Trimethyl phosphate
Synonym(s):TMP;TMPA;TMPO;Trimethyl phosphate
- CAS NO.:512-56-1
- Empirical Formula: C3H9O4P
- Molecular Weight: 140.07
- MDL number: MFCD00008348
- EINECS: 208-144-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-15 16:23:17
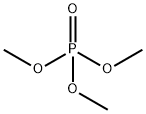
What is Trimethyl phosphate?
Chemical properties
Trimethyl phosphate (TMP), the simplest trialkyl ester of phosphoric acid, It is a colourless, nonvolatile liquid. soluble in most organic solvents, low solubility in water. TMP is stable in neutral, acidic or alkaline solutions, and is classified as "not readily biodegradable". Direct photodegradation is not expected because trimethyl phosphate does not absorb UV light.
The Uses of Trimethyl phosphate
Trimethyl phosphate is used as an intermediate in organic synthesis. Its industrial applications are much fewer than those of other organic phosphates.Trimethyl phosphate undergoes hydrolysis in contact with water, so it should be stored in a moisture-proof manner. Due to its hydrolysis and release of PO43-, thus becoming a homogeneous precipitant for the formation of insoluble phosphate precipitation, often used as a precipitation reagent for zirconium and hafnium and as a diffusion source for the determination of semiconductors. In addition, trimethyl phosphate is also a phospholipid extractant for the extraction and separation of certain metal ions.
The Uses of Trimethyl phosphate
Trimethyl Phosphate is used as an electrolyte additive in the synthesis of lithium ion batteries. for controlling spark plug fouling, surface ignition and rumble in gasoline engines.
Trimethyl phosphate used as a reagent for determination of zirconium, solvent, extractant and gas chromatography stationary phase.
Definition
ChEBI: Trimethyl phosphate is a trialkyl phosphate that is the trimethyl ester of phosphoric acid. It has a role as an insect attractant.
Production Methods
Trimethyl phosphate is prepared by treating phosphorus oxychloride with methanol in the presence of an amine base:
POCl3 + 3 CH3OH + 3 R3N → PO(OCH3)3 + 3 R3NH+Cl
It is a tetrahedral molecule that is a weakly polar solvent.
Synthesis Reference(s)
The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 39, p. 3178, 1974 DOI: 10.1021/jo00935a041
Tetrahedron Letters, 28, p. 2981, 1987 DOI: 10.1016/S0040-4039(00)96262-2
General Description
Trimethyl phosphate appears as a pale straw colored liquid. Inhalation may irritate respiratory tract. Vapor or liquid may irritate skin or eyes. Ingestion may irritate the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract.
Reactivity Profile
TRIMETHYL PHOSPHATE may explode when heated. Residue from a large scale atmospheric pressure distillation of Trimethyl phosphate has exploded violently. Trimethyl phosphate is incompatible with nitrates. . Organophosphates are susceptible to formation of highly toxic and flammable phosphine gas in the presence of strong reducing agents such as hydrides. Partial oxidation by oxidizing agents may result in the release of toxic phosphorus oxides.
Hazard
Toxic by ingestion and inhalation, strong irritant to skin and eyes. trimethyl phosphate (TMP) is absorbed rapidly and completely by inhalation of its vapour, through the skin and by ingestion (WHO).
Health Hazard
Trimethyl phosphate (TMP) is a mutagen, teratogen, and a cancercausing compound. The health hazard from this compound is somewhat different from those of the higher members of the organic phosphate series. While carcinogenicity is observed only for this phosphate, with mutagenicity and the teratogenic effects being more marked, higher alkyl phosphates are more neurotoxic but noncarcinogenic.
TMP is toxic at high dosages.LD50 value,oral(mice):1470 mg/kg(NIOSH 1986)
Laboratory tests on animals indicated clear evidence of its cancer-causing actions, producing uterine and skin tumors. There is so far no report on such carcinogenic actions in humans. The compound tested positive in mutagenic tests and caused fetal deaths and birth defects in mice, rats, and hamsters when given orally or intraperitoneally.
Fire Hazard
Trimethyl phosphate is nonflammable.
Flammability and Explosibility
Not classified
Industrial uses
1 Gasoline additive at 0.25 g/gal for controlling surface ignition and spark plug
fouling.
