Terlipressin acetate
- CAS NO.:14636-12-5
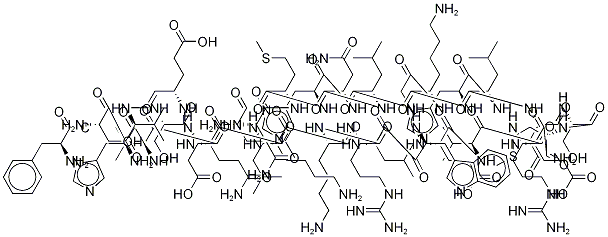
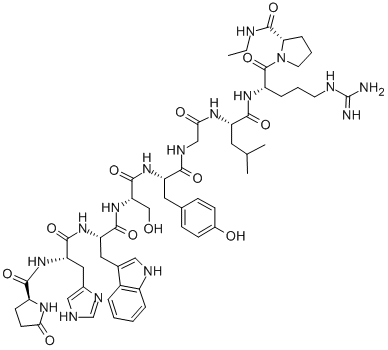
- Empirical Formula: C52H74N16O15S2
- Molecular Weight: 1227.37
- MDL number: MFCD00155450
- EINECS: 238-680-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-05 11:59:05
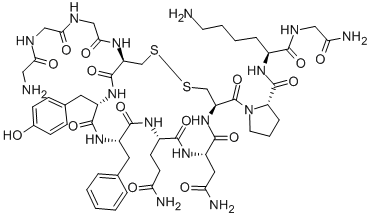
What is Terlipressin acetate?
Description
Terlipressin acetate is a novel synthetic long-acting vasopressin preparation. It is a kind of prodrug, which is inactive by itself. After the action of aminopeptidase in the body, after removing the three glycyl residues at its N-terminus, it slowly "releases" the active lysine vasopressin. Therefore, terlipressin acts as a reservoir that releases lysine vasopressin at a steady rate.
Chemical properties
N-(N-(N-Glycylglycyl)glycyl)-8-L-lysinevasopressin (Terlipressin acetate) is White Solid
The Uses of Terlipressin acetate
N-(N-(N-Glycylglycyl)glycyl)-8-L-lysinevasopressin is an analogue of vasopressin used as a vasoactive drug in the management of hypotension. N-(N-(N-Glycylglycyl)glycyl)-8-L-lysinevasopressin is used norepinephrine-resistant septic shock and hepatorenal syndrome. N-(N-(N-Glycylglycyl)glycyl)-8-L-lysinevasopressin is also used in the treatment of acute variceal bleeding.
What are the applications of Application
Terlipressin Acetate is an analogue of vasopressin used as a vasoactive for proteomics research
Definition
ChEBI: Terlipressin is a polypeptide.
Clinical Use
Treatment of bleeding oesophageal varices
Side Effects
In clinical trials, the most common side effects of terlipressin administration were paleness, increased blood pressure, peripheral ischemia, abdominal pain, nausea, diarrhea, and headache.
Terlipressin related adverse events are common and most of terlipressin related adverse events were mild or moderate, which can be resolved spontaneously without any intervention. As terlipressin acts mainly on the splanchnic vessels, the incidence of severe ischemic complications is lower with terlipressin than with vasopressin. However, it may cause serious complications such as myocardial infarction, intestinal ischemia, peripheral cyanosis, and skin necrosis[1].
Metabolism
Terlipressin is metabolised by tissue peptidases resulting in the slow release of lypressin. Terlipressin is almost completely metabolised in the kidneys and liver, with less than 1% of terlipressin and less than 0.1% of lypressin excreted in the urine.
References
[1] Chiang C, et al. Terlipressin-Induced Peripheral Cyanosis in a Patient with Liver Cirrhosis and Hepatorenal Syndrome. American Journal of Case Reports, 2019.
Properties of Terlipressin acetate
| Melting point: | >170°C (dec.) |
| Boiling point: | 1824.0±65.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.46±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Keep in dark place,Inert atmosphere,Store in freezer, under -20°C |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 9.90±0.15(Predicted) |
| color | White |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 14636-12-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Terlipressin acetate
Computed Descriptors for Terlipressin acetate
| InChIKey | BENFXAYNYRLAIU-ITQMCZIINA-N |
Terlipressin acetate manufacturer
Piramal Pharma Solutions
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 14636-12-5 Terlipressin 99%View Details
14636-12-5 Terlipressin 99%View Details
14636-12-5 -
 14636-12-5 98%View Details
14636-12-5 98%View Details
14636-12-5 -
 Terlipressin for NMR identification CAS 14636-12-5View Details
Terlipressin for NMR identification CAS 14636-12-5View Details
14636-12-5 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1