TITANIUM
- CAS NO.:16962-40-6
- Empirical Formula: F6H4NTi-
- Molecular Weight: 179.9
- MDL number: MFCD00010888
- EINECS: 241-036-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-09-09 18:15:22
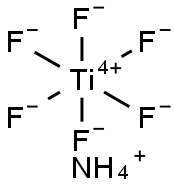
What is TITANIUM?
Chemical properties
white crystalline powder, crystals and/or chunks
History
Discovered by Gregor in 1791; named by Klaproth in 1795. Impure titanium was prepared by Nilson and Pettersson in 1887; however, the pure metal (99.9%) was not made until 1910 by Hunter by heating TiCl4 with sodium in a steel bomb. Titanium is present in meteorites and in the sun. Rocks obtained during the Apollo 17 lunar mission showed presence of 12.1% TiO2. Analyses of rocks obtained during earlier Apollo missions show lower percentages. Titanium oxide bands are prominent in the spectra of M-type stars. The element is the ninth most abundant in the crust of the Earth. Titanium is almost always present in igneous rocks and in the sediments derived from them. It occurs in the minerals rutile, ilmenite, and sphene, and is present in titanates and in many iron ores. Deposits of ilmenite and rutile are found in Florida, California, Tennessee, and New York. Australia, Norway, Malaysia, India, and China are also large suppliers of titanium minerals. Titanium is present in the ash of coal, in plants, and in the human body. The metal was a laboratory curiosity until Kroll, in 1946, showed that titanium could be produced commercially by reducing titanium tetrachloride with magnesium. This method is largely used for producing the metal today. The metal can be purified by decomposing the iodide. Titanium, when pure, is a lustrous, white metal. It has a low density, good strength, is easily fabricated, and has excellent corrosion resistance. It is ductile only when it is free of oxygen. The metal burns in air and is the only element that burns in nitrogen. Titanium is resistant to dilute sulfuric and hydrochloric acid, most organic acids, moist chlorine gas, and chloride solutions. Natural titanium consists of five isotopes with atomic masses from 46 to 50. All are stable. Eighteen other unstable isotopes are known. The metal is dimorphic. The hexagonal α form changes to the cubic β form very slowly at about 880°C. The metal combines with oxygen at red heat, and with chlorine at 550°C. Titanium is important as an alloying agent with aluminum, molybdenum, manganese, iron, and other metals. Alloys of titanium are principally used for aircraft and missiles where lightweight strength and ability to withstand extremes of temperature are important. Titanium is as strong as steel, but 45% lighter. It is 60% heavier than aluminum, but twice as strong. Titanium has potential use in desalination plants for converting sea water into fresh water. The metal has excellent resistance to sea water and is used for propeller shafts, rigging, and other parts of ships exposed to salt water. A titanium anode coated with platinum has been used to provide cathodic protection from corrosion by salt water. Titanium metal is considered to be physiologically inert; however, titanium powder may be a carcinogenic hazard. When pure, titanium dioxide is relatively clear and has an extremely high index of refraction with an optical dispersion higher than diamond. It is produced artificially for use as a gemstone, but it is relatively soft. Star sapphires and rubies exhibit their asterism as a result of the presence of TiO2. Titanium dioxide is extensively used for both house paint and artist’s paint, as it is permanent and has good covering power. Titanium oxide pigment accounts for the largest use of the element. Titanium paint is an excellent reflector of infrared, and is extensively used in solar observatories where heat causes poor seeing conditions. Titanium tetrachloride is used to iridize glass. This compound fumes strongly in air and has been used to produce smoke screens. The price of titanium metal (99.9%) is about $1100/kg.
The Uses of TITANIUM
Ammonium hexafluorotitanate is used as an anti-corrosive cleaning agent. It is also used for the production of ceramics and glass. Further, it is used in the preparation of synthetic gems.
Safety Profile
Poison by intravenous route. See also FLUORIDES, AMMONIA, and TITANIUM COMPOUNDS. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of Fand NOx,.
Properties of TITANIUM
| Melting point: | 1660 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 3287 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 4.5 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| solubility | H2O: slightly soluble(lit.) |
| form | wire |
| color | White |
| PH | pH(50g/l, 25℃) : 2.0~4.0 |
| Water Solubility | Insoluble in water. |
| Hydrolytic Sensitivity | 0: forms stable aqueous solutions |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 2.5 mg/m3 NIOSH: IDLH 250 mg/m3 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 16962-40-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Titanate(2-), hexafluoro-, diammonium, (OC-6-11)- (16962-40-6) |
Safety information for TITANIUM
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H312:Acute toxicity,dermal H332:Acute toxicity,inhalation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P321:Specific treatment (see … on this label). P304+P340:IF INHALED: Remove victim to fresh air and Keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing. |
Computed Descriptors for TITANIUM
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
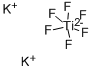
You may like
-
 Ammonium hexafluorotitanate CAS 16962-40-6View Details
Ammonium hexafluorotitanate CAS 16962-40-6View Details
16962-40-6 -
 Ammonium hexafluorotitanate CAS 16962-40-6View Details
Ammonium hexafluorotitanate CAS 16962-40-6View Details
16962-40-6 -
 Ammonium hexafluorotitanate CAS 16962-40-6View Details
Ammonium hexafluorotitanate CAS 16962-40-6View Details
16962-40-6 -
 Ammonium hexafluorotitanate CAS 16962-40-6View Details
Ammonium hexafluorotitanate CAS 16962-40-6View Details
16962-40-6 -
 Grade Standard: Industrial Grade TITANIUM METAL POWDER 7440-32-6 CASView Details
Grade Standard: Industrial Grade TITANIUM METAL POWDER 7440-32-6 CASView Details
7440-32-6 -
 Gray Titanium Metal PowderView Details
Gray Titanium Metal PowderView Details
7440-32-6 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
