Quinoline
Synonym(s):1-Azanaphthalene;1-Benzazine;2,3-Benzopyridine;Quinoline
- CAS NO.:91-22-5
- Empirical Formula: C9H7N
- Molecular Weight: 129.16
- MDL number: MFCD00006736
- EINECS: 202-051-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:07:02
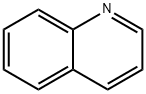
What is Quinoline?
Description
Quinoline is a colourless hygroscopic liquid with characteristic odour. On exposure
to light, it turns brown in colour. Quinoline decomposes on heating, and on burning
produces toxic fumes including nitrogen oxides. Quinoline reacts with strong oxidants,
acids, and anhydrides. Quinoline is only slightly soluble in cold water but dissolves readily
in hot water and most organic solvents. Quinoline is combustible. It gives off irritating
or toxic fumes (or gases) in a fire. Quinoline is incompatible with strong acids, oxidisers,
dinitrogen tetroxide, linseed oil, thionyl chloride, maleic anhydride, and perchromates
and reacts violently with most incompatibles. Quinoline is used extensively in the manufacturing
of dyes, preparation of hydroxyquinoline sulphate and niacin, as a solvent for
resins and terpenes, and as an intermediate in the manufacture of other products.
Quinoline is used mainly as an intermediate in the manufacture of other several products,
as a catalyst, as a corrosion inhibitor, in metallurgical processes, in the manufacture of
dyes, as a preservative for anatomical specimens, in polymers and agricultural chemicals,
and as a solvent for resins and terpenes. Quinoline is also used as an anti-malarial medicine.
Because of its solubility in water, quinoline has significant potential for mobility in the
environment, which may promote water contamination. Potential exposure to quinoline
also occurs from the inhalation of cigarette smoke. Quinoline breaks down quickly in the
atmosphere and water.
Chemical properties
colourless to brown liquid
Chemical properties
Quinoline is a colorless liquid with a penetrating amine odor. Turns brown on exposure to light.
Chemical properties
Quinoline has a heavy, penetrating and nauseating, yet sweet odor of good tenacity.
Occurrence
Quinoline was discovered in coal tar distillate in 1834 by Runge. It is released to the environment through natural combustion processes and has been isolated from air particulates (Dong et al 1977). Quinoline may be a significant aqueous byproduct of synthetic fuel production (shale oil, coal processing) and from wood preservation production and use facilities. Small amounts also have been detected in tobacco smoke (Schmeltz and Hoffmann 1977).
The Uses of Quinoline
Quinoline is used in the manufacture of dyesand hydroxyquinoline salts; as a solvent forresins and terpenes; and therapeutically as anantimalarial agent. It occurs in coal tar insmall amounts.
The Uses of Quinoline
Preserving anatomical specimens; manufac- ture of quinolinol sulfate; niacin and copper-8- quinolinolate; flavoring.
The Uses of Quinoline
Quinoline is used as an intermediate in the production of quinoline-related compounds (e.g., 8-hydroxyquinoline). Its multiple uses include solvent, preservative, flavoring agent in medicine, colorant in dyes and paints, and also a component of some fungicides. It is also a solvent for resins and terpenes and is used in the production of paint. Quinoline used as a coloring additive in foods, such as Quinoline Yellow, has increased the concern that quinoline that is found in these processes may contribute to the development of cancers later in life. Quinoline is also an antimalarial agent. Sources of quinoline include petroleum and coal processing, wood preservation, and the use of shale oil.
Definition
ChEBI: The simplest member of the quinoline class of compounds, comprising a benzene ring ortho fused to C-2 and C-3 of a pyridine ring.
Production Methods
Quinoline may be synthesized by heating aniline with glycerol and nitrobenzene in sulfuric acid (Skraup method) or by reacting aniline, acetaldehyde, and a formaldehyde hemiacetal (Windholz et al 1983). Commercial production is by isolation from coal tar with greater than 100,000 lbs being produced in 1977. Production of refined quinoline has almost ceased due to low demand (Parris et al 1983).
Definition
A colorless two-ring heterocyclic compound with an unpleasant odor, which acts as a base and forms salts with acids. First made from the alkaloid quinine, it is found in bone oil and coal tar and used for making drugs and dyestuffs.
Definition
quinoline: A hygroscopic unpleasant-smelling colourless oily liquid,C9H7N; b.p. 240°C. Its molecules consistof a benzene ring fused to a pyridinering. It occurs in coal tar andbone oil, and is made from phenylamineand nitrobenzene. Quinolineis a basic compound, forming saltswith mineral acids and forming quaternaryammonium compounds withhaloalkanes. It is used for makingmedicines and dyes. In quinoline, thenitrogen atom is one atom awayfrom the position at which the ringsare fused. In an isomer, isoquinoline,the nitrogen atom is positioned twoatoms away from the fused ring.
Aroma threshold values
Detection: 710 ppb
Taste threshold values
Taste characteristics at 2 to 10 ppm: earthy, musty, nutty, coumarinic with a chemical nuance.
