Silver iodide
- CAS NO.:7783-96-2
- Empirical Formula: AgI
- Molecular Weight: 234.77
- MDL number: MFCD00003412
- EINECS: 232-038-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:30
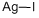
What is Silver iodide ?
Chemical properties
Yellow Crystalline Powder
Physical properties
Light yellow hexagonal crystals or powder; darkens on exposure to light; density 5.68 g/cm3 ; melts at 558°C; vaporizes at 1,506°C; insoluble in water, most acids and ammonium carbonate solution; moderately soluble in concentrated solutions of alkali chloride, bromide, and thiosulfate; readily soluble in solutions of alkali cyanides, iodides and in hot concentrated hydriodic acid.
The Uses of Silver iodide
Silver iodide is a yellow powder formed by the combination of a soluble iodide combined with silver nitrate. Silver iodide could also be formed by exposing metallic silver to the fumes of bromine as in the daguerreotype process. This was the primary halide used for all of the 19th century camera processes until the introduction of the silver bromide gelatin plate. With the exception of the daguerreotype, all silver iodide processes relied on physical development using a reducing agent such as gallic acid, pyrogallic acid, or ferrous sulfate, an acid restrainer, and excess silver.
The Uses of Silver iodide
In cloud precipitation (rain-making).
The Uses of Silver iodide
Used in medicine for its caustic, astringent and antiseptic effects. Used in photography, and in the estimation of silver. Through heterogeneous nucleation, it is used in cloud seeding, relying on its beta-AgI crystal structure being similar to that of Ice.
What are the applications of Application
Silver Iodide is a specialty product for proteomics research applications
Preparation
Silver iodide is prepared by adding a solution of sodium or potassium iodide to a hot solution of silver nitrate: Ag+ (aq) + Iˉ (aq) → Ag I (s) The precipitate is washed with boiling water. The preparation is done in the dark under ruby red light.
Definition
T3DB: Silver iodide is an iodide of silver. It is a photosensitive solid used in photography, as an antiseptic in medicine, and in rainmaking. Silver is a metallic element with the chemical symbol Ag and atomic number 47. It occurs naturally in its pure, free form, as an alloy with gold and other metals, and in minerals such as argentite and chlorargyrite.
Hazard
Silver iodide may cause irritation and psoriasis, and the main hazards encountered in the use and handling of silver iodide arise from its toxicological properties. It is toxic by a variety of routes (i.e. inhalation, ingestion and dermal contact) and exposures may include rashes, conjunctivitis, psoriasis (permanent greyish-grey discolouration of the skin, conjunctiva, and internal organs), headache, fever, hypersensitivity reactions, laryngitis and bronchitis.
Health effects
Silver itself is not toxic to humans, but most silver salts are. In large doses, silver and compounds containing it can be absorbed into the circulatory system and become deposited in various body tissues, leading to argyria, which results in a blue-grayish pigmentation of the skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. Argyria is rare, and although, so far as known, this condition does not otherwise harm a person's health, it is disfiguring and usually permanent. Mild forms of argyria are sometimes mistaken for cyanosis.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Properties of Silver iodide
| Melting point: | 557°C |
| Boiling point: | 1506°C |
| Density | 5.68 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| RTECS | VW4450000 |
| solubility | insoluble in acid solutions |
| form | Solid |
| Specific Gravity | 6.01 |
| color | Yellow |
| Odor | odorless |
| Water Solubility | 0.03 mg/L |
| Sensitive | Light Sensitive |
| Crystal Structure | Cubic, Sphalerite Structure - Space Group F(-4)3m |
| Merck | 14,8516 |
| Solubility Product Constant (Ksp) | pKsp: 16.07 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 0.01 ppm |
| Stability: | Stability Light-sensitive. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7783-96-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Silver iodide(7783-96-2) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Silver iodide (AgI) (7783-96-2) |
Safety information for Silver iodide
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H400:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, acute hazard H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P273:Avoid release to the environment. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Silver iodide
Silver iodide manufacturer
Micron Platers
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
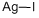

You may like
-
 Silver iodide 99%View Details
Silver iodide 99%View Details -
 Silver iodide 98%View Details
Silver iodide 98%View Details
7783-96-2 -
 Silver iodide CAS 7783-96-2View Details
Silver iodide CAS 7783-96-2View Details
7783-96-2 -
 Silver iodide CAS 7783-96-2View Details
Silver iodide CAS 7783-96-2View Details
7783-96-2 -
 Silver iodide CAS 7783-96-2View Details
Silver iodide CAS 7783-96-2View Details
7783-96-2 -
 Silver iodide CAS 7783-96-2View Details
Silver iodide CAS 7783-96-2View Details
7783-96-2 -
 Silver Iodide AR CAS 7783-96-2View Details
Silver Iodide AR CAS 7783-96-2View Details
7783-96-2 -
 Silver iodide, 99.9% CAS 7783-96-2View Details
Silver iodide, 99.9% CAS 7783-96-2View Details
7783-96-2