Sodium phosphate monobasic
Synonym(s):Monosodium dihydrogen orthophosphate;Monosodium phosphate;Sodium biphosphate;Sodium dihydrogen phosphate;Sodium dihydrogen phosphate anhydrous
- CAS NO.:7558-80-7
- Empirical Formula: H3O4P.Na
- Molecular Weight: 119.977
- MDL number: MFCD00003527
- EINECS: 231-449-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:56
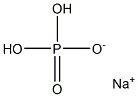
What is Sodium phosphate monobasic?
Absorption
Tmax for phosphate absorption with orally administered liquid sodium phosphate is 1-3h .
Toxicity
Intamuscular LD50 of 250mg/kg and oral LD50 of 8290 mg/kg reported in rats . Phosphate toxicity is likely due to the disturbance of other electrolytes when phosphate levels are high, producing symptoms including tetany, dehydration, hypotension, tachycardia, hyperpyrexia, cardiac arrest and coma . Risk of raising phosphate levels through use of sodium phosphate appears to be higher in smaller patients .
Chemical properties
White, slightly deliquescent crystals or granules.
The Uses of Sodium phosphate monobasic
Sodium phosphate monobasic monohydrate is used as sequestrant, emulsifier, mordant in dyeing, reagent and buffer in foods and analytical chemistry. It was applied as a fireproofing agent and for weighting silk in tanning. Sodium phosphate monobasic, anhydrous is a high buffering capacity reagent used in molecular biology, biochemistry, and chromatography. It is employed in manufacturing of enamels, ceramics, detergents, boiler compounds, in soldering and brazing instead of borax.
Indications
Used to treat constipation or to clean the bowel before a colonoscopy .
Preparation
Monobasic sodium phosphate can be prepared by partial neutralization of phosphoric acid with sodium hydroxide in equimolar amounts: H3PO4 + NaOH → NaH2PO4 + H2O
It also can be made by treating disodium hydrogen phosphate with phosphoric acid in proper stoichiometric amount: Na2HPO4 + HPO4 → 2NaH2PO4.
Definition
ChEBI: Sodium dihydrogenphosphate is a sodium phosphate.
General Description
Sodium phosphate is a saline laxative that is thought to work by increasing fluid in the small intestine. It is used for colonic cleansing before endoscopic examination of colon.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Monobasic sodium phosphate is used in a wide variety of pharmaceutical formulations as a buffering agent and as a sequestering agent. Therapeutically, monobasic sodium phosphate is used as a mild saline laxative and in the treatment of hypophosphatemia. It inceases fecal water content to increase mobility through the large intestine. Monobasic sodium phosphate is also used in food products, for example, in baking powders, and as a dry acidulant and sequestrant.
Safety
Monobasic sodium phosphate is widely used as an excipient in
parenteral, oral, and topical pharmaceutical formulations.
Phosphate occurs extensively in the body and is involved in
many physiological processes since it is the principal anion of
intracellular fluid. Most foods contain adequate amounts of
phosphate, making hypophosphatemia virtually unknown except
in certain disease states or in patients receiving total parenteral
nutrition. Treatment is usually by the oral administration of up to
100 mmol of phosphate daily.
Approximately two-thirds of ingested phosphate is absorbed
from the gastrointestinal tract, virtually all of it being excreted in the
urine, and the remainder is excreted in the feces.
Excessive administration of phosphate, particularly intravenously,
rectally, or in patients with renal failure, can cause
hyperphosphatemia that may lead to hypocalcemia or other severe
electrolyte imbalances. Adverse effects occur less frequently
following oral consumption, although phosphates act as mild saline
laxatives when administered orally or rectally (2–4 g of monobasic
sodium phosphate in an aqueous solution is used as a laxative).
Consequently, gastrointestinal disturbances including diarrhea,
nausea, and vomiting may occur following the use of monobasic
sodium phosphate as an excipient in oral formulations. However,
the level of monobasic sodium phosphate used as an excipient in a pharmaceutical formulation is not usually associated with adverse
effects.
LD50 (rat, IM): 0.25 g/kg(10)
LD50 (rat, oral): 8.29 g/kg
Incompatibilities
Monobasic sodium phosphate is an acid salt and is therefore
generally incompatible with alkaline materials and carbonates;
aqueous solutions of monobasic sodium phosphate are acidic and
will cause carbonates to effervesce.
Monobasic sodium phosphate should not be administered
concomitantly with aluminum, calcium, or magnesium salts since
they bind phosphate and could impair its absorption from the
gastrointestinal tract. Interaction between calcium and phosphate,
leading to the formation of insoluble calcium phosphate precipitates,
is possible in parenteral admixtures.
Regulatory Status
GRAS listed. Accepted for use as a food additive in Europe. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (injections; infusions; ophthalmic, oral, topical, and vaginal preparations). Included in nonparenteral and parenteral medicines licensed in the UK. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients.
Properties of Sodium phosphate monobasic
| Melting point: | <0°C |
| Boiling point: | 100°C |
| Density | 1.40 g/mL at 20 °C |
| vapor pressure | 0Pa at 20℃ |
| storage temp. | room temp |
| solubility | H2O: 5 M, clear, colorless |
| form | powder |
| appearance | White powder |
| color | White |
| PH | 4.0 - 4.5 (25℃, 50g/L in water) |
| pka | (1) 2.15, (2) 6.82, (3) 12.38 (at 25℃) |
| Odor | at 100.00?%. odorless |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water. Insoluble in alcohol,ether and chloroform. |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| λmax | λ: 260 nm Amax: ≤0.025 λ: 280 nm Amax: ≤0.02 |
| Merck | 14,8660 |
| BRN | 3903772 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with heavy metals, strong acids. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7558-80-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Monosodium phosphate (7558-80-7) |
Safety information for Sodium phosphate monobasic
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P304+P340:IF INHALED: Remove victim to fresh air and Keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P405:Store locked up. |
Computed Descriptors for Sodium phosphate monobasic
| InChIKey | AJPJDKMHJJGVTQ-UHFFFAOYSA-M |
Sodium phosphate monobasic manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
H. K. Group
ASM Organics
Cotex Chem. Private Limited
Attar Global
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Sodium phosphate, monobasic 98%View Details
Sodium phosphate, monobasic 98%View Details -
 Phosphate CAS 7558-80-7View Details
Phosphate CAS 7558-80-7View Details
7558-80-7 -
 Phosphate CAS 7558-80-7View Details
Phosphate CAS 7558-80-7View Details
7558-80-7 -
 Sodium dihydrogen phosphate CAS 7558-80-7View Details
Sodium dihydrogen phosphate CAS 7558-80-7View Details
7558-80-7 -
 Sodium dihydrogen phosphate CAS 7558-80-7View Details
Sodium dihydrogen phosphate CAS 7558-80-7View Details
7558-80-7 -
 Sodium Dihydrogen Phosphate AnhydrousView Details
Sodium Dihydrogen Phosphate AnhydrousView Details
7558-80-7 -
 Powder Sodium Phosphate Monobasic, Grade Standard: Technical GradeView Details
Powder Sodium Phosphate Monobasic, Grade Standard: Technical GradeView Details
10049-21-5 -
 White Sodium Dihydrogen Phosphate Anhydrous, 98%, 25Kg BagView Details
White Sodium Dihydrogen Phosphate Anhydrous, 98%, 25Kg BagView Details
7558-80-7
