Isoquinoline
- CAS NO.:119-65-3
- Empirical Formula: C9H7N
- Molecular Weight: 129.16
- MDL number: MFCD00006898
- EINECS: 204-341-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-08-26 17:33:40
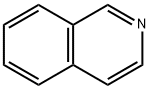
What is Isoquinoline?
Description
Isoquinoline, also known as 2-azanaphthalene, benzo[c]pyridine, or 2-benzanine, is a structural isomer of quinoline. It has structural and spectroscopic properties similar to quinoline. Isoquinoline was first isolated in 1885 by Hoogewerf and van Dorp from the quinoline fraction of coal tar by fractional crystallization. It is used to prepare dyes, insecticides, and antimalarial compounds, among other things.
Chemical properties
Isoquinoline is a colorless hygroscopic liquid at temperatures above its melting point with a heavy sweet balsamic, herbaceous odor. Impure samples can appear brownish, as is typical for nitrogen heterocycles. Isoquinoline is a slightly stronger base than quinoline (pKa=5.14) and has a larger dipole of 2.60D.
The Uses of Isoquinoline
Isoquinolines are used in the manufacture of dyes, paints, insecticides and antifungals. It is also used as a solvent for the extraction of resins and terpenes, and as a corrosion inhibitor.
Isoquinoline (isq) has been used:
in the preparation of cis-[(dcbH2)2Ru(isq)2](ClO4)2 [dcbH2 = 4,4′-(CO2H)2-2,2′-bipyridine].
to investigate the toxicity of three two-ring and five three-ring azaarenes to the green alga Scenedesmus acuminatus and its relationship with molecular structure.
Definition
ChEBI: Isoquinoline is an ortho-fused heteroarene that is a benzopyridine in which the N atom not directly attached to the benzene ring. It is a mancude organic heterobicyclic parent, an azaarene, an ortho-fused heteroarene and a member of isoquinolines.
Preparation
Bischler-Napieralski synthesis is used to synthesize isoquinolines. β-phenylethylamine is acylated, and then cyclodehydrated using phosphoryl chloride, phosphorus pentoxide or other Lewis acids to yield dihydroisoquinoline, which can be aromatized by dehydrogenation with palladium, for example in the synthesis of papaverine, a pharmacologically active isoquinoline alkaloid.
Pictet-Spengler synthesis is another method of preparing isoquinolines. β-phenylethylamine reacts with an aldehyde to produce an imine, which undergoes acid-catalysed cyclization, resulting in the synthesis of the tetrahydroisoquinoline system. Again, tetrahydroisoquinoline can be aromatized by palladium dehydrogenation to produce an isoquinoline system.
Production Methods
High-temperature coal tar contains an average of 0.2% isoquinoline. It is separated by distillation from the lower-boiling quinoline and the higherboiling 2-methylquinoline of the quinoline base mixture. Further refining is based on the fact that isoquinoline, in contrast to quinoline and 2-methylquinoline, cannot be hydrated but can be crystallized at low temperature.
Isoquinoline can by synthesized, for example, via the Bischler–Napieralski reaction by cyclodehydration of N-acyl derivatives of b-phenylethylamine with Lewis acids and subsequent dehydrogenation.
Synthesis Reference(s)
The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 29, p. 2240, 1964 DOI: 10.1021/jo01031a031
Synthesis, p. 288, 1974
General Description
Isoquinoline is one of the very few heterocyclic compounds in which numbering of the ring atoms does not start on the hetero atom.It consists of a benzene ring fused to the β- and Y-positions of a pyridine ring.
Isoquinoline has an odor reminiscent of benzaldehyde and anise. Isoquinoline may be obtained from coal tar (238 - 250°C boiling fraction); it is isolated as the sulfate or as is by repeated freezing.
Health Hazard
The toxic properties of this compound aresimilar to those of quinoline. It is moderatelytoxic in rats and rabbits by oral routeand skin absorption. The oral LD50 value inrats is 360 mg/kg. The irritation effects onskin and eyes in rabbits were moderate tosevere. Carcinogenicity due to isoquinolinein animals or humans is not known. The histidinereversion–Ames test for mutagenicitywas inconclusive.
Chemical Reactivity
Isoquinoline is aromatic with a resonance energy of 143 kJ/ mol and is considered to be a resonance hybrid of the following contributing structures. Structures I, II, and II, which are of lower energy, are the major contributors to the resonance hybrid. Additional charged structures IV-VIII are also possible, but there is disruption of the π system of both rings in these structures.
