Pullulan
Synonym(s):Pullulan Standard Set
- CAS NO.:9057-02-7
- Empirical Formula: C20H36O16
- Molecular Weight: 532.49024
- MDL number: MFCD00081940
- EINECS: 232-945-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-04 20:04:50
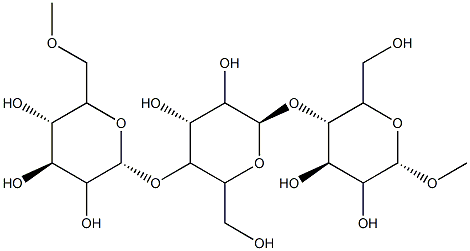
What is Pullulan?
Description
Pullulan is a linear homopolysaccharide of glucose, which is produced as a water-soluble, extracellular polysaccharide by certain strains of the polymorphic fungus Aureobasidium pullulans (De Bary) Arnaud.
Pullulan has adhesive properties and can be used to form fibers, compression moldings, and strong, oxygen-impermeable films. In food industry, pullulan films can be employed as coating or packaging materials of dried foods, as a binder for tobacco, seed coatings and plant fertilizers, as low viscosity filler in beverages and sauces, as binder and stabilizer in food pastes, to inhibit fungal growth in foods. In pharmaceutical industry, pullulan can be used as a denture adhesive, in the sugar coated pharmaceutical compositions to prevent brownish color change of the composition. Pullulan can also be used in cosmetics, lotions, and shampoos.
Chemical properties
It is a white, tasteless, and odorless non-crystalline powder that dissolves easily in water and dimethylformamide, but not in alcohol, ether, or oil. Its solution is viscous, stable, and neutral, with no gelling effect. The viscosity of the solution is the same as that of gum arabic, and it has a very good thickening effect of salt resistance, enzyme resistance, heat resistance, and pH value change resistance. It has strong film-forming properties, and the film formed after its aqueous solution is dried on a metal plate has strong gas barrier properties to oxygen and nitrogen. Moreover, it is suitable for making water-soluble edible films and is compatible with other water-soluble polymers.
The Uses of Pullulan
pullulan is used as a binder and film former in a variety of formulation categories (skin, make-up and hair), it is a polysaccharide derived from the Aureobasidium pullulans yeast.
Pullulan is a polysaccharide polymer consisting of D-Maltotriose (M159000) units; a trisaccharide resulting from the digestion of Amalose by α-Amalase. Pullulan has been used in a study to assess bone tissue engineering. Addition of pullulan has improved the elongation at break of gelatin based edible film when the amount was 50% (wt. %).
The Uses of Pullulan
Pullulan has been used in a study to assess bone tissue engineering. It has also been used in a study that investigated anti-fog applications.
What are the applications of Application
Pullulan from Aureobasidium pullulans is a natural polysaccharide
Definition
pullulan: A water-soluble polysaccharidecomposed of glucose unitsthat are polymerized in such a wayas to make it viscous and impermeableto oxygen. Pullulan is used in adhesives, food packaging, andmoulded articles. It is derived fromthe fungus Aureobasidium pullulans.
What are the applications of Application
Pullulan is a hemocompatible, nonimmunogenic, and noncarcinogenic agent. In the food industry are mainly filler, edible, and tasteless polymers. Furthermore, in pharmaceuticals and electronics pullulan is used in tissue engineering, drug and gene delivery systems, as a coating agent, and as a film- and fiber-forming agent, due to its excellent physicochemical properties. Pullulan is the backbone of a polymeric system capable of forming hydrogels and nanogels. These systems show potential applications in the preparation of green smart materials, biomimetics, biosensors, artificial muscles, drug delivery systems, and chemical separations. Pullulan-based nanosystems can act as carriers of different drugs. It has been used as a carrier for oral, nasal, and lung transmucosal drug delivery systems because it is not attacked by the digestive enzymes in the human gut[3-4].
