Sodium tetraborate decahydrate
Synonym(s):Borax decahydrate;Sodium borate decahydrate;di-Sodium tetraborate decahydrate;Sodium Borate, Decahydrate;Sodium Tetraborate, Dodecahydrate, Borax
- CAS NO.:1303-96-4
- Empirical Formula: B4H20Na2O17
- Molecular Weight: 381.37
- MDL number: MFCD00149193
- EINECS: 603-411-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:22
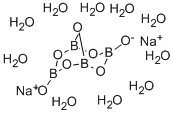
What is Sodium tetraborate decahydrate?
Description
Borax is a noncombustible (an inherent fireretardant), bluish-gray or green, odorless crystalline powderor granules. Molecular weight=301.37; Boilingpoint=320℃; Freezing/Melting point=75℃ (rapid heating). Borax is soluble in water; solubility=6% at 20℃.Borax pentahydrate is a white crystalline solid or free-flowing powder. Odorless. Molecular weight=291.4; Specificgravity (H2O:1)=1.82; Melting Point: 200℃; Density:1.82 g/cm3. Soluble in water; solubility=3%.
Chemical properties
White cryst. powder
Chemical properties
Borax is a noncombustible (an inherent fire retardant), bluish-gray or green, odorless crystalline powder or granules.
Chemical properties
Sodium borate occurs as white, hard crystals, granules, or crystalline powder. It is odorless and efflorescent.
Physical properties
White monoclinic crystal; density 1.73 g/cm3; decomposes at 75°C; soluble in water; the vapor pressure of the pure compound 1.6 torr at 20°C and that of a saturated solution 130 torr at 58°C; the pH of a 1% aqueous solution 9.24 (the pH is nearly independent of concentration); readily dissolves in alcohols.
Occurrence
Borax decahydrate occurs in nature as mineral, borax (tincal). It is one of the most common sodium borate ores. The compound has several industrial applications. The refined material is mostly used in household cleaning products. It is used to make pyrex and other borosilicate glasses. Borax is added to fertilizers in small quantities as a source of boron, as a trace nutrient for plants. High purity grade borax is used in cosmetics, toilet products and electrolytic capacitors. It also is used in fire retardants, adhesives and herbicides.
The Uses of Sodium tetraborate decahydrate
Sodium Tetraborate Decahydrate is used as a buffer in antigetn-retrieval procedure for bromodeoxyuridine immunolabeling with concurrent labeling of nuclear DNA and antigens damaged by hydrochloric acid pretreatment.
The Uses of Sodium tetraborate decahydrate
metabolite
The Uses of Sodium tetraborate decahydrate
Buffers; complexing or masking agent.
The Uses of Sodium tetraborate decahydrate
Soldering metals; manufacture of glazes and enamels; tanning; in the production of adhesives and in anticorrosion systems; in cleaning Compounds; artificially aging wood; as preservative, either alone or with other antiseptics against wood fungus; fireproofing fabrics and wood; curing and preserving skins; in cockroach control. Pharmaceutic aid (alkalizer).
The Uses of Sodium tetraborate decahydrate
A natural, colorless salt crystal found in some lake beds. It is soluble in water and glycerin but not in alcohol. When mixed with water, it produces a slight alkaline reaction. Its use in photography was principally as a pH modifier in gold toning baths, but it was also used as a restrainer in pyrogallic acid developers and as an accelerator in hydroquinone developers.
Production Methods
Sodium borate can be prepared from minerals such as borosodium calcite, pandermite, or tinkal; these are natural sodium or calcium borates. Treatment of the mineral with sodium carbonate and sodium hydrogencarbonate yields the sodium borate decahydrate. In the USA, brine from salt lakes is also an important source of sodium borate.
Hazard
Toxic by inhalation.
Health Hazard
Borates are irritants of the eyes, nose, and throat; at high concentrations ingestion of the compounds can result in gastrointestinal irritation, kidney injury, and even death from central nervous system depression or cardiovascular collapse.