1. Reaction with bases: Strong bases like Grignard reagent and organolithium tend to react like nucleophiles with isoquinoline. There are examples where isoquinoline has been converted into Grignard reagent by treatment with (iPr)2NMgCl, which has been shown to add to the variety of iodobenzenes.
2. Reaction with acids: Isoquinoline being basic reacts with acids to form salts. Protonation usually takes place under strong acidic conditions at position 5. When isoquinoline is exposed to strong acidic conditions, reduction of the benzene ring takes place.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Medicinal Uses of Isoquinoline
Isoquinoline is important because this nucleus is present in a large number of alkaloids like berberine and papavarine, and is also a useful template for medicinal chemistry. Papaverine, an opium alkaloid, finds use as a muscle relaxant and a vasodilator. Antihypertensive drugs like debrisoquine, quinalapril, and quinalaprilat all contain an isoquinoline nucleus. Quinisocaine or dimethisoquin is a topical anesthetic, which finds use as an antipruritic. Hexadecamethylenedisoquinolium dichloride, which is used as a topical antiseptic, is prepared by Nalkylation of isoquinoline with an appropriate allkyl halide.
Synthesis
Isoquinoline is synthesized by isolation from coal tar. It represents 10% of the total Quinoline fraction.
Solubility in organics
Miscible with alcohol and oils
Purification Methods
Dry isoquinoline with Linde type 5A molecular sieves or Na2SO4 and fractionally distil at reduced pressure. Alternatively, it can be refluxed with, and distilled from, BaO. It is also purified by fractional crystallisation from the melt and distilled from zinc dust. It forms a phosphate (m 135o) and a picrate (m 223o), which are purified by crystallisation, and the free base can be recovered and distilled. [Packer et al. J Am Chem Soc 80 905 1958.] The procedure for purification via the picrate comprises the addition of quinoline to picric acid dissolved in the minimum volume of 95% EtOH to yield yellow crystals which are washed with EtOH and air dried before recrystallising from acetonitrile. The crystals are dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (previously dried over 4A molecular sieves) and passed through a basic alumina column, on which picric acid is adsorbed. The free base in the effluent is extracted with n-pentane and distilled under vacuum. Traces of solvent from small quantities are removed by vapour phase chromatography. The hydrochloride crystallises from EtOH with m 193o. [Mooman & Anton J Phys Chem 80 2243 1976, Beilstein 20 II 236, 20 III/IV 3410, 20/7 V 333.]
Properties of Isoquinoline
| Melting point: | 26-28 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 242-243 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 1.099 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| vapor pressure | 5Pa at 20℃ |
| FEMA | 2978 | ISOQUINOLINE |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 225 °F |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | 5g/l |
| form | Low Melting Solid |
| pka | 5.42(at 20℃) |
| color | Light brown |
| PH | 7.5 (5g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| Odor | at 0.10 % in triacetin. sweet balsam herbal benzaldehyde anise |
| Water Solubility | practically insoluble |
| Merck | 14,5222 |
| JECFA Number | 1303 |
| BRN | 107549 |
| Dielectric constant | 10.7(20℃) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 119-65-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Isoquinoline(119-65-3) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Isoquinoline (119-65-3) |
Safety information for Isoquinoline
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H311:Acute toxicity,dermal H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H412:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Isoquinoline
| InChIKey | AWJUIBRHMBBTKR-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Isoquinoline manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 119-65-3 98%View Details
119-65-3 98%View Details
119-65-3 -
 Isoquinoline 98%View Details
Isoquinoline 98%View Details -
 Isoquinoline, 96% 99%View Details
Isoquinoline, 96% 99%View Details
119-65-3 -
 Isoquinoline CAS 119-65-3View Details
Isoquinoline CAS 119-65-3View Details
119-65-3 -
 Isoquinoline 97% CAS 119-65-3View Details
Isoquinoline 97% CAS 119-65-3View Details
119-65-3 -
 Isoquinoline, tech, 95% CAS 119-65-3View Details
Isoquinoline, tech, 95% CAS 119-65-3View Details
119-65-3 -
 Isoquinoline, 97% CAS 119-65-3View Details
Isoquinoline, 97% CAS 119-65-3View Details
119-65-3 -
 Isoquinoline CAS 119-65-3View Details
Isoquinoline CAS 119-65-3View Details
119-65-3