Synthesis Reference(s)
Tetrahedron Letters, 29, p. 953, 1988 DOI: 10.1016/S0040-4039(00)82491-0
Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 26, p. 1015, 1978 DOI: 10.1248/cpb.26.1015
General Description
A colorless liquid with a peculiar odor. Slightly denser than water. Contact may irritate to skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. May be toxic by ingestion. Used to make other chemicals.
Air & Water Reactions
Hygroscopic. Soluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Quinoline is hygroscopic. Quinoline absorbs as much as 22% water. Quinoline is sensitive to light and moisture. Quinoline darkens on storage. Quinoline is a weak base. A potentially explosive reaction may occur with hydrogen peroxide. Quinoline reacts violently with dinitrogen tetraoxide. Quinoline also reacts violently with perchromates. Quinoline is incompatible with (linseed oil + thionyl chloride) and maleic anhydride. Quinoline is also incompatible with strong oxidizers and strong acids. Quinoline can be unpredictably violent. Quinoline dissolves sulfur, phosphorus and arsenic trioxide. Quinoline may attack some forms of plastics. Quinoline is a preparative hazard.
Health Hazard
Vapors are irritating to nose and throat and may cause headaches, dizziness, and nausea if inhaled. Ingestion causes irritation of mouth and stomach; vomiting may occur. Contact with eyes or skin causes irritation.
Health Hazard
No industrial injuries from quinoline exposure have been reported. Handling
precautions similar to those taken for pyridine are recommended (EOHS 1971).
Clinical signs of toxicity include lethargy, respiratory distress, and coma; cause
of death is respiratory paralysis.
Quinoline is a skin and eye irritant; it may cause permanent corneal injury
(EOHS 1971).
Routine occupational exposure to quinoline probably constitutes low risk for
acute toxicity. Long-term exposure to low concentrations may increase cancer
risk.
Health Hazard
There is little information in the publishedliterature on the toxic properties of quinoline.The acute toxicity is moderate in rodentsfrom oral and dermal administration. Thereported oral LD50 values in rats showinconsistent values ranging between 300 and500 mg/kg. Its irritant action was mild onrabbits’ skin and severe in the animals’ eyes.Quinoline exhibited carcinogenicity inrats and mice, causing liver cancer. There isno evidence of its carcinogenicity in humans.It tested positive to the histidine reversion–Ames test for mutagenicity.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Chemical Reactivity
Reactivity with Water No reaction; Reactivity with Common Materials: Attacks some forms of plastics; Stability During Transport: Stable; Neutralizing Agents for Acids and Caustics: Not pertinent; Polymerization: Not pertinent; Inhibitor of Polymerization: Not pertinent.
Industrial uses
Quinoline is used as a solvent for resins and terpenes. It also is used as an antimalarial, an antioxidant, a catalyst and as an intermediate in the manufacture of various products (Parris et al 1983).
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion, subcutaneous, and intraperitoneal routes. Moderately toxic by skin contact. A skin and severe eye irritant. Mutation data reported. Questionable carcinogen with experimental neoplastigenic and tumorigenic data. It can cause retinitis sdar to that caused by naphthalene but without causing opacity of the lens. Combustible when exposed to heat or flame. Its preparation has caused many industrial explosions. Potentially explosive reaction with hydrogen peroxide. Violent reaction with dmtrogen tetraoxide, perchromates. Incompatible with linseed oil + thionyl chloride, maleic anhydride, Unpredctably violent. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx.
Potential Exposure
In manufacture of quinoline deriva- tives (dyes and pesticides); in synthetic fuel manufacture. Occurs in cigarette smoke.
Carcinogenicity
Liver tumors were observed in rats administered diets containing 0.05–0.25% quinoline. The incidence of hepatocellular carcinomas was 3/11 at 0.05%, 3/16 at 0.1%, and 0/19 at 0.25% versus 0/6 in controls. At 0.25%, most of the rats died within 40 weeks. The incidences of hemangioendotheliomas were 6/11, 12/16, 18/19, and 0/6, respectively. Hepatocellular carcinomas and hemangioendotheliomas were seen in livers of rats fed 500, 1000, or 2500 ppm for 16–40 weeks. Typical hyperplasias were also observed in the liver.
Environmental Fate
biodegradative processes occur under aerobic conditions. Anaerobic degradation is minimal (Mill et al 1981). Breakdown of quinoline in natural waters has been correlated with bacterial concentration (Rogers et al 1984). Adsorption was high in acidic soils (pH<6) and low in basic soils (pH>7). The presence of pyridine decreased quinoline adsorption on acidic, but not basic, soils. Sorption did not correlate with organic carbon or clay content (Felice et al 1984). Soil bacteria have been grown with quinoline as the sole carbon source (Grant and Al-Najjar 1976). Quinoline did not bioconcentrate to a significant extent in fathead minnows (Southworth et al 1980).
Shipping
UN2656 Quinoline, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials.
