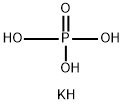
Potassium Phosphate Monobasic
Synonym(s):Potassium dihydrogen phosphate;Monopotassium phosphate;Potassium phosphate monobasic;p65;PSK
- CAS NO.:7778-77-0
- Empirical Formula: H2KO4P
- Molecular Weight: 136.085541
- MDL number: MFCD00011401
- EINECS: 231-913-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:55
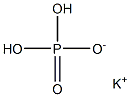
What is Potassium Phosphate Monobasic?
Absorption
Potassium salts are well absorbed from the GI tract. Ingested phosphates are absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. However, the presence of large amounts of calcium or aluminum may lead to formation of insoluble phosphate and reduce the net absorption. Vitamin D stimulates phosphate absorption.
Toxicity
Rabbit : LD50 >4640mg/kg (skin) Rat : LdLo : 4640mg/kg (Oral)
Chemical properties
White powder
Description
Potassium phosphate monobasic, anhydrous, is a versatile chemical compound widely utilized in various industries due to its unique properties. This compound, also known as monopotassium phosphate (MKP), is highly soluble in water, making it an excellent choice for applications in agriculture, food production, and pharmaceuticals.
Physical properties
Colorless crystals or white granular powder; tetragonal structure; deliquesces; density 2.338 g/cm3; melts at 252.6°C; soluble in water 33 g/100mL at 25°C; pH 4.4-4.7; insoluble in alcohol.
The Uses of Potassium Phosphate Monobasic
Monopotassium phosphate (MKP) is a specialty fertilizer that is a good source of phosphorus and potassium.It is an acid, chloride-free, dry soluble fertilizer,and is a natural pH buffer with a buffer pH in pure water of 4.5. Monopotassium phosphate can be solubilized and blended with liquid fertilizers that will not salt out at a low pH, and is also safe to use as a foliar fertilizer. It is also soluble in water. It is used as a buffer, neutraliser, chelator, nutritional supplement, pharmaceutical ingredient and fertiliser.
Background
Monopotassium phosphate, MKP, (also potassium dihydrogenphosphate, KDP, or monobasic potassium phosphate), KH2PO4, is a soluble salt of potassium and the dihydrogen phosphate ion. It is a source of phosphorus and potassium as well as a buffering agent. It can be used in fertilizer mixtures to reduce escape of ammonia by keeping pH low.
Indications
Used in buffers (determination of pH, pharmaceutical production, urinary acidifier, paper processing, baking powder, and food), nutrient solutions, yeast foods, special liquid fertilizers, sonar systems and other electronic applications; Used as a nutritional supplement in foods, a nonlinear optical material for laser use, and in wastewater treatment;
What are the applications of Application
Potassium Phosphate Monobasic solution is a convenient 0.2 μm filtered, 1M stock solution for making phosphate buffers. Potassium Phosphate, Monobasic is a useful reagent in formulating buffered solutions for equilibrium dialysis, HPLC, and ACE.
Preparation
Monopotassium phosphate may be prepared by partial neutralization of phosphoric acid with potassium hydroxide in equimolar amounts:H3PO4+ KOH →KH2PO4+ H2O.
Definition
ChEBI: Potassium dihydrogen phosphate is a potassium salt in which dihydrogen phosphate(1-) is the counterion. It has a role as a fertilizer. It is a potassium salt and an inorganic phosphate.
General Description
Monobasic potassium phosphate crystals are colorless, soluble in water and hygroscopic in nature.Upon heating through 187°C, phase transition occurs in KH2PO4, crystal system changes from tetragonal to monoclinic, lattice parameters at 195°C are α=7.47?, b =7.33?, c =14.49?, α=?=90° and γ=92.2.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Potassium phosphate monobasic also referred to as monopotassium phosphate or potassium dihydrogen phosphate is a soluble salt of potassium that serves as a buffering agent. It enhances the solubility of calcium and phosphorus in amino acid plus dextrose solutions and hence assists in improving the mineral balance of parenterally fed low birth weight infants.
