Furan
Synonym(s):Furan;Furfuran
- CAS NO.:110-00-9
- Empirical Formula: C4H4O
- Molecular Weight: 68.07
- MDL number: MFCD00003222
- EINECS: 203-727-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
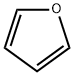
What is Furan?
Description
Furan occurs naturally in oils distilled from rosin containing pinewood. In addition, many natural foods contain the furan ring structure and substituted furans may be formed through cooking of simple carbohydrates. Furan is also found in tobacco smoke as well as wood smoke and gas emissions from gasoline and diesel engines. Furan has also been detected in industrial effluents and can be emitted to the air from petroleum refineries and coal-mining and gasification plants.
Chemical properties
Furan is a cyclic dienic ether stabilized by benzene-like resonance. Because of its conjugated unsaturation and heterocyclic atom, furan will undergo many types of reactions. It is, therefore, of interest as a chemical intermediate for pharmaceuticals, insecticides and fine chemicals. The heterocyclic oxygen atom in a ring with conjugated unsaturation gives furan a combination of ether, aromatic and olefinic characteristics. This polyfunctionality permits it to undergo a variety of reactions. Compared to benzene, the furan ring has greater reactivity, and is more susceptible to cleavage, thus resembling the vinyl ethers. Like the vinyl ethers, the furan ring is cleaved by aqueous acids. This reaction is accompanied by resinification .
Chemical properties
Furan is a colorless liquid; turns brown on standing. Strong ethereal odor.
The Uses of Furan
Furan is a valuable chemical intermediate for pharmaceuticals, insecticides, and other organic compounds. The furan ring is cleaved by aqueous acid which can lead to polymer formation.
The Uses of Furan
Furan is used as an intermediate in organicsynthesis.
The Uses of Furan
Furan is a five-membered heterocyclic aromatic ring. Furan is used as a building block for the preparation of many heterocyclic compounds.
The Uses of Furan
In organic syntheses. Furan is occasionally used in the composing of artificial essential oils. It finds a little - rare - use in industrial fragrances for certain masking purposes, e. g. when the problem is: to mask very volatile, undesirable odors. It is used in special fragrances such as “smokey” odors for certain products, directly or indirectly connected with food products.
Definition
A heterocyclic liquid organic compound. Its five-membered ring contains four carbon atoms and one oxygen atom. The structure is characteristic of some monosaccharide sugars (furanoses).
Definition
furan: A colourless liquid compound,C4H4O; r.d. 0.94; m.p. –86°C;b.p. 31.4°C. It has a five-memberedring consisting of four CH2 groupsand one oxygen atom.
Preparation
By decarboxylation of Furoic acid. Furan can also be prepared directly from Furfural.
Definition
A heterocyclic compound.
General Description
Furan is a stable, colourless chemical liquid. It is highly flammable and forms explosive mixtures with air. It is incompatible with many other chemical substances, for example, strong oxidising agents, acids, peroxides, and oxygen. Furan is produced commercially by decarbonylation of furfural. It is used mainly in the production of tetrahydrofuran, thiophene, and pyrrole. It also occurs naturally in certain woods and during the combustion of coal and is found in engine exhausts, wood smoke, and tobacco smoke.
Air & Water Reactions
Highly flammable. When uninhibited, Furan forms explosive peroxides on exposure to air. Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Furan is sensitive to heat and may turn brown upon standing. Furan may be light sensitive. When uninhibited, Furan forms explosive peroxides on exposure to air. Furan may react with oxidizers, acids, peroxides and oxygen. Furan resinifies on evaporation or when in contact with mineral acids, but Furan is stable in alkalis. .
Hazard
Flammable, dangerous fire risk, flammable limits 2–24%, forms peroxides on exposure to air. Absorbed by skin. Possible carcinogen.
Health Hazard
Furan is a highly toxic compound. Inhalationof its vapors can cause acute pulmonaryedema and lung damage. The intraperitonealLD50 value in rodents is between 5 and7 mg/kg. The inhalation LC50 value in micefor a 1-hour exposure is 120 mg/m3.