Agricultural Uses
Borate is a salt of boric acid (H3BO3). There are two known types of borates - orthoborate and metaborate which are used as fertilizers. Besides these, polyborates, boric acid, calcium polyborate (colemanite), sodium tetraborate, solubor and complex borosilicate (boron frits) are also used as fertilizers to reduce boron deficiency. Borate minerals like kernite and tincal are the main sources of borax.
Borax, a source of boron, is the salt of boric acid, sodium hydroxide and sodium carbonate. Borax, otherwise called disodium tetraborate decahydrate(Na2B4O7·10H2O)is a water-soluble white compound. It occurs as a mineral in some alkaline salt deposits. The main sources of borax are borate minerals, kernite(Na2B4·4H2O),a sorite and heal(Na2B4O7·10H2O)which are purified by recrystallization. On treatment with an acid, borax gives boric acid which is absorbed as boron by plants. Borax contains 10.5 to 11.4% boron or 36.5% boric oxide (B2O3).
Borax is a supplier of micronutrient boron for plants and is applied as such or as a foliar spray. Solubor is preferred to borax for its greater solubility and because it causes minimum changes in the crystallization temperature.
Borax is a very important substance in other industries too. It is used as a metallurgical flux in glass and ceramic industries, a buffer, a mild alkaline antiseptic and a source of boron compounds.
Agricultural Uses
Solubor is a type of borate containing 20.3% boron. It is chemically a polyborate, similar to borax, and is represented as Na2B2O7?5H2O +Na2B10O16?10H2O. is a finely-ground, white product specially designed for foliar, liquid or dust applications, to correct boron deficiency.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Sodium borate is used in pharmaceutical applications similarly to
boric acid (see Boric Acid). It has been used externally as a mild
astringent and as an emulsifying agent in creams. It has also been
used in lozenges, mouthwashes, otic preparations (0.3% w/v), and
ophthalmic solutions (0.03–1.0% w/v). Sodium borate has additionally
been investigated in the prevention of crystal formation in
freeze-dried solutions.
Preparations of sodium borate in honey have historically been
used as paints for the throat, tongue, and mouth, but such use is
now inadvisable because of concerns about toxicity in such applications. Sodium borate is also used in cosmetics
such as moisturizers, deodorants, and shampoos.
Safety Profile
Experimental poison by subcutaneous route. Moderately toxic to humans by ingestion. Moderately toxic experimentally by ingestion, intravenous, and intraperitoneal routes. Experimental reproductive effects. Mutation data reported. Ingestion of 5-10 g of borax by children can cause severe vomiting, diarrhea, shock, death. Incompatible with acids, metallic salts. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of Na2O, boron. See also BORON COMPOUNDS. Used in ant poisons, for fly control around refuse and manure piles, as a larvicide, in manufacture of glazes, enamels, cleaning compounds, and in soldering metals.
Safety
Sodium borate has weak bacteriostatic and astringent properties.
Historically, sodium borate has been used as a disinfectant in skin
lotions and eye-, nose-, and mouthwashes. However, boric acid is
easily absorbed via mucous membranes and damaged skin, and
severe toxicity has been observed, especially in babies and
children. Consequently, the use of sodium borate as a disinfectant
is now considered somewhat obsolete and careful use is recommended.
The toxic effects of sodium borate include vomiting,
diarrhea, erythema, CNS depression, and kidney damage. The
lethal oral intake is approximately 20 g in adults and 5 g in
children.
LD50 (guinea pig, oral): 5.33 g/kg
LD50 (mouse, IP): 2.711 g/kg
LD50 (mouse, IV): 1.320 g/kg
LD50 (mouse, oral): 2.0 g/kg
LD50 (rat, oral): 2.66 g/kg
Potential Exposure
Borax is used as a soldering flux, preservative against wood fungus; and as an antiseptic. Used in ant poisons, for fly control around refuse and manure piles, as a larvicide. It is used in the manufacture of enamels and glazes, fiberglass insulation; sodium perborate bleach; in tanning, cleaning compounds; for fireproofing fabrics and wood; and in artificial aging of wood.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPRif heart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and inducevomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.
Carcinogenicity
Sodium borate tested negatively in the Ames bioassay but was found to be cytotoxic to cultured human fibroblasts.
