Sodium pentachlorophenolate
- CAS NO.:131-52-2
- Empirical Formula: C6Cl5NaO
- Molecular Weight: 288.32
- MDL number: MFCD00149086
- EINECS: 205-025-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:30
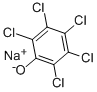
What is Sodium pentachlorophenolate?
Description
Pentachlorophenol (PCP) can be found in two forms: pentachlorophenol itself or as the sodium salt of pentachlorophenol (NaPCP). These two forms have some different physical properties, but are expected to have similar toxic effects. PCP is a synthetic substance, made from other chemicals, and does not occur naturally in the environment. Although PCP was first synthesized in 1841, it was not produced commercially until 1936. It has since been registered for use as an insecticide, fungicide, herbicide, algicide, and disinfectant. By 1967, PCP and its sodium salt, NaPCP, were used extensively in industry and agriculture, due in large part to the solubility of PCP in organic solvents and of NaPCP in water. In 1977, both were listed together as the second most heavily used pesticide in the United States.
Chemical properties
White or tan powder. Soluble in water, ethanol, and acetone; insoluble in benzene.
Chemical properties
Sodium pentachlorophenate is a crystalline solid. Phenolic odor.
The Uses of Sodium pentachlorophenolate
Fungicide; herbicide; slimicide; fermentation disinfectant, especially in finishes and papers.
The Uses of Sodium pentachlorophenolate
PCP and its water soluble salt, NaPCP, are commercially produced organochlorine compounds used primarily as the preservatives of wood and wood products, and secondarily as herbicides, insecticides, fungicides, molluscicides, and bactericides.
General Description
Sodium pentachlorophenolate is a white or tan, powdered solid. Sodium pentachlorophenolate is soluble in water and may burn, but Sodium pentachlorophenolate is not easily ignited. Sodium pentachlorophenolate may be toxic by ingestion, inhalation and skin absorption. Sodium pentachlorophenolate is used as a fungicide, herbicide and as a disinfectant.
Air & Water Reactions
Soluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Sodium pentachlorophenolate is incompatible with strong oxidizing agents.
Hazard
Toxic by ingestion, inhalation; skin irritant.
Health Hazard
Exposure can cause irritation of eyes, nose and throat. May cause weakness, excessive sweating, headache, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, and difficulty in breathing.
Fire Hazard
Special Hazards of Combustion Products: Irritating vapors and toxic gases, such as hydrogen chloride, polychlorodibenzodioxins and carbon monoxide, may be formed when involved in fire.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion, inhalation, skin contact, intravenous, intraperitoneal, subcutaneous, and intratracheal routes. An experimental teratogen. Experimental reproductive effects. Mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of Cland Na2O. See also CHLOROPHENOLS.
Potential Exposure
Uses include: wood preservative; as a fungicide in water-based latex paints; preservation of cellulose products, textiles, adhesives, leather, pulp, paper, and industrial waste systems; a contact and preemergence herbicide; general disinfectant and control of the intermediate snail host of schistosomiasis. The technical grade of sodium pentachlorophenate usually contain toxic microcontaminants including polychlorinated dibenzodioxins and dibenzofurans (132-64-9, and others).
Carcinogenicity
Data from a wide range and large number of studies evaluating the carcinogenic potential of pentachlorophenol are available. These include three longterm carcinogenicity studies in mice, three in rats, two studies evaluating the potential of pentachlorophenol to act as promoter in the carcinogenic process, and a “stop exposure” study. The results of the initiation and/or promotion studies are uniformly negative, as are the results of all the rat studies and two of the three long-term mouse studies. In addition, a very large body of genotoxicity evidence suggests that pentachlorophenol is nonmutagenic.
Environmental Fate
Routes and pathways, relevant physicochemical properties
Solubility: in water 330 g l-1 at 25 °C; soluble in ethanol,
acetone; insoluble in benzene and petroleum oils.
Partition behavior in water, sediment, and soil
If released to air, NaPCP will exist solely in the aerosol
phase in the ambient atmosphere. The aerosol phase will be
removed from the atmosphere by wet and dry deposition. If released to soil and water under typical ambient conditions
(pH 5–9), NaPCP is expected to exist predominately in
its dissociated form (pKa 4.7). Releases to soil can decrease
in concentration due to slow biodegradation (half-life is
weeks to months) and leaching into groundwater. Releases
to water may photolyze (half-life is hours to days with
rate decreasing with depth of water), biodegrade, adsorb
to sediments, or bioaccumulate in aquatic organisms.
Biodegradation probably becomes significant after a period
of acclimation.
Environmental persistency
NaPCP is not persistent in water, sewage, or soil because of
bacterial decomposition. PCP readily decomposes in sunlight
to monomeric and dimeric oxidation products in water.
Principal decompose products are tetrachlororesorcinol,
chloranilic acid, and dimeric products.
Bioaccumulation and biomagnification
Sodium pentachlorophenol did not appear to bioaccumulate
in aquatic organisms to very high concentrations.
BCFs for the compound were <1000 for most species
tested.
Shipping
UN2567 Sodium pentachlorophenate, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials
Toxicity evaluation
The biochemical action of pentachlorophenol is active uncoupling of oxidation phosphorylation. PCP binds to mitochondrial protein and inhibits mitochondrial ATP-ase activity. Thus, both the formation of ATP and the release of energy to the cell from the breakdown of ATP to ADP are prevented. Electron transport is not inhibited by PCP, although reactions dependent on available high-energy bonds, such as oxidative and glycolytic phosphorylation, are affected. Binding to enzymatic protein has been reported and may lead to the inhibition of other cellular enzymes. There is also an increase in cellular oxygen demand during the uncoupling of oxidative phosphorylation. This causes the initial rise in respiration rate reported in individuals poisoned by PCP.
Incompatibilities
Uses include: wood preservative; as a fungicide in water-based latex paints; preservation of cellulose products, textiles, adhesives, leather, pulp, paper, and industrial waste systems; a contact and preemergence herbicide; general disinfectant and control of the intermediate snail host of schistosomiasis. The technical grade of sodium pentachlorophenate usually contain toxic microcontaminants including polychlorinated dibenzodioxins and dibenzofurans (132-64-9, and others).
Waste Disposal
Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform to EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal.
Properties of Sodium pentachlorophenolate
| Melting point: | >300°C |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| color | Off-White to Pale Purple |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 131-52-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Sodium pentachlorophenate (131-52-2) |
Safety information for Sodium pentachlorophenolate
Computed Descriptors for Sodium pentachlorophenolate
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Sodium pentachlorophenate CAS 131-52-2View Details
Sodium pentachlorophenate CAS 131-52-2View Details
131-52-2 -
 SODIUM PENTACHLOROPHENATE Extra Pure CAS 131-52-2View Details
SODIUM PENTACHLOROPHENATE Extra Pure CAS 131-52-2View Details
131-52-2 -
 Sodium pentachlorophenate 80% CAS 131-52-2View Details
Sodium pentachlorophenate 80% CAS 131-52-2View Details
131-52-2 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8