Sodium metabisulfite
Synonym(s):E223;Natrii metabisulfis;Sodium disulfite;Sodium metabisulfite;Sodium pyrosulfite
- CAS NO.:7681-57-4
- Empirical Formula: H2O5S2.2Na
- Molecular Weight: 192.12
- MDL number: MFCD00213787
- EINECS: 231-673-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:50:42
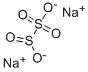
What is Sodium metabisulfite?
Chemical properties
Sodium metabisulfite is a white crystalline powder with a sulfur dioxide odor and can be regarded as the anhydride of two molecules of sodium disulfite.
The Uses of Sodium metabisulfite
Sodium metabisulfite is a preservative and antioxidant that exists as crystals or a powder with a sulfur dioxide odor, and is readily soluble in water. It is used in dried fruits to preserve flavor and color while inhibiting microbial growth, prevents oxidative "black spots" in shrimp, and serves as a preservative in maraschino cherries and lemon drinks. For further details, see sulfur dioxide.
What are the applications of Application
Sodium metabisulfite is an antioxidant reducing agent, with antimicrobial and antifungal properties
Production Methods
Sodium metabisulfite is prepared by saturating a solution of sodium hydroxide with sulfur dioxide and allowing crystallization to occur; hydrogen is passed through the solution to exclude air. Sodium metabisulfite may also be prepared by saturating a solution of sodium carbonate with sulfur dioxide and allowing crystallization to occur, or by thermally dehydrating sodium bisulfite.
General Description
Sodium metabisulfite (MBS, also known as sodium disulfite) is an inorganic salt and the sodium salt of disulfurous acid. It is widely used in textile dyeing, photography, and the paper industry, and is commonly added as a preservative to various food products and wines.
Health Hazard
Sodium metabisulfite may cause bronchospasm, oculonasal symptoms, and urticaria in sulfite-sensitive individuals; irritation of mucous membranes may occur from inhalation of the dust.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Pharmaceutical Applications
Sodium metabisulfite is used as an antioxidant in oral, parenteral, and topical pharmaceutical formulations at concentrations of 0.01–1.0% w/v, and approximately 27% w/v in intramuscular injections. It is primarily employed in acidic preparations, with sodium sulfite preferred for alkaline systems. Exhibiting antimicrobial activity that is most effective at acid pH, it also serves as a preservative in oral preparations such as syrups. In the food and wine industries, it functions as an antioxidant, antimicrobial preservative, and antibrowning agent, though concentrations above approximately 550 ppm impart a noticeable flavor. Commercial sodium metabisulfite typically contains small amounts of sodium sulfite and sodium sulfate.
Contact allergens
This agent is frequently used as a preservative in pharmaceutical products, in the bread-making industry as an antioxidant, and it can induce contact dermatitis. It can be used as a reducing agent in photography and caused dermatitis in a photographic technician, probably acting as an aggravating irritative factor. Sodium metabisulfite contains a certain amount of sodium sulfite and sodium sulfate.
Safety Profile
An inhalation hazard. Poison by intravenous route. Moderately toxic by parenteral route. Experimental reproductive effects. Mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of SOx and Na2O.
Carcinogenicity
Sodium metabisulfite was genotoxic in mice in vivo as determined by chromosomal aberration, micronucleus, and sperm shape assays. It was not mutagenic in bacterial assays.
Storage
On exposure to air and moisture, sodium metabisulfite is slowly
oxidized to sodium sulfate with disintegration of the crystals.
Addition of strong acids to the solid liberates sulfur dioxide.
In water, sodium metabisulfite is immediately converted to
sodium (Na+) and bisulfite (HSO3-) ions. Aqueous sodium
metabisulfite solutions also decompose in air, especially on heating.
Solutions that are to be sterilized by autoclaving should be filled into
containers in which the air has been replaced with an inert gas, such
as nitrogen. The addition of dextrose to aqueous sodium
metabisulfite solutions results in a decrease in the stability of the
metabisulfite.
The bulk material should be stored in a well-closed container,
protected from light, in a cool, dry place.
Incompatibilities
A strong reducing agent. Keep away from oxidizers. Mixtures with water forms a strong corrosive. Contact with acids releases toxic fumes. Heat causes decomposition. Slowly oxidized to the sulfate on exposure to air and moisture. Attacks metals
Regulatory Status
GRAS listed. Accepted for use as a food additive in Europe. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (epidural;inhalation; IM and IV injections; ophthalmic solutions; oral preparations; rectal, topical, and vaginal preparations). Included in nonparenteral and parenteral medicines licensed in the UK. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients.
Properties of Sodium metabisulfite
| Melting point: | >300 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 1.48 |
| storage temp. | Store at +5°C to +30°C. |
| solubility | 540 g/L (20°C) |
| form | Powder/Solid |
| color | White to slightly yellow |
| Specific Gravity | 1.48 |
| PH Range | 4.5 at 50 g/l at 20 °C |
| PH | 3.5-5 (50g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| Odor | Sulphorous |
| Water Solubility | 540 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Sensitive | Air & Moisture Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,8638 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 5 mg/m3 NIOSH: TWA 5 mg/m3 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong acids. Contact with strong acids releases a poisonous gas. May be moisture and air sensitive. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7681-57-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Sodium metabisulfite (7681-57-4) |
Safety information for Sodium metabisulfite
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Sodium metabisulfite
| InChIKey | HRZFUMHJMZEROT-UHFFFAOYSA-L |
Sodium metabisulfite manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Sodium metabisulfite 99%View Details
Sodium metabisulfite 99%View Details -
 Sodium metabisulfite 98%View Details
Sodium metabisulfite 98%View Details -
 Sodium metabisulfite CAS 7681-57-4View Details
Sodium metabisulfite CAS 7681-57-4View Details
7681-57-4 -
 Sodium metabisulfite CAS 7681-57-4View Details
Sodium metabisulfite CAS 7681-57-4View Details
7681-57-4 -
 Sodium metabisulfite, For analysis ACS CAS 7681-57-4View Details
Sodium metabisulfite, For analysis ACS CAS 7681-57-4View Details
7681-57-4 -
 Sodium metabisulfite, For analysis ACS CAS 7681-57-4View Details
Sodium metabisulfite, For analysis ACS CAS 7681-57-4View Details
7681-57-4 -
 Sodium Metabisulfite CASView Details
Sodium Metabisulfite CASView Details -
 Sodium Pyrosulphite ChemicalView Details
Sodium Pyrosulphite ChemicalView Details
7440-23-5