Storage
Sodium borate should be stored in a well-closed container in a cool, dry, place.
Shipping
UN3077 Environmentally hazardous substances, solid, n.o.s., Hazard class: 9; Labels: 9—Miscellaneous hazardous material, Technical Name Required.
Purification Methods
Crystallise the borate from water (3.3mL/g), keeping below 55o to avoid formation of the pentahydrate. Filter it off at the pump, wash it with water and equilibrate it for several days in a desiccator containing an aqueous solution saturated with respect to sucrose and NaCl. Borax can be prepared more quickly (but its water content is somewhat variable) by washing the recrystallised material at the pump with water, followed by 95% EtOH, then Et2O, and dried in air at room temperature for 12-18hours on a clock glass. [Becher in Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry (Ed. Brauer) Academic Press Vol I pp 794-795 1963.]
Incompatibilities
Dissolves in water forming a basic solution. Boron dust may form explosive mixture with air. Contact with strong oxidizers may be violent. Boron is incompatible with ammonia, bromine tetrafluoride, cesium carbide, chlorine, fluorine, interhalogens, iodic acid, lead dioxide, nitric acid, nitric oxide, nitrosyl fluoride, nitrous oxide, potassium nitrite, rubidium carbide, silver fluoride.
Incompatibilities
Sodium borate is incompatible with acids and with metallic and alkaloidal salts.
Waste Disposal
Borax, dehydrated: The material is diluted to the recommended provisional limit (0.10 mg/L) in water. The pH is adjusted to between 6.5 and 9.1 and then the material can be discharged into sewers or natural streams.
Regulatory Status
Accepted for use as a food additive in Europe. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (otic preparations; ophthalmic solutions and suspensions). Included in nonparenteral medicines licensed in the UK, Italy, France, Germany, and Japan. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients.
Properties of Sodium tetraborate decahydrate
| Melting point: | 75 °C |
| Boiling point: | 320°C |
| Density | 1.73 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor pressure | 0.213 hPa (20 °C) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | H2O: 0.1 M at 20 °C, clear, colorless |
| form | Powder/Solid |
| color | White, gray, bluish or greenish white streaked |
| Specific Gravity | 1.73 |
| PH Range | 9.2 |
| Odor | Odorless |
| PH | 9.21(1 mM solution);9.17(10 mM solution);9.05(100 mM solution); |
| Water Solubility | 60 g/L (20 ºC) |
| λmax | λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.012 λ: 280 nm Amax: 0.010 |
| Merck | 14,8590 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 2 mg/m3; STEL 6 mg/m3 NIOSH: TWA 5 mg/m3 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 1303-96-4 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Borax (1303-96-4) |
Safety information for Sodium tetraborate decahydrate
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. P337+P313:IF eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Sodium tetraborate decahydrate
| InChIKey | CDMADVZSLOHIFP-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Sodium tetraborate decahydrate manufacturer
M/S Rajvi Chemical Corporation LLP
Meru Chem Private Limited
DS Fine Chem
Paresh Impex
ASM Organics
Bazayan & Co.
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 10303-96-4 Borax Decahydrate 99%View Details
10303-96-4 Borax Decahydrate 99%View Details
10303-96-4 -
 Borax Decahydrate 10303-96-4 99%View Details
Borax Decahydrate 10303-96-4 99%View Details
10303-96-4 -
 BORAX 98%View Details
BORAX 98%View Details -
 BORAX DECAHYDRATE 99%View Details
BORAX DECAHYDRATE 99%View Details -
 Sodium tetraborate decahydrate 98%View Details
Sodium tetraborate decahydrate 98%View Details -
 Di-Sodium Tetraborate (SQ) CAS 1303-96-4View Details
Di-Sodium Tetraborate (SQ) CAS 1303-96-4View Details
1303-96-4 -
 Borax CAS 1303-96-4View Details
Borax CAS 1303-96-4View Details
1303-96-4 -
 Borax (ER) CAS 1303-96-4View Details
Borax (ER) CAS 1303-96-4View Details
1303-96-4