Production Methods
Pullulan is produced by fermentation from a food-grade hydrolyzed search with a non-toxin-producing strain of Aureobasidium pullulans. After fermentation, the fungal biomass is removed by microfiltration, the filtrate is heat-sterilized, and pigments and other impurities are removed by adsorption and ion exchange chromatography. The product contains not less than 90% glucan on a dried basis. The main impurities from the starting material are mono-, di-, and oligosaccharides. The average relative molecular mass of pullulan varies considerably depending on the conditions of the culture. A commercially available product has an average relative molecular mass of 200 000 Da.
Biological Functions
Pullulan is a polysaccharide polymer that is derived from the Aureobasidium pullulans yeast and consists of D-Maltotriose units. It is used as a binder and film former in a variety of formulation categories (skin, make-up, and hair). Pullulan has been used in a study to assess bone tissue engineering. Addition of pullulan has improved the elongation at break of gelatin based edible film when the amount was 50% (wt. %).
General Description
Pullulan Standards are mostly used to obtain molecular mass distribution of cellulosic samples. It mainly consists of polymaltotriose units linked together by α-(1→6) linkages. Pullulan is a biodegradable polysaccharide made by yeast fermentation, originally developed in Japan. Its adhesive and oxygen impermeable properties enable it to be used to coat pharmaceutical products. It is water soluble, odorless, and edible.
Structure and conformation
Pullulan is a naturally occurring, fungal polysaccharide produced by fermentation of liquefied corn starch by Aureobasidium pullulans, a ubiquitous yeast-likefungus. It has a linear structure consisting predominantly of repeating maltotriose units, which are made up of three o-1,4-linked glucose molecules linked by a-1,6-glycosidic bonds. The maltotriose units are interspersed with about 6% maltotetraose units consisting of four o-1,4-linked glucose molecules; rarely, branch points occur, at which poly-maltotriose side chains are attached to the main chain by a 1,3-glycosidic bond.
References
[1] Timothy D. Leathers, Biopolymers Online, 2005,
[2] Ram S. Singh, Gaganpreet K. Saini and John F. Kennedy, Pullulan: Microbial sources, production and applications, Carbonhydrate Polymers, 2008, vol. 73, 515-531.
[3] Nasrollahzadeh M, et al. Green Nanotechnology. Interface Science and Technology, 2019; 28: 145-198.
[4] Narayanaswamy R, et al. Basics to different imaging techniques, different nanobiomaterials for image enhancement. Nanobiomaterials in Medical Imaging, 2016; 101-129.
Properties of Pullulan
| Melting point: | >248°C (dec.) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | H2O: 50 mg/mL, slightly hazy, colorless |
| form | Powder |
| color | White to Off-white |
| Odor | at 100.00?%. odorless |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Pullulan (9057-02-7) |
Safety information for Pullulan
Computed Descriptors for Pullulan
Abamectin manufacturer
HRV Global Life Sciences
New Products
4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium SODIUM AAS SOLUTION ZINC AAS SOLUTION BUFFER SOLUTION PH 10.0(BORATE) GOOCH CRUCIBLE SINTERED AQUANIL 5 BERYLLIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran








You may like
-
 9057-02-7 Pullulan 99%View Details
9057-02-7 Pullulan 99%View Details
9057-02-7 -
 Pullulan CAS 9057-02-7View Details
Pullulan CAS 9057-02-7View Details
9057-02-7 -
 Pullulan CAS 9057-02-7View Details
Pullulan CAS 9057-02-7View Details
9057-02-7 -
 Pullulan 95% CAS 9057-02-7View Details
Pullulan 95% CAS 9057-02-7View Details
9057-02-7 -
 Pullulan, from aureobasidium pullulans CAS 9057-02-7View Details
Pullulan, from aureobasidium pullulans CAS 9057-02-7View Details
9057-02-7 -
 Pullulan CAS 9057-02-7View Details
Pullulan CAS 9057-02-7View Details
9057-02-7 -
 Pullulan Standard Set Mp ~350 - 700′000 CAS 9057-02-7View Details
Pullulan Standard Set Mp ~350 - 700′000 CAS 9057-02-7View Details
9057-02-7 -
 Pullulan CAS 9057-02-7View Details
Pullulan CAS 9057-02-7View Details
9057-02-7