of multi-drug resistant tuberculosis (MDRTB). Bedaquiline is the first drug approved for MDR-TB and is the first approval from a new class of antituberculosis agents in the past 40 years. Due to the high unmetmedical need for treating MDR-TB, the FDA granted bedaquiline accelerated approval based on Phase II results, providing patients access to the drug while additional clinical studies are carried out. Bedaquiline (also known as TMC207 and R207910) is a diarylquinoline that was discovered from a high-throughput, whole-cell screening strategy with Mycobacterium smegmatis used as a surrogate for M. tuberculosis. Bedaquiline is a single enantiomer of an initial screening hit. Bedaquiline has potent and selective activity against mycobacteria, and is active against both drug-sensitive and drug-resistant M. tuberculosis. The mechanism of action of bedaquiline is unique amongst anti-TB drugs and involves inhibition of mycobacterial ATP synthase; it is not active against human ATP synthase. Bedaquiline has in vivo activity in numerous preclinical models of TB infection, alone and in combination with other anti-TB agents, and has bactericidal activity in established TB infection models. Bedaquiline is synthesized in five steps from 3-phenylpropionic acid and para-bromoaniline. Following amide formation, treatment with POCl3 and DMF under Vilsmeier–Hack conditions gave a 2-chloroquinoline product. Treatment with sodium methoxide, followed by condensation with 3-(dimethylamino)-1-(naphthalen-1-yl)propan-1-one, and separation of isomers gave bedaquiline.
Description
TMC207 is a diarylquinoline that selectively inhibits the proton pump of the mycobacterial ATP synthase. It demonstrates potent activity against both drug-sensitive and drug-resistant M. tuberculosis and other mycobacterial species with MIC50 values of ~0.03 μg/ml.
Originator
Janssen (Belgium)
The Uses of TMC-207
(αS,βR)-Bedaquiline is a diarylquinoline derivative that acts as a mycobacterial inhibitor. Bedaquiline shows promise as potential drug in the treatment of tuberculosis.
The Uses of TMC-207
Labeled Bedaquiline, intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of Bedaquiline by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry.
Indications
Bedaquiline is indicated as part of combination therapy in the treatment of adult and pediatric patients (5 years and older and weighing at least 15 kg) with pulmonary multi-drug resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB). Reserve SIRTURO for use when an effective treatment regimen cannot otherwise be provided.
This indication is approved under FDA accelerated approval based on time to sputum culture conversion. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in confirmatory trials.
Background
Bedaquiline is a bactericidal antimycobacterial drug belonging to the class of diarylquinoline. The quinolinic central heterocyclic nucleus with alcohol and amine side chains is responsible for bedaquiline-mediated antimycobacterial activity. Although it is closely related to fluoroquinolones, bedaquiline does not affect DNA gyrase; instead, bedaquiline inhibits the c subunit of ATP synthase responsible for synthesizing ATP. Consequently, bedaquiline can be used to treat mycobacterial infection, particularly tuberculosis (TB). Although the current standard of TB treatment of anti-TB drugs for 2 months, including 2 key drugs isoniazid and rifampin, is highly effective, the emergence of multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB) to isoniazid and rifampin has substantially worsened patients outcome.
Bedaquiline was approved by the FDA on December 28, 2012, to treat pulmonary MDR-TB, following favorable results in multiple pre-clinical and clinical studies. It is the first drug that was approved in the last 40 years by the FDA for TB unresponsive to current treatments on the market. Currently, bedaquiline is the last-line anti-TB drug and must only be used in an appropriate combination regimen.
Definition
ChEBI: Bedaquiline is a quinoline-based antimycobacterial drug used (as its fumarate salt) for the treatment of pulmonary multi-drug resistant tuberculosis by inhibition of ATP synthase, an enzyme essential for the replication of the mycobacteria. It has a role as an antitubercular agent and an ATP synthase inhibitor. It is a member of quinolines, a member of naphthalenes, an organobromine compound, an aromatic ether, a tertiary alcohol and a tertiary amino compound. It is a conjugate base of a bedaquiline(2+).
brand name
Sirturo
Pharmacokinetics
Bedaquiline is primarily subjected to oxidative metabolism leading to the formation of N-monodesmethyl metabolite (M2). M2 is not thought to contribute significantly to clinical efficacy given its lower average exposure (23% to 31%) in humans and lower antimycobacterial activity (4-fold to 6-fold lower) than the parent compound. However, M2 plasma concentrations appeared to correlate with QT prolongation.
