RETAPAMULIN
- CAS NO.:224452-66-8
- Empirical Formula: C30H47NO4S
- Molecular Weight: 517.76
- MDL number: MFCD11045316
- EINECS: 639-491-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
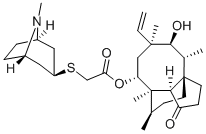
What is RETAPAMULIN?
Description
Antibacterial retapamulin is a derivative of the natural product pleuromutilin and was developed by Glaxo and approved in the US in 2007 for the treatment of skin infections. It has a unique mechanism of action, inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis by inhibiting the larger subunit of the ribosome, and thus has no cross resistance to other antibacterial agents. Pleuromutilin is a tricyclic diterpenoid that was first isolated in 1951 from the edible mushroom Pleurotus mutilus. The first semisynthetic analogs tiamulin and valnemulin, developed for veterinary use, have been shown to interact uniquely with bacterial ribosomes by high affinity binding to a site on the 50S subunit. Binding to this site interferes with ribosomal peptidyl transferase activity, blocks P-site interactions, and prevents the evolution of active 50S ribosomal subunits. Retapamulin, the first pleuromutilin approved for human use, behaves similarly to selectively inhibit bacterial protein synthesis. This novel mechanism of action has been implicated in the lack of in vitro target-specific cross-resistance with other classes of antibiotics.
Originator
GlaxoSmithKline (US)
The Uses of RETAPAMULIN
Retapamulin is a topical antibiotic, which binds to both E. coli and S. aureus ribosomes with similar potencies with Kd of 3 nM
The Uses of RETAPAMULIN
Retapamulin is a semi-synthetic pleuormutilin prepared by reacting pleuromutilin tosylate with tropine-3-thiol to give a more hydrophobic analogue with a tertiary amine. This enables formulation as a stable hydrochloride salt. Retapamulin is a broad spectrum antibiotic with no cross resistance to existing antibiotic classes, and is the first pleuromutilin approved for human use. Like all the pleuromutilins, retapamulin inhibits protein synthesis by binding to domain V of 23S rRNA.
The Uses of RETAPAMULIN
A broad spectrum antibiotic with no cross resistance to existing classes
The Uses of RETAPAMULIN
Retapamulin is a semi-synthetic pleuromutilin prepared by reacting pleuromutilin tosylate with tropine-3-thiol to give a more hydrophobic analogue with a tertiary amine. This enables formulation as a stable hydrochloride salt. Retapamulin is a broad spectrum antibiotic with no cross resistance to existing antibiotic classes, and is the first pleuromutilin approved for human use. Like all the pleuromutilins, retapamulin inhibits protein synthesis by binding to domain V of 23S rRNA.
Background
Retapamulin, marketed by GlaxoSmithKline as the ointment Altabax, is an antibiotic for skin infections like impetigo. It was approved by the FDA in April 2007.
Indications
For use in adults and pediatric patients aged 9 months and older for the topical treatment of impetigo (up to 100 cm2 in total area in adults or 2% total body surface area in pediatric patients aged 9 months or older) due to Staphylococcus aureus (methicillin-susceptible isolates only) or Streptococcus pyogenes.
What are the applications of Application
Retapamulin is a broad spectrum antibiotic with no cross resistance to existing classes
Definition
ChEBI: Retapamulin is a carbotricyclic compound, a carboxylic ester and a cyclic ketone.
brand name
Altabax
Pharmaceutical Applications
A semisynthetic pleuromutilin formulated as a 1% ointment
for topical use. It is active against staphylococci
(MIC 0.12 mg/L), including methicillin-resistant strains, and
against streptococci (MIC 0.03–0.25 mg/L), including Str.
pyogenes and Str. pneumoniae. Most enterococci and Gramnegative
bacilli are resistant. Propionibacteria are susceptible,
suggesting that it might be useful in acne. Early indications
suggest that resistance does not emerge readily, but experience
with veterinary pleuromutilins indicates that chromosomal
resistance may develop with extended use.
It is metabolized in the liver and rapidly excreted, precluding
use in systemic infection. Systemic exposure is said to be
low following topical application and it appears safe, but there
are few data on absorption through broken and unbroken skin.
Principal side effects noted include local irritation and occasional
allergic reactions. Licensed use is presently restricted to
the treatment of impetigo and uncomplicated skin infections.
Possible value in methicillin-resistant Staph. aureus (MRSA)
infection or carriage has not yet been established.
Pharmacokinetics
Retapamulin is a semisynthetic pleuromutilin antibiotic. This drug is usually bacteriostatic in action, but may become bactericidal at highed concentrations (when MBC is 1000 times higher than MIC). Retapamulin acts by selectively inhibiting the initiation of protein synthesis in bacteria at the level of bacterial 50S ribosome.
Side Effects
The most frequent adverse event was application site irritation, but other side effects, occurring in o2% of patients, included headache, diarrhea, nausea, and nasopharyngitis. While there are no contraindications, it is recommended that pregnant women only use retapamulin when the potential benefits outweigh the potential risks since animal reproductive studies are not always predictive of human response. Likewise, nursing mothers are cautioned about the unknown possibility of retapamulin excretion in breast milk.
Synthesis
The synthesis of retapamulin begins with generation of the mesylate of pleuromutilin, isolated through fermentation of Clitopilus passeckerianus, followed by nucleophilic substitution with exo-8-methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]octan-3-thiol under basic conditions Shridhar Hegde and Michelle Schmidt (potassium-tert-butoxide in ethanol or tetrabutylammonium hydrogen sulfate in dichloromethane/water and sodium hydroxide at pH 12.5). The azabicyclic thiol derivative may be prepared via a Mitsunobu reaction between tropine and thioacetic acid.
Metabolism
In vitro studies with human liver microsomes demonstrated that retapamulin is extensively metabolized to numerous metabolites, of which the predominant routes of metabolism were mono-oxygenation and N-demethylation. The major enzyme responsible for metabolism of retapamulin in human liver microsomes was cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4).
References
[1] jones r n, fritsche t r, sader h s, et al. activity of retapamulin (sb-275833), a novel pleuromutilin, against selected resistant gram-positive cocci. antimicrobial agents and chemotherapy, 2006, 50(7): 2583-2586.
[2] rittenhouse s, biswas s, broskey j, et al. selection of retapamulin, a novel pleuromutilin for topical use. antimicrobial agents and chemotherapy, 2006, 50(11): 3882-3885.
Properties of RETAPAMULIN
| Boiling point: | 594.9±50.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.16±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | insoluble in H2O; ≥114.8 mg/mL in EtOH; ≥16.15 mg/mL in DMSO |
| form | solid |
| pka | 14.65±0.70(Predicted) |
| color | White to off-white |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 224452-66-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for RETAPAMULIN
Computed Descriptors for RETAPAMULIN
| InChIKey | STZYTFJPGGDRJD-IFPFAXJDNA-N |
RETAPAMULIN manufacturer
Ralington Pharma
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 224452-66-8 Retapamulin 98%View Details
224452-66-8 Retapamulin 98%View Details
224452-66-8 -
 224452-66-8 98%View Details
224452-66-8 98%View Details
224452-66-8 -
 Retapamulin 98% CAS 224452-66-8View Details
Retapamulin 98% CAS 224452-66-8View Details
224452-66-8 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1