2 Methylating agent, chemical intermediate in the production of polymethyl
polyphosphates.
3 Flame retardant solvent for paints and polymers.
4 Catalyst in the preparation of polymers and resins.
Safety Profile
Suspected carcinogen with experimental carcinogenic, neoplastigenic, tumorigenic, and teratogenic data. Moderately toxic by ingestion, skin contact, intraperitoneal, and intravenous routes. Experimental reproductive effects. Human mutation data reported. Explodes when heat distilled. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of POx. See also ESTERS.
Metabolism
A system utilizing isolated anterior forearm stratum corneum conjunctum of man
to study skin penetrating capacity of a series of organic phosphates was developed.
Trimethyl phosphate was tested in the system and had the greatest skin-penetrating
capacity of the 8 related compounds tested (Marzulli et al 1965).
Rats treated orally at 100 mg/kg and mice treated i.p. at 1000 mg/kg with
[32]P-labeled trimethyl phosphate excreted primarily dimethyl phosphate in the
urine. Only traces of the parent compound were detected, and only in the rats at
less than 6 h after treatment. S-Methyl cysteine and S-methyl cysteine N-acetate
were also isolated. Small amounts of S-methyl glutathione were detected, presumably
the initial methylation product in this series of metabolites (Jones 1970).
Metabolism of trimethyl phosphate was faster in the mouse than in the rat, but
there was no evidence of further conversion to monomethyl phosphate or inorganic
phosphate in either species (Jackson and Jones 1968).
Purification Methods
Purify the phosphate by fractionation through an efficient column at high reflux ratio. It is quite soluble in H2O; the solubility is 1:1 at 25o. [Becker J Am Chem Soc 74 2923 1952, IR: Bergmann et al. J Chem Soc 847 1952, McIvor et al. Can J Chem 36 820 1958, Kosolapoff Organophosphorus Compounds, Wiley p 258 1950, and Cherbuliez in Organo Phosphorus Compounds (Kosolapoff & Maier eds) Wiley Vol 6 pp 211-577 1973, Beilstein 1 IV 1259.]
Waste Disposal
TMP is mixed with a combustible solvent and destroyed by burning in a chemical incinerator.
Properties of Trimethyl phosphate
| Melting point: | -46 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 197 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 1.197 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| vapor pressure | 1.133 hPa (25 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 107 °C |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | 1000g/l |
| form | Liquid |
| Specific Gravity | 1.197 |
| color | Clear |
| Water Solubility | 500 G/L (25 ºC) |
| Sensitive | Moisture Sensitive |
| BRN | 1071731 |
| Dielectric constant | 21.260000000000002 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 512-56-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Phosphoric acid, trimethyl ester(512-56-1) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Trimethyl phosphate (512-56-1) |
Safety information for Trimethyl phosphate
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H340:Germ cell mutagenicity H351:Carcinogenicity |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Trimethyl phosphate
| InChIKey | WVLBCYQITXONBZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Trimethyl phosphate manufacturer
Cosmos Plastics & Chemicals
Antares Chem Private Limited
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Trimethyl phosphate 95% CAS 512-56-1View Details
Trimethyl phosphate 95% CAS 512-56-1View Details
512-56-1 -
 Trimethyl Phosphate CASView Details
Trimethyl Phosphate CASView Details -
 Trimethyl Phosphate CASView Details
Trimethyl Phosphate CASView Details -
 Liquid Trimethyl Phosphate, Grade Standard: Technical Grade, for IndustrialView Details
Liquid Trimethyl Phosphate, Grade Standard: Technical Grade, for IndustrialView Details
512-56-1 -
 Powder Trimethyl PhosphateView Details
Powder Trimethyl PhosphateView Details
512-56-1 -
 Trimethyl Phosphate Tmp, For IndustrialView Details
Trimethyl Phosphate Tmp, For IndustrialView Details
512-56-1 -
 solid Trimethyl Phosphate, For Industrial, Grade Standard: Technical GradeView Details
solid Trimethyl Phosphate, For Industrial, Grade Standard: Technical GradeView Details
512-56-1 -
 Powder Tri Methyl Phosphate, for Industrial, 50 KgView Details
Powder Tri Methyl Phosphate, for Industrial, 50 KgView Details
512-56-1
