Ferrous chloride
- CAS NO.:7758-94-3
- Empirical Formula: Cl2Fe
- Molecular Weight: 126.75
- MDL number: MFCD00011004
- EINECS: 231-843-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-09-25 17:15:13
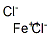
What is Ferrous chloride?
Description
Ferrous chloride is a pale greenish salt-likecrystal or power. Molecular weight = 126.75; Specific gravity (H2O:1) = 1.93 at 20 C; Boiling point=1012 C;Freezing/Melting point = 675.8 C. Hazard Identification(based on NFPA-704 M Rating System): Health 3,Flammability 0, Reactivity 1. Soluble in water.
Chemical properties
Greenish-white crystals. readily oxidized. Soluble in alcohol and water.
Chemical properties
Ferrous chloride is a pale greenish salt-like crystal or power.
Physical properties
White hexagonal crystal; hygroscopic; density 3.16g/cm3; melts at 677°C;vaporizes at 1,023°C; vapor pressure 20 torr at 737°C and 200 torr at 897°C;highly soluble in water, ethanol and acetone; slightly soluble in benzene. Thedihydrate and tetrahydrate are greenish monoclinic crystals; densities 2.39and 1.39 g/cm3, respectively; decomposing at 120 and 105°C, respectively;both the hydrates soluble in water.
The Uses of Ferrous chloride
Ferrous chloride (FeCl2) is used in pharmaceutical preparations, for sewage treatment, and as a mordant (which fixes dyes so that they will not run) in textiles.
The Uses of Ferrous chloride
Used in the synthesis of a novel cis-Fe(BPE5)2Cl2 (BPE5=1,2-diphospholanoethane) complex, which has potential application in many types of reactions such as intra- or intermolecular activation.1
The Uses of Ferrous chloride
A paramagnetic solid.
What are the applications of Application
Iron(II) chloride is a paramagnetic solid
Preparation
Iron(II) chloride is prepared by passing chlorine or hydrogen chloride gasover iron at red heat or 700°C:
Fe + 2HCl → FeCl2 + H2
Fe + Cl2 → FeCl2
It also may be produced by the reduction of iron(III) chloride with hydrogenor other reducing agents at elevated temperatures:
2FeCl3 + H2 → 2FeCl2 + 2HCl
The tetrahydrate is obtained by dissolving the metal in hydrochloric acidfollowed by crystallization at room temperature.
Fe + 2HCl + 4H2O → FeCl2•4H2O + H2
The tetrahydrate gradually loses water when heated above 105°C formingdihydrate, monohydrate and the anhydrous salt. At 220°C it loses all its waterof crystallization.
Definition
ChEBI: Iron dichloride is an iron coordination entity.
General Description
Ferrous chloride is a greenish white crystalline solid. Ferrous chloride is soluble in water. Ferrous chloride is noncombustible. Ferrous chloride is used in sewage treatment, in dyeing of fabrics, and for many other uses.
Air & Water Reactions
Water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
Alkali metal hydroxides, acids, anhydrous chlorides of iron, tin, and aluminum, pure oxides of iron and aluminum, and metallic potassium are some of the catalysts that may cause ethylene oxide to rearrange and polymerize, liberating heat, [J. Soc. Chem. Ind. 68:179(1949)]. Explosions occur , although infrequently, from the combination of ethylene oxide and alcohols or mercaptans, [Chem. Eng. News 20:1318(1942)].
Health Hazard
Inhalation of dust irritates nose and throat. Ingestion causes irritation of mouth and stomach. Dust irritates eyes and may cause skin irritation on prolonged contact.
Fire Hazard
Special Hazards of Combustion Products: Irritating hydrogen chloride fumes may form in fire.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion and intraperitoneal routes. Mutation data reported. Corrosive. Probably an irritant to the eyes, skin, and mucous membranes. Can react violently with ethylene oxide, K, Na. di%en heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of Cl-. See also CHLORIDES and IRON.
Potential Exposure
It is used in textile dyeing, metallurgy, the pharmaceutical industry and sewage treatment.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. If victim is conscious, administer water ormilk. Do not induce vomiting.Note to physician: For severe poisoning do not use BAL[British Anti-Lewisite, dimercaprol, dithiopropanol(C3H8OS2)] as it is contraindicated or ineffective in poisoning from iron.
Storage
Color Code—White: Corrosive or Contact Hazard;Store separately in a corrosion-resistant location. Prior toworking with this chemical you should be trained on itsproper handling and storage. Store in tightly closed containers in a cool, well-ventilated area away from potassium,sodium metals, or ethylene oxide.
Shipping
UN1759 Ferrous chloride, solid, Hazard class: 8; Labels: 8-Corrosive material. UN1760 Ferrous chloride, solution, Hazard class: 8; Labels: 8-Corrosive material.
Purification Methods
It forms white hygroscopic rhombohedral crystals with a green tint which oxidise in air to FeCl3 and Fe2O3. It is soluble in H2O, EtOH Me2CO but insoluble in Et2O. The tetrahydrate is pale green to pale blue in colour and loses 2H2O at 105-115o. The dihydrate loses H2O at 120o. [Anhydrous FeBr2 can be obtained by carefully dehydrating the tetrahydrate in a stream of HBr and N2, and it can be sublimed under N2.] The ferrous iron in aqueous solutions of these salts readily oxidises to ferric iron. (See above.) [Kovacuumic & Brace Inorg Synth VI 172 1960, Lux in Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry (Ed Brauer) Academic Press Vol II p 1491 1965.]
Incompatibilities
Solution attacks metals. Contact with ethylene oxide may initiate polymerization. Contact with potassium or sodium forms an impact-sensitive material.
Properties of Ferrous chloride
| Melting point: | 677 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 1023°C |
| Density | 3.16 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| vapor pressure | 0Pa at 20℃ |
| Flash point: | 1023°C |
| solubility | H2O: soluble |
| form | beads |
| color | Off-white |
| Specific Gravity | 3.162 |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water, alcohol and acetone. Slightly soluble in benzene. Insoluble in ether. |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| Merck | 14,4043 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 1 mg/m3 NIOSH: TWA 1 mg/m3 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7758-94-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Iron dichloride(7758-94-3) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Ferrous chloride (7758-94-3) |
Safety information for Ferrous chloride
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Ferrous chloride
| InChIKey | NMCUIPGRVMDVDB-UHFFFAOYSA-L |
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Ferrous Chloride 98%View Details
Ferrous Chloride 98%View Details -
 Iron(II) chloride, Ultra dry CAS 7758-94-3View Details
Iron(II) chloride, Ultra dry CAS 7758-94-3View Details
7758-94-3 -
 Iron(II) chloride, Ultra dry CAS 7758-94-3View Details
Iron(II) chloride, Ultra dry CAS 7758-94-3View Details
7758-94-3 -
 Iron(II) chloride, Ultra dry CAS 7758-94-3View Details
Iron(II) chloride, Ultra dry CAS 7758-94-3View Details
7758-94-3 -
 Iron(II) chloride, anhydrous CAS 7758-94-3View Details
Iron(II) chloride, anhydrous CAS 7758-94-3View Details
7758-94-3 -
 Iron(II) chloride, anhydrous CAS 7758-94-3View Details
Iron(II) chloride, anhydrous CAS 7758-94-3View Details
7758-94-3 -
 Iron(II) chloride, anhydrous CAS 7758-94-3View Details
Iron(II) chloride, anhydrous CAS 7758-94-3View Details
7758-94-3 -
 Iron Chloride FeCL2 CAS 7758-94-3View Details
Iron Chloride FeCL2 CAS 7758-94-3View Details
7758-94-3
