Sodium dithionite
Synonym(s):Sodium dithionite;Sodium hydrosulfite;Sodium hydrosulfite, Sodium hypodisulfite;Sodium hypodisulfite
- CAS NO.:7775-14-6
- Empirical Formula: Na2O4S2
- Molecular Weight: 174.11
- MDL number: MFCD00011640
- EINECS: 231-890-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:22
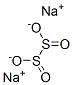
What is Sodium dithionite?
Description
Sodium dithionite (Na2S2O4) is a white crystalline salt that is also known by the somewhat confusing name sodium hydrosulfite. Its solutions are stable unless heated or acidified. It is produced by reducing NaHSO3 with zinc metal. Na2S2O4 has many industrial uses, including reduction of water-soluble organic compounds, primarily in the dyeing industry.
Chemical properties
White solid
The Uses of Sodium dithionite
Sodium dithionite is a reducing agent for vat dyes,reducing hair bleaching agents,vat dyes printing auxiliaries, silk scouring and bleaching agents, coloring agents and objects stripping vat cleaning agent, particularly in dyeing with indigo and vat dyes; bleaching soaps, straw; removing dyes from dyed fabrics.
The Uses of Sodium dithionite
Sodium hydrosulfite is used as a reducing agent in aqueous solutions, sulfonating agent , chelating agent and decolorizing agent in organic reactions. It finds application in water treatment, gas purification, cleaning, leather, polymers, photography, and many others. It is involved in chemical enhanced oil recovery to stabilize polyacrylamide polymers against radical degradation in the presence of iron. It plays an important role to determine the iron content in soil chemistry.
Definition
ChEBI: An inorganic sodium salt that is the disodium salt of dithionous acid.
Production Methods
An alternative route for dithionite production is the reduction of sodium bisulfite with sodium borohydride. Sodium borohydride is obtained by reacting boron trimethyl ester, B(OCH3)3, with sodium hydride, NaH. The resulting product is hydrolyzed with water, and methanol is evaporated. An alkaline, aqueous solution is obtained, containing about 12% NaBH4 and 40% NaOH. This solution is commercially available. Reaction to dithionite is made on-site by adding sulfur dioxide and some additional caustic soda. Storages, handling and mixing of sulfur dioxide and of the Borol® liquid are not everywhere cost competitive.
NaBH4+8NaOH+8SO2 → 4Na2S2O4+NaBO2+6H2O.
Preparation
Sodium dithionite is today produced mainly from sodium formate and sulfur dioxide. Zinc dithionite, prepared on-site from sulfur dioxide and zinc dust, was formerly more important than the sodium salt. The heavy metal zinc ended up in the effluent, which caused environmental problems. Today in pulp mills on-site production of zinc dithionite is no longer practiced. The number of plants using sodium amalgam and sulfur dioxide for dithionite production is decreasing with the number of amalgam cells in electrolysis. On-site generation of dithionite from alkaline sodium borohydride solution, sodium bisulfite, and sulfur dioxide is used by some mills.
Sodium dithionite is available as crystalline powder (&90% Na2S2O4) or as a refrigerated 150 g/L solution stabilized with alkali. The white crystals can decompose on heating. Low alkalinity, pH8 to 13, stabilizes dithionite solution at low temperature.
These solutions should be kept well below 10 °C with the exclusion of air. In presence of air, oxidation rapidly yields sulfate and sulfite.
The powder product prepared via the amalgam route dissolves into an alkaline solution as it contains sodium carbonate and sulfite. This can trigger the precipitation of calcium carbonate (water hardness) in the solution tank. Therefore, it is recommended to add small amounts of chelants during the dissolution step. (Chelants are not required to stabilize the bleaching reaction.) Sodium dithionite prepared by the formate route dissolves into a slightly acidic solution. Dithionite powder can ignite if exposed to high humidity or elevated temperature.
General Description
Sodium dithionite is a whitish to light yellow crystalline solid having a sulfur dioxide-like odor. Sodium dithionite spontaneously heats on contact with air and moisture. This heat may be sufficient to ignite surrounding combustible materials. Sodium dithionite is soluble in water. Under prolonged exposure to fire or intense heat containers of Sodium dithionite may violently rupture. Sodium dithionite is used in dyeing and to bleach paper pulp.