Pharmacokinetics
Potassium is the major cation of intracellular fluid and is essential for maintenance of acid-base balance, isotonicity, and electrodynamic characteristics of the cell. Potassium is an important activator in many enzymatic reactions and is essential to a number of physiologic processes including transmission of nerve impulses; contraction of cardiac, smooth, and skeletal muscles; gastric secretion; renal function; tissue synthesis; and carbohydrate metabolism. Phosphate is a major intracellular anion that participates in providing energy for metabolism of substrates and contributes to important metabolic and enzymatic reactions in almost all organs and tissues. Phosphate exerts a modifying influence on calcium concentrations, a buffering effect on acid-base equilibrium, and has a major role in the renal excretion of hydrogen ions.
Biological half-life
In healthy children with phosphate overdose, half-life was 4.8 to 10.6 hours, and was prolonged to 17 hours in a child with renal insufficiency.
Solubility in organics
Insoluble to slightly soluble in ethanol, insoluble in alcohol.
Purification Methods
Dissolve it in boiling distilled water (2mL/g), keep on a boiling water-bath for several hours, then filter it through paper pulp to remove any turbidity. Cool rapidly with constant stirring, and the crystals are collected on to hardened filter paper, using suction, washed twice with ice-cold water, once with 50% EtOH, and dried at 105o. Alternative crystallisations are from water, then 50% EtOH, and again water, or from concentrated aqueous solution by addition of EtOH. It is freed from traces of Cu by extracting its aqueous solution with diphenylthiocarbazone in CCl4, followed by repeated extraction with CCl4 to remove traces of diphenylthiocarbazone.
Properties of Potassium Phosphate Monobasic
| Melting point: | 252.6 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | > 450 °C |
| Density | 2.338 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| vapor pressure | 0Pa at 25℃ |
| storage temp. | Store at +5°C to +30°C. |
| solubility | H2O: 1.5 M at 20 °C, clear, colorless |
| form | powder |
| appearance | White powder |
| color | White transparent |
| Specific Gravity | 2.338 |
| Odor | Odorless |
| PH | 4.2-4.6 (20g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| pka | (1) 2.15, (2) 6.82, (3) 12.38 (at 25℃) |
| Water Solubility | 222 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| λmax | λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.046 λ: 280 nm Amax: 0.040 |
| Decomposition | 253 °C |
| Merck | 14,7659 |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7778-77-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Monopotassium phosphate (7778-77-0) |
Safety information for Potassium Phosphate Monobasic
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H313:Acute toxicity,dermal H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P321:Specific treatment (see … on this label). P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P332+P313:IF SKIN irritation occurs: Get medical advice/attention. P337+P313:IF eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Potassium Phosphate Monobasic
| InChIKey | GNSKLFRGEWLPPA-UHFFFAOYSA-M |
Potassium Phosphate Monobasic manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
Zama Chemical
Endeavour Industries
H. K. Group
Mangalore Chemicals & Fertilizers Limited
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Potassium Phosphate Monobasic 99%View Details
Potassium Phosphate Monobasic 99%View Details -
 Mono pottasium phosphate 99%View Details
Mono pottasium phosphate 99%View Details -
 Potassium phosphate, monobasic 99%View Details
Potassium phosphate, monobasic 99%View Details -
 Potassium phosphate, monobasic 98%View Details
Potassium phosphate, monobasic 98%View Details -
 Potassium dihydrogen phosphate, For analysis ACS CAS 7778-77-0View Details
Potassium dihydrogen phosphate, For analysis ACS CAS 7778-77-0View Details
7778-77-0 -
 Potassium Dihydrogen Phosphate, For analysis ACS CAS 7778-77-0View Details
Potassium Dihydrogen Phosphate, For analysis ACS CAS 7778-77-0View Details
7778-77-0 -
 Potassium dihydrogen phosphate 99%View Details
Potassium dihydrogen phosphate 99%View Details -
 Phosphate standard solution CASView Details
Phosphate standard solution CASView Details
