Pirfenidone
Synonym(s):5-Methyl-1-phenyl-2-(1H)-pyridone
- CAS NO.:53179-13-8
- Empirical Formula: C12H11NO
- Molecular Weight: 185.22
- MDL number: MFCD00866047
- EINECS: 621-260-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-23 21:30:31
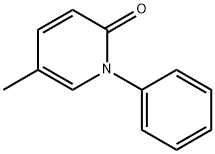
What is Pirfenidone?
Description
Until recently, IPF therapy consisted of a combination of corticosteroids and immunosuppressive agents (azathioprine and cyclophosphamide) to target the inflammation that was believed to be the pathogenic stimulus.Since IPF is now considered to be predominantly a disorder of fibroproliferation, agents that intervene in fibrogenesis have moved to the forefront of treatment options. With demonstrated efficacy in a bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis animal model, pirfenidone has been developed and launched as an approved therapy for IPF. Its antifibrotic activity is derived from the inhibition of p38 MAP kinase that is upstream of transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β), a cytokine implicated in the stimulation of collagen synthesis and the inhibition of its degradation. Pirfenidone also inhibits the expression of TNF-α, IL-1, and ICAM-1, so it possesses the dual benefit of an anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic agent. This relatively simplistic drug is constructed by the copper-catalyzed reaction of 5-methyl-2(1H)-pyridinone with bromo- or chlorobenzene. .
Chemical properties
Off-White Solid
Originator
Marnac (United States)
The Uses of Pirfenidone
Pirfenidone is in a group of medicines called antifibrotic agents. Pirfenidone has demonstrated activity in multiple fibrotic conditions, including those of the lung, kidney and liver. It affects your body’s immune system and reduces the amount of fibrosis (scarring) in the lungs. Pirfenidone is one of two medicines that are approved in Canada to treat Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF). Another name for this medicine is Esbriet.
The Uses of Pirfenidone
Pirfenidone has been used:
- as a post-operative eye drop in rabbits to analyse its antifibrotic effect to improve glaucoma filtration surgery
- as an anti-scarring agent to examine whether it affects the foreign body reaction after glaucoma drainage device (GDD) implantation in a rabbit
- to test its antifibrotic potential in primary cultures of human orbital fibroblasts (hOFs)
- as tumor necrosis factor (TNFα) inhibitor to study its effect in hypoxia
Indications
Pirfenidone is indicated for the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). In Canada and Europe, it is approved in adults only.
Background
Pirfenidone is a synthetic pyridone drug. It is an antifibrotic agent with anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties that is used to treat idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), which is a chronic, progressive form of interstitial pneumonia. While its mechanism of action is not yet fully understood, pirfenidone is proposed to primarily regulate tumor necrosis factor (TNF) pathways and modulate cellular oxidation. The FDA first approved pirfenidone alongside nintedanib as one of the first drugs to treat IPF.
Definition
ChEBI: A pyridone that is 2-pyridone substituted at positions 1 and 5 by phenyl and methyl groups respectively. An anti-inflammatory drug used for the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
brand name
Pirespa
General Description
Pirfenidone?(5-methyl-1-phenyl-2-[1H]-pyridone) is a synthetic derivative of pyridine.
Biological Activity
Antifibrotic agent, effective in models of pulmonary and lung fibrosis. Inhibits collagen production and fibroblast proliferation. Regulates cytokine levels following oral administration in vivo . Potent scavenger of free radicals and inhibitor of lipid peroxidation.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Pirfenidone inhibits collagen production and fibroblast proliferation. It has shown antifibrotic and anti-inflammatory properties in variety of animal models of pulmonary fibrosis, and in clinical trials.
Pharmacokinetics
Pirfenidone is a novel agent with anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antifibrotic properties. It may improve lung function and reduce the number of acute exacerbations in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF).
Synthesis
Pirfenidone may inhibit collagen synthesis, down-regulate production of multiple cytokines, and block fibroblast proliferation and stimulation in response to cytokines. Pirfenidone was prepared via a two step sequence as detailed in the scheme.2-Amino-5-methylpyridine (91) was converted to pyridone 92 by reaction with sulfuric acid and sodium nitrate at low temperature in 73% yield. Condensation of 5-methyl-2- (1H)-pyridone (92) with iodobenzene (93) in the presence of K2CO3 and CuCl at reflux gave pirfenidone (XIII) in 85% yield.

in vitro
in raw264.7 cells, pirfenidone (< 300 μg/ml) suppressed the proinflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis factor-α (tnf-α) through a translational mechanism, which was independent of activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (mapk)2, p38 map kinase, and c-jun n-terminal kinase (jnk)[1]. in ln-18, t98g, lnt-229 and ln-308 cell lines, pirfenidone (< 10 mm) reduced glioma cell density in a concentration-dependent manner. in ccl-64 cells, pirfenidone (< 5 mm) reduced tgf-β bioactivity by affecting tgf-β2 mrna expression and processing of pro-tgf-β. pirfenidone (< 8.3 mm) inhibited the activity of recombinant furin and downregulated the expression of mmp-11 in a dose-dependent manner in ln-308 cells[2].in cultured myometrial and leiomyoma smooth muscle cells, pirfenidone inhibited serum-stimulated increases in dna synthesis and cell proliferation in a dose-dependent manner[3].
in vivo
in animals, pirfenidone treatment significantly decreased gene expression of collagens i, iii and iv, transforming growth factor β-1, smad-7, timp-1 and pai-1 [4]. pirfenidone at a dose of 30 mg/kg/day t.i.d. attenuated the bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosi. pirfenidone (30, 100 mg/kg/day t.i.d) suppressed lung inflammatory edema and pulmonary fibrosis. pirfenidone suppressed the bleomycin-induced increase in lung interleukin (il)-1β, il-6, il-12\p40 and monocyte chemoattractant protein (mcp)-1 levels and prevented the bleomycin-induced decrease in lung interferon (ifn)-γ levels. furthermore, pirfenidone suppressed elevation of lung basic-fibroblast growth factor (bfgf), transforming growth factor (tgf)-β1 levels, lung stroma cell derived factor (sdf)-1α and il-18[5].