Purification Methods
Dry quinoline with Na2SO4 and distil it from zinc dust in a vacuum. It has also been dried by boiling with acetic anhydride, then fractionally distilled. Calvin and Wilmarth [J Am Chem Soc 78 1301 1956] cooled redistilled quinoline in ice and added enough HCl to form its hydrochloride. Diazotization removed aniline, the diazo compound being broken down by warming the solution to 60o. Non-basic impurities were removed by ether extraction. Quinoline was then liberated by neutralising the hydrochloride with NaOH, then dried with KOH and fractionally distilled at low pressure. Addition of cuprous acetate (7g/L of quinoline) and shaking under hydrogen for 12hours at 100o removed impurities due to the nitrous acid treatment. Finally the hydrogen was pumped off, and the quinoline was distilled. Other purification procedures depend on conversion to the phosphate (m 159o, precipitated from MeOH solution, filtered, washed with MeOH, then dried at 55o) or the picrate (m 201o) which, after recrystallisation, were reconverted to quinoline. The method using the picrate [Packer et al. J Am Chem Soc 80 905 1958] is as follows: quinoline is added to picric acid dissolved in the minimum volume of 95% EtOH, giving yellow crystals which were washed with EtOH, air-dried and crystallised from acetonitrile. These were dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (previously dried over 4A molecular sieves) and passed through a basic alumina column, onto which the picric acid is adsorbed. The free base in the effluent is extracted with n-pentane and distilled under vacuum. Traces of solvent can be removed by vapour-phase chromatography. [Moonaw & Anton J Phys Chem 80 2243 1976.] The ZnCl2 and dichromate complexes have also been used [Cumper et al. J Chem Soc 1176 1962]. [Beilstein 20 H 339, 20 I 134, 20 II 222, 20 III/IV 3334, 20/7 V 276.]
Toxicity evaluation
Quinoline undergoes Phase I metabolism to form an enamine oxide, a rapid transitional epoxide, which can then form DNA adducts. This epoxide is formed on the pyridine moiety of quinoline. Fluorination at position 3 completely prevents the mutagenicity of quinoline. The major metabolic enzyme is the CYP2E1 isoform with the primary end product from this reaction being 3-hydroxyquinoline. Refer to the sections on ‘Genotoxicity’ and ‘Carcinogenicity’ for more specific descriptions of quinoline toxicity. The primary and most severe, toxic outcome following quinoline exposure is genotoxicity followed by tumor formation.
Incompatibilities
Reacts, possibly violently, with strong oxidants, strong acids; perchromates, nitrogen tetroxide; and maleic anhydride. Keep away from moisture, steam, and light. Contact with hydrogen peroxide may cause explosion. Unpredictably violent, this substance has been the source of various plant accidents.
Waste Disposal
Dissolve or mix the material with a combustible solvent and burn in a chemical incinera- tor equipped with an afterburner and scrubber. All federal, state, and local environmental regulations must be observed.
Properties of Quinoline
| Melting point: | -17--13 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 113-114 °C/11 mmHg (lit.)
237 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 1.093 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| vapor density | 4.5 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 0.07 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 214 °F |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | 6g/l |
| form | Liquid |
| pka | 4.9(at 20℃) |
| color | Purple to dark grey |
| Odor | Strong, unpleasant. |
| PH | 7.3 (5g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| explosive limit | 1.2-7%(V) |
| Water Solubility | slightly soluble |
| Sensitive | Light Sensitive & Hygroscopic |
| Merck | 14,8068 |
| BRN | 107477 |
| Dielectric constant | 2.6(-180℃) |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong acids, strong oxidizing agents. May discolour on exposure to light. Hygroscopic - protect from moisture. Reacts violently and unpredictably with some materials, especially strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 91-22-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 2B (Vol. 121) 2019 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Quinoline(91-22-5) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Quinoline (91-22-5) |
Safety information for Quinoline
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H301:Acute toxicity,oral H312:Acute toxicity,dermal H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H341:Germ cell mutagenicity H350:Carcinogenicity H411:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Quinoline
| InChIKey | SMWDFEZZVXVKRB-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Quinoline manufacturer
ARRAKIS INDUSTRIES LLP
GLR Innovations
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Quinoline High quality high purity, size packaging, large supplyView Details
Quinoline High quality high purity, size packaging, large supplyView Details
91-22-5 -
 QUINOLINE 99%View Details
QUINOLINE 99%View Details -
 Quinoline CAS 91-22-5View Details
Quinoline CAS 91-22-5View Details
91-22-5 -
 Quinoline CAS 91-22-5View Details
Quinoline CAS 91-22-5View Details
91-22-5 -
 Quinoline 98% CAS 91-22-5View Details
Quinoline 98% CAS 91-22-5View Details
91-22-5 -
 Quinoline 98%View Details
Quinoline 98%View Details -
 Quinoline CAS 91-22-5View Details
Quinoline CAS 91-22-5View Details
91-22-5 -
 Quinoline CASView Details
Quinoline CASView Details