Bedaquiline inhibits mycobacterial TB at a minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) from 0.002-0.06 μg/ml and with a MIC50 of 0.03 μg/ml. The proportion of naturally resistant bacteria is low, estimated to be in one strain over 107/108 bacteria. Bacteria that have smaller ATP stores (such as dormant, nonreplicating bacilli) are more susceptible to bedaquiline.
Additionally, bedaquiline is also effective against nontuberculous mycobacteria, with MICs ranging from 0.06 to 0.5 μg/ml.
A potential for the development of resistance to bedaquiline in M. tuberculosis exists. Modification of the atpE target gene, and/or upregulation of the MmpS5-MmpL5 efflux pump (Rv0678 mutations) have been associated with increased bedaquiline MIC values in isolates of M. tuberculosis. Target-based mutations generated in preclinical studies lead to 8- to 133-fold increases in bedaquiline MIC, resulting in MICs ranging from 0.25 to 4 micrograms per mL. Efflux-based mutations have been seen in preclinical and clinical isolates. These lead to 2- to 8-fold increases in bedaquiline MICs, resulting in bedaquiline MICs ranging from 0.25 to 0.5 micrograms per mL.
Metabolism
CYP3A4 was the major CYP isoenzyme involved in the in vitro metabolism of bedaquiline and the formation of the N-monodesmethyl metabolite (M2).
References
Andries et al. (2005), A diarylquinoline drug active on the ATP synthase of Mycobacterium tuberculosis; Science, 307 223 Koul et al. (2007), Diarylquinolines target subunit c of mycobacterial ATP synthase; Nat. Chem. Biol., 3 323 Biukovic et al. (2013), Variations of subunit {varepsilon} of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis F1F0 ATP synthase and a novel model for mechanism of action of the tuberculosis drug TMC207; Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., 57 168 Sarathy et al. (2019), Re-Understanding the Mechanisms of Action of the Anti-Mycobacterial Drug Bedaquiline; Antibiotics (Basel), 8 261 Ghahremanpour et al. (2020), Identification of 14 Known Drugs as Inhibitors of the Main Protease of SARS-CoV-2; ACS Med. Chem. Lett., 11 2526
Properties of TMC-207
| Melting point: | 104 °C |
| Boiling point: | 702.7±60.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.322±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Room temperature |
| solubility | Soluble in DMSO (10 mg/ml) |
| form | solid |
| pka | 13.05±0.29(Predicted) |
| color | White |
| Stability: | Stable for 1 year from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions in DMSO may be stored at -20°C for up to 1 month. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 843663-66-1 |
Safety information for TMC-207
Computed Descriptors for TMC-207
TMC-207 manufacturer
Kavya Pharma
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
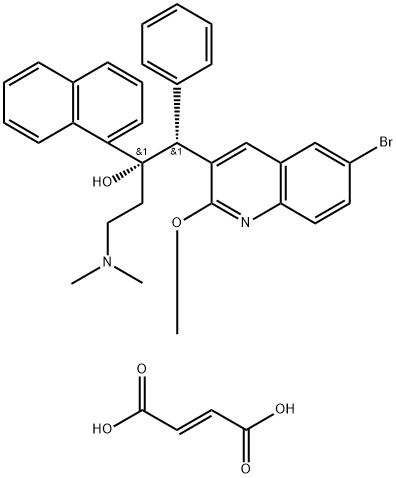
 843663-66-1 Bedaquline Fumarate 98%View Details
843663-66-1 Bedaquline Fumarate 98%View Details
843663-66-1 -
 Bedaquiline 95% CAS 843663-66-1View Details
Bedaquiline 95% CAS 843663-66-1View Details
843663-66-1 -
 Bedaquiline Cas No : 843663-66-1View Details
Bedaquiline Cas No : 843663-66-1View Details
843663-66-1 -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