Absorption
After a single oral-dose administration of 801 mg pirfenidone (as three 267 mg capsules), the Tmax ranged from 30 minutes to four hours. Food affects the absorption and safety profile of pirfenidone: in one study, food increased Tmax; decreased Cmax and AUC by 49% and 16%, respectively; and decreased the incidence of pirfenidone-induced adverse reactions.
Metabolism
According to in vitro studies, about 70-80% of pirfenidone metabolism is mediated by CYP1A2, as well as some minor contributions from CYP2C9, 2C19, 2D6, and 2E1. Four metabolites have been detected after oral administration of pirfenidone. In vitro data suggest that metabolites are not expected to be pharmacologically active at observed metabolite concentrations. The exact metabolic pathways of pirfenidone have not been fully characterized; however, one of the pathways involve CYP1A2-mediated 5-hydroxylation and subsequent oxidation to form 5-carboxy pirfenidone. In humans, only pirfenidone and 5-carboxy pirfenidone are present in plasma in significant quantities. The mean metabolite-to-parent ratio ranged from approximately 0.6 to 0.7.
Toxicity
In rats, the oral and intraperitoneal LD50 are 1295 mg/kg and 430 mg/kg, respectively.
There is limited clinical experience with overdosage of pirfenidone. A maximum tolerated pirfenidone dose of 4005 mg per day was tolerated when the drug was administered as five 267 mg capsules three times daily to healthy adult volunteers over a 12-day dose escalation. Overdosage should be managed with supportive and symptomatic care, including monitoring of vital signs and observation of the clinical status of the patient.
Storage
Store at RT
References
1) Kehrer and Margolin (1997),?Pirfenidone diminishes cyclophosphamide-induced lung fibrosis in mice; Toxicol.Lett.,?90?125 2) Iyet?et al.?(1999),?Effects of pirfenidone on procollagen gene expression at the transcriptional level in bleomycin hamster model of lung fibrosis; J.Pharmacol.Exp.Ther.,?289?211 3) Xie?et al.?(2002),?Upregulation of RGS2: a new mechanism for pirfenidone amelioration of pulmonary fibrosis; Respir.Res.,?17?103 4) Li?et al.?(2016),?Oral pirfenidone protects against fibrosis by inhibiting fibroblast proliferation and TGF-b signaling in a murine colitis model;?Biochem.Pharmacol.,?117?57 5) Nakazato?et al.?(2002),?A novel anti-fibrotic agent pirfenidone suppresses tumor necrosis factor-alpha at the translational level, Eur.J.Pharmacol.?446?177 6) Misra and Rabideau (2000),?Pirfenidone inhibits NADPH-dependent microsomal lipid peroxidation and scavenges hydroxyl radicals, Mol.Cell Biochem.?204?119 7) Canestaro?et al.?(2016),?Drug Treatment of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Systemic Review and Network Meta-Analysis; Chest,?149?756
Properties of Pirfenidone
| Melting point: | 96-97°C |
| Boiling point: | 329.1±15.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.137±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Room Temperature |
| solubility | DMSO: ≥10 mg/mL, soluble |
| form | solid |
| pka | -0.16±0.63(Predicted) |
| color | Off-white |
| Water Solubility | Soluble to 20 mM in water |
| Stability: | Stable for 2 years from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions in DMSO may be stored at -20°C for up to 1 month. |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C12H11NO/c1-10-7-8-12(14)13(9-10)11-5-3-2-4-6-11/h2-9H,1H3 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 53179-13-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Pirfenidone
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
Computed Descriptors for Pirfenidone
| InChIKey | ISWRGOKTTBVCFA-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | C1(=O)N(C2=CC=CC=C2)C=C(C)C=C1 |
Pirfenidone manufacturer
SRINI PHARMACEUTICALS PVT LTD
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 PIRFENIDONE 99%View Details
PIRFENIDONE 99%View Details -
 Pirfenidone 99%View Details
Pirfenidone 99%View Details -
 Pirfenidone 99%View Details
Pirfenidone 99%View Details -
 Pirfenidone 98%View Details
Pirfenidone 98%View Details -
 53179-13-8 Pirfenidone 98%View Details
53179-13-8 Pirfenidone 98%View Details
53179-13-8 -
 Pirfenidone 53179-13-8 95-99 %View Details
Pirfenidone 53179-13-8 95-99 %View Details
53179-13-8 -
 Pirfenidone 98%View Details
Pirfenidone 98%View Details -
 Pirfenidone 98% CAS 53179-13-8View Details
Pirfenidone 98% CAS 53179-13-8View Details
53179-13-8
