Resveratrol
Synonym(s):trans-3,4ʹ,5-Trihydroxystilbene;3,4′,5-Trihydroxy-trans-stilbene;5-[(1E)-2-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)ethenyl]-1,3-benzenediol;Resveratrol;Resveratrol - CAS 501-36-0 - Calbiochem
- CAS NO.:501-36-0
- Empirical Formula: C14H12O3
- Molecular Weight: 228.24
- MDL number: MFCD00133799
- EINECS: 610-504-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-26 18:10:20
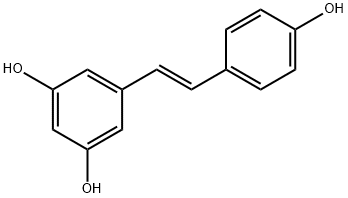
What is Resveratrol?
Description
trans-Resveratrol is a naturally occurring stilbene phytoalexin found in grapes, peanuts, and soybeans. Food chemists are investigating its antioxidative and anticarcinogenic properties.
Chemical properties
Off-White to Tan Powder
The Uses of Resveratrol
Minor constituent of wine, correlated with serum lipid reduction and inhibition of platelet aggregation. Resveratrol is a specific inhibitor of COX-1, and it also inhibits the hydroperoxidase activity of COX-1. It has been shown to inhibit events associated with tumor initiation, promotion and progression.
The Uses of Resveratrol
raw material for Tamiflu; Oseltamivir
The Uses of Resveratrol
Resveratrol is a natural antioxidant. It reduces blood viscosity, inhibits platelet aggregation and vasodilation, keeps blood flowing smoothly, and prevents the occurrence and development of cancer. It has the effect of preventing and treating atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease, ischemic heart disease and hyperlipidemia. It has tumor-inhibiting effects. Resveratrol also has estrogen-like effects and can be used to treat breast cancer and other diseases. It slows down aging and prevents cancer. Red grape skins, red wine and grape juice contain high concentrations of resveratrol. Studies have shown that as humans age, the integrity of chromosomes is disrupted. However, resveratrol activates proteins that can repair chromosomes, thus slowing down aging.
Resveratrol is effective in preventing aging, in part due to its antioxidant properties, and is recommended for use in pre- or post-sun products. Resveratrol can cross the stratum corneum and be found in the dermis and epidermis. It has been shown to protect dermal collagen and may be effective in enhancing glycosaminoglycans, thereby improving tissue hydration. It has been shown to stimulate cell renewal in the skin and to help increase skin thickness. It has been shown to inhibit tyrosinase, which suggests it may be used to reduce hyperpigmentation.
What are the applications of Application
Resveratrol is a natural phenolic antioxidant that is a potent activator of SIRT1 and inhibitor of Cox-1
Definition
ChEBI:Resveratrol is a stilbenol that is stilbene in which the phenyl groups are substituted at positions 3, 5, and 4' by hydroxy groups. It has a role as a phytoalexin, an antioxidant, a glioma-associated oncogene inhibitor and a geroprotector. It is a stilbenol, a polyphenol and a member of resorcinols.
Synthesis Reference(s)
Tetrahedron Letters, 43, p. 597, 2002 DOI: 10.1016/S0040-4039(01)02227-4
Description
Resveratrol, a non-flavonoid polyphenolic compound, is widely found in the skin of red grapes, nuts, berries, Polygonum cuspidatum root, etc. It is reportedly known to exhibit pharmacological properties including anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, neuroprotectant, anti-atherogenic property and reduces the synthesis of pro-atherosclerotic substances.
Biological Activity
A phytoestrogen with antitumor, antioxidant, antiplatelet, anti-inflammatory and antifungal effects. Inhibits cytochrome P450 1A1 (IC 50 = 23 μ M) and displays mixed agonist/antagonist actions at ER α and ER β estrogen receptors. Converted into the anticancer agent piceatannol (4-[(1E)-2-(3,5-Dihydroxyphenyl)ethenyl]-1,2-benzenediol ) by cytochrome P450 1B1
Biochem/physiol Actions
ED50 = 15 μM against COX-1
Mechanism of action
Resveratrol can be found in the skins and seeds of grapes and in peanuts. It has demonstrated potent antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-proliferative activities. Topical application of resveratrol in mice demonstrated photoprotection by significantly decreasing UVB-mediated generation of hydrogen peroxide and infiltration of leukocytes. Its antiproliferative properties are related to the inhibition of cellular events associated with tumor initiation, promotion, and progression, and the triggering of apoptosis in tumor cells.
Anticancer Research
Resveratrol is a stilbinoid, found in the skin of grapes, peanuts, berries, and otherfruits. The cytotoxic effect of resveratrol is mediated via the inhibition of severaltranscription factors; upregulation of caspases, Bax, and p53; and downregulationof survivin, cyclins, and Bcl-2. Increase in Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and upregulation ofcaspases lead to apoptosis. The beneficial effects of resveratrol against cancer havebeen shown in all the stages of cancer including carcinogenesis, initiation,promotion, and progression. It could inhibit Wnt target gene expression in normalcolonic mucosa of the colorectal cancer patients. It increases the caspase-3 inmalignant hepatic tissue and induces anticarcinogenic effects in humangastrointestinal tract (Hosseini and Ghorbani 2015). It has the ability to inhibit thedevelopment of DMBA-induced phenoblastic lesions in the mammary gland organculture (MMOC) model of carcinogenesis and in two-stage full-term mouse model(Balunas and Kinghorn 2005). It prevents carcinogenesis by upregulating Bax andp53 proteins and downregulating NF-κB, COX-2, AP-1, cyclin-dependent kinases,hypoxia-induced factor 1α (HIF-1α), cyclins, MMPs, cytokines, and Bcl-2 proteins(Singh et al. 2016b). It plays a pivotal role in preventing the initiation, promotion,and progression of cancer by inducing phase II drug metabolizing enzymes, bymediating anti-inflammatory effects and inhibiting COX and hydroperoxidasefunctions, and by inducing cell differentiation, respectively, in human promyelocyticleukemic cells (Jang et al. 1997; Aggarwal et al. 2004).