Reactivity Profile
Inorganic reducing agents, such as Sodium dithionite, react with oxidizing agents to generate heat and products that may be flammable, combustible, or otherwise reactive. Their reactions with oxidizing agents may be violent. Sulfites and hydrosulfites (dithionites) can react explosively with strong oxidizing agents (sodium chlorite). Sulfites generate gaseous sulfur dioxide in contact with oxidizing acids and nonoxidizing acids.
Hazard
Fire risk in contact with moisture. To extin- guish fires, flood the reacting mass with water.
Health Hazard
Fire will produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Inhalation of decomposition products may cause severe injury or death. Contact with substance may cause severe burns to skin and eyes. Runoff from fire control may cause pollution.
Fire Hazard
Flammable/combustible material. May ignite on contact with moist air or moisture. May burn rapidly with flare-burning effect. Some react vigorously or explosively on contact with water. Some may decompose explosively when heated or involved in a fire. May re-ignite after fire is extinguished. Runoff may create fire or explosion hazard. Containers may explode when heated.
Flammability and Explosibility
Not classified
Safety Profile
Toxic and an irritant. An allergen. Flammable when exposed to heat or flame. Ignites on contact with water or sodium chlorite. To extinpsh fires, flood the reacting mass with water. Decomposes violently when heated to 19OOC and emits toxic fumes of SOx and NazO
Storage
Sodium dithionite crystals are available in steel containers (1 or 2 tons) or in steel drums (200 kg). Because of the danger of spontaneous ignition in humid air, sodium dithionite must be stored under dry and cool conditions. The sites for the preparation of dithionite solutions must permit handling without risks, high humidity should be avoided and remote fire control should be available.
Commercial dithionite products are classified as self-igniting hazardous goods (Class 4.2, UN 1384). Local rules for transportation and storage must be obeyed.
Properties and Applications
|
INDEX/GRADE |
SH-90 |
SH-88 |
SH-85 |
|
CONTENT |
90% |
88% |
85% |
|
Na 2 S 2 O 4 |
≥90% |
≥88% |
≥85% |
|
Fe |
≤20ppm |
≤20ppm |
≤20ppm |
|
Zinc (Zn) |
≤1ppm |
≤1ppm |
≤1ppm |
|
Other heavy metal (calculated as Pb) |
≤1ppm |
≤1ppm |
≤1ppm |
|
Water Insolubles |
≤0.05% |
≤0.05% |
≤0.05% |
|
Shelf Life(month) |
12 |
12 |
12 |
Properties of Sodium dithionite
| Melting point: | 300 °C |
| Boiling point: | 1390°C |
| Density | 2.13 |
| Flash point: | >100°C |
| storage temp. | Store at +5°C to +30°C. |
| solubility | 250 g/L (20°C) |
| form | Powder/Solid |
| color | White |
| PH | 5.5-8.5 (50g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| Odor | None or slight scent of sulfur dioxide |
| Water Solubility | 250 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Sensitive | Moisture Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,8626 |
| Stability: | Stable, but air sensitive. Incompatible with strong acids, strong oxidizing agents, water, moisture. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7775-14-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Sodium hydrosulfite (7775-14-6) |
Safety information for Sodium dithionite
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H251:Self-heating substances and mixtures H302:Acute toxicity,oral H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P235:Keep cool. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Sodium dithionite
Sodium dithionite manufacturer
ASM Organics
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
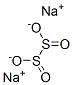
You may like
-
 Sodium Hydrosulfite CAS 7775-14-6View Details
Sodium Hydrosulfite CAS 7775-14-6View Details
7775-14-6 -
 Sodium hydrosulfite CAS 7775-14-6View Details
Sodium hydrosulfite CAS 7775-14-6View Details
7775-14-6 -
 Sodium dithionite, 85% 99%View Details
Sodium dithionite, 85% 99%View Details -
 Sodium Hydrosulphite CASView Details
Sodium Hydrosulphite CASView Details -
 Sodium Hydrosulphite CASView Details
Sodium Hydrosulphite CASView Details -
 Sodium Dithionite extrapure CAS 7775-14-6View Details
Sodium Dithionite extrapure CAS 7775-14-6View Details
7775-14-6 -
 Powder Sodium HydrosulfiteView Details
Powder Sodium HydrosulfiteView Details
7775-14-6 -
 Sodium Hydrosulphite Chemical, 90%View Details
Sodium Hydrosulphite Chemical, 90%View Details
7775-14-6