Health Hazard
The vapors are narcotic. Acute exposure to Furan by inhalation may involve both reversible and irreversible changes. Acute exposure by ingestion or skin absorption, as well as chronic exposure, are associated with high toxicity.
Fire Hazard
Very dangerous, upon exposure to heat or flame. Furan may form unstable peroxides on exposure to air. Contact with acids can initiate a violent, heat producing reaction. Avoid acids, oxidizing agents. Upon standing in air, Furan may form unstable peroxides.
Flammability and Explosibility
Extremely flammable
Safety Profile
Confirmed carcinogen. Poison by inhalation and intraperitoneal routes. Moderately toxic by ingestion and skin contact. Experimental reproductive effects. A narcotic. Mutation data reported. The exposure concentration limit of 10 ppm together with its low boiling point requires that adequate ventilation be provided in areas where ths chemical is handled. Contact with liquid must be avoided since this chemical can be absorbed through the skin. Washing thoroughly with soap and water followed by prolonged rinsing should be done immedlatelp after accidental contact. A very dangerous fire hazard when exposed to heat or flame; can react with oxidzing materials. Unstabdized, it may form unstable peroxides on exposure to air and should always be tested before ddlation. Washing with an aqueous solution of ferrous sulfate slightly acidified with sodum bisulfate will remove these peroxides. Confirm by test. Contact with acids can initiate a violent exothermic reaction. Moderate explosion hazard when exposed to flame. Furan's low bohg point makes it easy to obtain explosive concentrations of the vapor in inadequately ventilated areas. To fight fire, use CO2, dr). chemical. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes. See also PEROXIDES.
Potential Exposure
Furan is used as a chemical intermedi ate in the production of herbicides and pharmaceuticals; for making tetrahydrofuran; in formation of lacquers; as a sol vent for resins in organic synthesis, especially for pyrrole, thiophene.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and inducevomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.Medical observation is recommended for 24-48 h afterbreathing overexposure, as pulmonary edema may bedelayed. As first aid for pulmonary edema, a doctor orauthorized paramedic may consider administering a corticosteroid spray.
Carcinogenicity
Furan is reasonably anticipated to be a human carcinogen based on sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity from studies in experimental animals.
Environmental Fate
Furan may be released to the environment as a waste industrial product or from unintentional or accidental releases. If released to soil, it is expected to volatilize. If released to water, furan is not expected to adsorb to suspended particles and sediment and is likely to volatilize to ambient air. Sulfate-reducing bacteria can degrade furan. However, under nonsulfate-reducing conditions, biodegradation in soil and water is expected to be slow. In the air, furan will exist as a vapor and will be subject to degradation by reacting with hydroxyl radicals.
storage
Color Code—Red: Flammability Hazard: Store ina flammable liquid storage area or approved cabinet awayfrom ignition sources and corrosive and reactive materials.Prior to working with this chemical you should be trainedon its proper handling and storage. Before entering confinedspace where this chemical may be present, check to makesure that an explosive concentration does not exist. Store inan explosion-proof refrigerator. Keep in a tightly closedcontainer under an inert atmosphere and protect from lightfor long-term storage. A regulated, marked area should beestablished where this chemical is handled, used, or storedin compliance with OSHA Standard 1910.1045.
Shipping
UN2389 Furan, Hazard Class: 3; Labels: 3-Flammable liquid.
Purification Methods
Shake it with aqueous 5% KOH, dry it with CaSO4 or Na2SO4, then distil it under nitrogen, from KOH or sodium, immediately before use. A trace of hydroquinone could be added as an inhibitor of oxidation. [Beilstein 17 H 27, 17 I 16, 17 II 34, 17/1 V 291.]
Toxicity evaluation
Furan can cause eye, skin, and mucus membrane irritation,
burning sensation and, in severe cases, corrosion. If inhaled,
furan may produce pulmonary edema and bronchiolar
necrosis. When absorbed, furan can cause central nervous
system (CNS) depression to the point of narcosis and tonic
seizures.