Resveratrol, a noteworthy polyphenol occurring in different plants such as grapesand peanuts, has appeared to be required in cell reinforcement, anti-proliferative,anti-inflammatory, and chemopreventive activities. Various potential medicaladvantages, including decreased danger of malignancy and coronary illness, arebelieved to be related to the utilization of resveratrol. It can successfully and proficientlyrepress endothelial cell multiplication and migration, with little cell toxicityin the HUVEC and ARPE19 lines (Cao et al. 2010). Also, there have been perceptionsof inhibitory consequences for smooth muscle cell migration (Venkatesanet al. 2009) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha-incited monocyte adhesion and migration(Kim et al. 2007). As of late, it was recognized that the restraint of PDGF-BB-actuatedcell migration by resveratrol and the particular inhibitors PDGF-R, PI3K,MEK, or p38 in wound healing test agreed with diminished enactment of PDGFBB-incited PDGFR-β, PI3K/Akt, ERK, and p38 phosphory-lation in Western blotinvestigation, recommending that resveratrol hinders cell migration through theinhibition of PI3K/Akt, PDGFR-β, and MAPK cascade (Chan et al. 2013).
Biological Activity
The reported anti-aging and disease-fighting properties of red wine have garnered significant attention. Researchers have long speculated about the potential health benefits of compounds found in red wine. In the 1990s, attention shifted to resveratrol, an antioxidant compound present in red wine, prompting extensive study. Subsequent animal and laboratory investigations have revealed promising antiviral, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer effects associated with resveratrol.
Side Effects
To date, studies have not identified any significant adverse effects associated with resveratrol, even at high doses.
Individuals with pre-existing health conditions such as bleeding disorders should consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating resveratrol into their regimen.
Prior to initiating resveratrol supplementation, individuals who regularly take medications or other dietary supplements should seek guidance from their healthcare provider. Resveratrol may interact with various medications, including blood thinners, antihypertensive drugs, cancer therapies, MAOI antidepressants, antiviral and antifungal agents, NSAID pain relievers, and supplements such as St. John's wort, garlic, and ginkgo.
Storage
+4°C
References
1) Fremont (2000), Biological effects of resveratrol ; Life Sci., 66 663 2) Howitz et al. (2003), Small molecule activators of sirtuins extend Saccharomyces cerevisiae lifespan; Nature, 425 191 3) Park et al. (2012), Resveratrol ameliorates aging-related metabolic phenotypes by inhibiting cAMP phosphodiesterases; Cell, 148 421
Properties of Resveratrol
| Melting point: | 253-255°C |
| Boiling point: | 449.1±14.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.359±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | Soluble in DMSO (up to 25 mg/ml) or in Ethanol (up to 20 mg/ml). |
| form | Powder |
| pka | 9.22±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | Off-white |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water (3 mg/100mL), ethanol (50 mg/mL), DMSO (16 mg/mL), DMF (~65 mg/mL), PBS (pH 7.2) (~100µg/mL), methanol, and acetone (50 mg/mL). |
| Merck | 14,8158 |
| Stability: | Stable for 2 years as supplied. Solutions in DMSO or ethanol may be stored at -20°C for up to 1 month. |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C14H12O3/c15-12-5-3-10(4-6-12)1-2-11-7-13(16)9-14(17)8-11/h1-9,15-17H/b2-1+ |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 501-36-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 1,3-Benzenediol, 5-[(1E)-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)ethenyl]- (501-36-0) |
Safety information for Resveratrol
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P337+P313:IF eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Resveratrol
| InChIKey | LUKBXSAWLPMMSZ-OWOJBTEDSA-N |
| SMILES | C1(O)=CC(/C=C/C2=CC=C(O)C=C2)=CC(O)=C1 |
Resveratrol manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Resveratrol 98%View Details
Resveratrol 98%View Details -
 Resveratrol 501-36-0 99%View Details
Resveratrol 501-36-0 99%View Details
501-36-0 -
 Resveratrol, 98%+ CAS 501-36-0View Details
Resveratrol, 98%+ CAS 501-36-0View Details
501-36-0 -
 Resveratrol CAS 501-36-0View Details
Resveratrol CAS 501-36-0View Details
501-36-0 -
 Resveratrol CAS 501-36-0View Details
Resveratrol CAS 501-36-0View Details
501-36-0 -
 Resveratrol 98% CAS 501-36-0View Details
Resveratrol 98% CAS 501-36-0View Details
501-36-0 -
 Resveratrol 98 POWDERView Details
Resveratrol 98 POWDERView Details
501-36-0 -
 Resveratrol 98 Powder, Packaging Type: Hdpe BagView Details
Resveratrol 98 Powder, Packaging Type: Hdpe BagView Details
501-36-0
