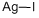CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Light yellow odorless solid; Gradually darkened by light; [Merck Index] Insoluble in water (28X10-7 g/l at 25 deg C); [HSDB] |
|---|---|
| Color/Form | Light yellow, powder; crystals are hexagonal or cubic |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Taste | Tasteless |
| Boiling Point | 1506 °C |
| Melting Point | 552 °C |
| Solubility | Sol in hydriodic acid, /aqueous solutions of/ potassium iodide, sodium chloride, potassium cyanide, ammonium hydroxide, and sodium thiosulfate. |
| Density | 5.67 |
| Vapor Pressure | 1 MM HG @ 820 °C |
| Stability/Shelf Life | LIGHT SENSITIVE |
| Other Experimental Properties | Slowly attacked by boiling concn acids, not affected by hot soln of alkali hydroxides; slowly darkened by light. |
| Chemical Classes | Metals -> Metals, Inorganic Compounds |
SAFETY INFORMATION
| Signal word | Warning |
|---|---|
| Pictogram(s) |
 Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H400:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, acute hazard H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P273:Avoid release to the environment. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 234.773 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 0 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 233.80956 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 233.80956 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 0 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 2 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 2 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
Silver iodide is an iodide of silver. It is a photosensitive solid used in photography, as an antiseptic in medicine, and in rainmaking. Silver is a metallic element with the chemical symbol Ag and atomic number 47. It occurs naturally in its pure, free form, as an alloy with gold and other metals, and in minerals such as argentite and chlorargyrite. (L808, L809, L820)