Furan is metabolized by the cytochrome P450 enzymes
in the liver and other tissues. Furan is metabolized to cis-2-
butene-1,4-dial. This active metabolite is acutely toxic to
liver cells. The furan ring undergoes oxidative cleavage and
forms highly reactive furan radical cations or epoxides,
which react directly with cellular nucleophiles. These reactive
metabolites may react directly with deoxyribonucleic acid
(DNA) or with cellular proteins to produce disruption of
cellular functions and cell death. Chronic cell death and
regeneration produced by chronic furan exposure may be
a significant factor in the carcinogenicity potential of the
chemical. In addition, there is some evidence to suggest that
the reactive metabolites of furan may induce mutations in
cellular genes.
Incompatibilities
May form explosive mixture with air. Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong acids, amines, strong bases, reducing agents. Unless stabilized with an inhibitor, air exposure forms unstable peroxides.
Waste Disposal
Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform with EPA regulations govern ing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal.
Properties of Furan
| Melting point: | -85.6 °C |
| Boiling point: | 67 °C10 mm Hg(lit.) |
| Density | 0.936 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor density | 2.35 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 1672 mm Hg ( 55 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 160 °F |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | alcohols: freely soluble |
| form | Liquid |
| color | Clear colorless to yellow |
| Specific Gravity | 0.94 |
| Odor | Peculiar spicy -smokey, slightly Cinnamon-like odor |
| explosive limit | 2.3-14.3%(V) |
| Odor Threshold | 9.9ppm |
| Water Solubility | insoluble |
| Sensitive | Air & Light Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,4296 |
| BRN | 103221 |
| Dielectric constant | 3.0(25℃) |
| Exposure limits | NIOSH: IDLH 13 ppm |
| Stability: | Stable. Substances to be avoided include strong oxidising agents, acids, peroxides and oxygen. Highly flammable; can form explosive mixtures with air. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 110-00-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Furan(110-00-9) |
| IARC | 2B (Vol. 63) 1995 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Furan (110-00-9) |
Safety information for Furan
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H224:Flammable liquids H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H341:Germ cell mutagenicity H350:Carcinogenicity H373:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H412:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P233:Keep container tightly closed. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. P403+P233:Store in a well-ventilated place. Keep container tightly closed. |
Computed Descriptors for Furan
| InChIKey | YLQBMQCUIZJEEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Furan manufacturer
New Products
3-Iodophenylacetic acid 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 3-(hexyloxy)-4-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,2,5-thiadiazole 2-Hexyn-1-ol Dibenzo-18-crown-6 Nickel(II) perchlorate hexahydrate, 98% 4-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 95% 3-Bromo-4-fluoroaniline, 97% Sodium tetraborate decahydrate, 98% Palladium(II) acetate, trimer, Pd 99% 4-Bromo-2-chlorotoluene, 97% N N Dimethylformamide Dimethyl Acetal (Dmf Dma) 2,3-Dichloro Benzoyl Cyanide [Side Chain] Bis(2-Chloroethyl) Amine Hydrochloride L-Glutamic Acid Diethyl Ester Hydrochloride 5-(Difluoromethoxy)-2-Mercaptobenzimidazole 1-Ethyl-3-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-Carbodiimide Hydrochloride [EDC Hcl] 1,4-Napthoquinone Bromoiodomethane Sodium Bicarbonate Methylene Dichloride (MDC) Ethyl Acetate Indole-3-Carbinol (I3C)Related products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Furan, 95% 110-00-9 99%View Details
Furan, 95% 110-00-9 99%View Details
110-00-9 -
 Furan CAS 110-00-9View Details
Furan CAS 110-00-9View Details
110-00-9 -
 Furan CAS 110-00-9View Details
Furan CAS 110-00-9View Details
110-00-9 -
 Furan 98% CAS 110-00-9View Details
Furan 98% CAS 110-00-9View Details
110-00-9 -
 Furan CAS 110-00-9View Details
Furan CAS 110-00-9View Details
110-00-9 -
 Furan (stabilized with BHT) CAS 110-00-9View Details
Furan (stabilized with BHT) CAS 110-00-9View Details
110-00-9 -
 Furan CAS 110-00-9View Details
Furan CAS 110-00-9View Details
110-00-9 -
 Furan CAS 110-00-9View Details
Furan CAS 110-00-9View Details
110-00-9
