Rotundine
- CAS NO.:10097-84-4
- Empirical Formula: C21H25NO4
- Molecular Weight: 355.43
- MDL number: MFCD00214191
- EINECS: 1592732-453-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 20:33:22
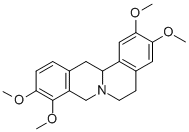
What is Rotundine?
Description
The roots of Stephania rotunda furnish this alkaloid which forms colourless plates when crystallized from EtOH. It is laevorotatory with [α]23D - 262° (EtOH) and gives a crystalline hydrochloride with m.p. 258-9°C (dec.) and the methiodide which decomposes at that same temperature. Three methoxyl groups and one methyl group are present.
Physical properties
Appearance: off-white solid, odorless, tasteless, and turns yellow under light and heat. It should be protected from light and air. Solubility: this product is usually dissolved in chloroform, slightly soluble in ethanol or ether, insoluble in water, and soluble in dilute sulfuric acid. Melting point: 141–144?°C. Specific optical rotation: ?290 to –300°.
History
From the 1920s, many researchers have focused on the alkaloid compounds contained in the Yan Hu Suo and extracted more than 30 different kinds of alkaloids.
Among them Rotundine is one of the most important active compounds and has
been successfully applied in clinical practice.
Tetrahydropalmatine (THP) was firstly discovered by Zhao Chenggu, a famous
medicinal phytochemist in China. He isolated 13 kinds of alkaloids and identified the structure of 6 of them. In 1936, Huang Minglong, a famous organic chemist,
proved THP is a racemate. From 1933, Wang Jingxi and Lu Zihui began to study the
pharmacological effects of THP and found that THP could induce catalepsy in animals. Rotundine is a levo-THP and obtained from the resolution of DL-THP during
1959–1964. From 1956 to 1965, the famous Chinese neuropharmacologist, Jin
Guozhang, identified Rotundine as the main effective component in Yan Hu Suo and
further studied its underlying mechanisms. He also found that Stephania contains
abundant L-THP, which could become the source of clinical medication.
In 1965, Rotundine was recorded in the textbooks of pharmacology. After over
20?years of clinical practices, people have proved that Rotundine has reliable efficacy and low side effect. In 1977, Rotundine was recorded in the Chinese
Pharmacopoeia. In 1979, THP achieved a full synthesis, and currently Rotundine is
mainly produced by artificial synthesis. From 1980, the study on the mechanisms of
Rotundine made great progress. The analgesic effect of Rotundine has nothing to do
with opioid receptors or prostaglandins. Rotundine does not belong to narcotic analgesics and antipyretic analgesics. Further, Rotundine has been found to have no
affinity with M-cholinergic receptor and GABA system in the brain. But it has affinity to dopamine receptors. The exact mechanisms and pharmacology effects of
Rotundine still need more research.
The Uses of Rotundine
An analgesic drug found in Chinese herbal medicine, used to treat heart disease and liver damage.
Definition
ChEBI: 2,3,9,10-tetramethoxy-6,8,13,13a-tetrahydro-5H-isoquinolino[2,1-b]isoquinoline is an alkaloid.
Pharmacology
1. Effects on the central nervous system: Rotundine has significant analgesic, sedative, and hypnotic effects, and its mechanism has nothing to do with opioid
receptors. It has no obvious addiction effect. Using Rotundine combined with
pethidine can enhance the analgesic effect, reduce the amount of pethidine, and
further reduce the occurrence of drug dependence. The present study suggests
that Rotundine is a central dopamine receptor blocker that inhibits the transmission of peripheral pain information by blocking the D2 receptor of the striatum
and nucleus accumbens and the PAG-RgpI-spinal dorsal horn nerve pathway.
In addition, Rotundine also has a suppression of the strengthening of the motor
response induced by drug abuse, that is, inhibition of behavioral sensitization.
2. Effects on the cardio-cerebrovascular system: Rotundine has inhibitory effect on
the injuries caused by cerebral ischemia and reperfusion and myocardial
ischemia and reperfusion. It also could lower the blood pressure. The
pharmacological mechanism of Rotundine on the cardiovascular and cerebrovascular aspects is quite complex and may relate to the regulation of inflammation
and inhibition of apoptosis. It is also found that Rotundine acts on α-receptors
and has a noncompetitive antagonistic effect on calcium.
3. Rotundine can reverse the drug resistance of tumor cells; the mechanism may be
through the downregulating of the expression of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) and the
upregulating of the expression of topo II in tumor cells.
4. Rotundine has an excitatory effect on the endocrine system, such as the pituitaryadrenal system, and also has a protective effect on the liver.
5. Drug metabolisms: The absorption of Rotundine by oral administration is complete. At 15?min it can be absorbed by 40–50%. It begins to work at 10–30?min,
and the effect can last 2–5?h. In vivo distribution is through fat and the lung, liver,
and kidney. If administered by subcutaneous injection, after 12?h, Rotundine will
be discharged by 80% with the urine.
Clinical Use
1. Pain induced by gastrointestinal and hepatobiliary disorders, menstrual pain, and
pain after childbirth.
2. Mild trauma and postoperative pain
3. Headache insomnia and spasmodic cough.
4. There is a report about the usage of Rotundine in arrhythmia caused by I–III
hypertension and other diseases.
5. The hypnotic effect of Rotundine happens in 15?min after administration and
then appears after 2?h. Because the analgesic effect happens at the same time,
Rotundine is particularly suitable for insomnia patients with pain.
6. Side effects: drowsiness, dizziness, fatigue, and nausea. Large dose of Rotundine
can inhibit the respiratory center and may cause extrapyramidal symptoms.
Purification Methods
Crystallise it from MeOH or EtOH by addition of water [see Kametani & Ihara J Chem Soc (C) 530 1967, Bradsher & Dutta J Org Chem 26 2231 1961]. When crystallised from Me2CO/Et2O, it has m 142o. The hydrate has m 115o(effervescence). The picrate has m 188o(dec) (from aqueous EtOH). [Bradsher & Datta J Org Chem 26 2231 1961, Beilstein 21 II 196, 21 III/IV 2769.]
References
Kondo, Matsuno., J. Pharm. Soc., Japan, 64, (9A), 28 (1944)
Properties of Rotundine
| Melting point: | 140-1°C |
| storage temp. | Hygroscopic, Refrigerator, under inert atmosphere |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to Off-White |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C21H25NO4/c1-23-18-6-5-13-9-17-15-11-20(25-3)19(24-2)10-14(15)7-8-22(17)12-16(13)21(18)26-4/h5-6,10-11,17H,7-9,12H2,1-4H3 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 10097-84-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Rotundine
Computed Descriptors for Rotundine
| InChIKey | AEQDJSLRWYMAQI-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | C12CC3=C(C(OC)=C(OC)C=C3)CN1CCC1C=C(OC)C(OC)=CC2=1 |
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Rotundine CAS 10097-84-4View Details
Rotundine CAS 10097-84-4View Details
10097-84-4 -
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1