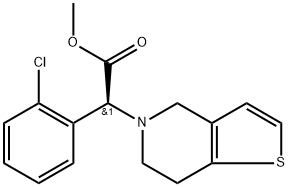
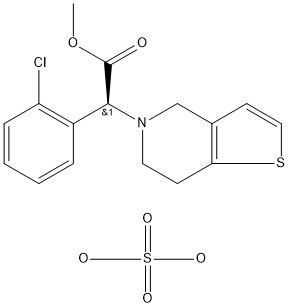
Prasugrel
Synonym(s):5-[2-Cyclopropyl-1-(2-fluorophenyl)-2-oxoethyl]-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridin-2-yl acetate;Effient;Efient;
- CAS NO.:150322-43-3
- Empirical Formula: C20H20FNO3S
- Molecular Weight: 373.44
- MDL number: MFCD09954140
- EINECS: 801-962-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-22 18:23:36
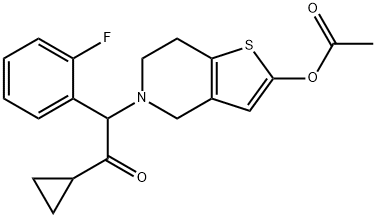
What is Prasugrel?
Absorption
79% or greater of the dose is absorbed after oral administration. Absorption and metabolism occur rapidly and peak plasma concentrations (Cmax) are reached approximately 30 minutes following oral administration. Administration with a high fat, high calorie meal did not affect the AUC of the active metabolite in healthy individuals, but the Cmax was decreased by ~49% and the Tmax was increased to 0.5 to 1.5 hours. Prasugrel may be administered with or without food.
Toxicity
LD50 (rat) 1,000 - 2,000 mg/kg; LD50 (rabbit) > 1,000 mg/kg
Description
Prasugrel is a third-generation thienopyridine that has been developed and launched for the prevention of atherothrombotic events in patients with ACS or following PCI. While the second-generation agent clopidogrel was an improvement over the first-generation ticlopidine, which suffered from gastrointestinal adverse effects and the risk of neutropenia with prolonged use, its delayed onset of action and considerable interpatient variability prompted the search for the next-generation thienopyridine. The mechanism of action of these platelet inhibitors involves initial biological activation to a sulfhydryl metabolite that irreversibly binds to the P2γ12 receptor on platelets via disulfide formation, thereby preventing platelet activation and aggregation by the endogenous agonist adenosine diphosphate (ADP). The advantage of prasugrel over its predecessors is its more efficient and consistent absorption and rapid conversion to its active metabolite. Co-administration of thienopyridines with acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin), an inhibitor of the synthesis of the platelet aggregation mediator thromboxane A2, is an effective antiplatelet strategy and joins antagonists of glycoprotein IIb/IIIa, which target the final step in platelet aggregation, in the medical arsenal combating atherothrombotic events.
Originator
Daiichi Sankyo (Japan)
The Uses of Prasugrel
Inhibits platelet aggregation (platelet ADPP 2Y12 antagonist).
The Uses of Prasugrel
Prasugrel is a platelet inhibitor that reduces aggregation of platelets by being a P2Y12(ADP receptor) inhibitor.
Definition
ChEBI: 5-[2-cyclopropyl-1-(2-fluorophenyl)-2-oxoethyl]-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridin-2-yl acetate is a member of the class of thienopyridines that is 2-acetoxy-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine in which the amino hydrogen is replaced by a 2-cyclopropyl-1-(2-fluorophenyl)-2-oxoethyl group. It is an acetate ester, a member of cyclopropanes, a ketone, a member of monofluorobenzenes, a tertiary amino compound and a thienopyridine.
What are the applications of Application
Prasugrel is a platelet inhibitor that reduces aggregation of platelets by being a P2Y12(ADP receptor) inhibitor
Background
Prasugrel, a thienopyridine derivative, is a platelet activation and aggregation inhibitor structurally and pharmacologically related to clopidogrel and ticlopidine. Similar to clopidogrel, prasugrel is a prodrug that requires enzymatic transformation in the liver to its active metabolite, R-138727. R-138727 irreversibly binds to P2Y12 type ADP receptors on platelets thus preventing activation of the GPIIb/IIIa receptor complex. As a result, inhibition of ADP-mediated platelet activation and aggregation occurs. Prasugrel was developed by Daiichi Sankyo Co. and is currently marketed in the United States and Canada in cooperation with Eli Lilly and Company for acute coronary syndromes planned for percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). FDA approved in 2009.
Indications
Indicated in combination with acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) to prevent atherothrombotic events in patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) who are to be managed with percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). May be used in patients with unstable angina (UA), non-ST elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI), ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) who are to be managed with PCI. Prasugrel is not recommended in patients 75 years of age or greater, those that weigh<60kg, and patients with a history of stroke or transient ischemic attack due to increased risk of fatal and intracranial bleeding.
brand name
Effient
Pharmacokinetics
Prasugrel is a thienopyridine ADP receptor inhibitors which inhibits platelet aggregation by irreversibly binding to P2Y12 receptors.
Clinical Use
Prasugrel is a platelet inhibitor developed by Daiichi Sankyo Co. and is marketed in the United States in cooperation with Eli Lilly and Company for acute coronary syndromes planned for percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). Prasugrel was approved for use in Europe in February 2009, and is currently available in the UK. In the U.S. prasugrel is also approved for the reduction of thrombotic cardiovascular events, including stent thrombosis, in patients with acute coronary syndrome who are to be managed with PCI. Prasugrel is a member of the thienopyridine class of ADP receptor inhibitors, and irreversibly binds to P2Y12 receptors.
Side Effects
In addition to the hemorrhagic side effect, other serious adverse events included AF, bradycardia, leucopenia, severe thrombocytopenia, angiodema, anemia, and abnormal hepatic function with hypertension, headache, back pain, dyspnea, nausea, dizziness, and diarrhea as less severe complaints. Prasugrel is contraindicated in patients with active pathological bleeding, such as peptic ulcers or intracranial hemorrhage, and in patients with a history of prior transient ischemic attack or stroke. In addition, in patients 75 years old, <60 kg, or likely to undergo urgent coronary artery bypass graft surgery, the risk may not outweigh the benefit. When possible, prasugrel treatment should be discontinued at least 7 days prior to any surgery. While warfarin and non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDS) may increase the risk of bleeding with coadministration of prasugrel, no drug interactions are anticipated with concomitant use of drugs that are inducers or inhibitors of the cytochrome P450 enzymes. Prasugrel may also be administered with aspirin (75-325 mg per day), heparin, GP IIb/IIIa inhibitors, statins, digoxin, and drugs that elevate gastric pH, including PPIs and H2 blockers.
Synthesis
The synthesis of prasugrel begins with the preparation of the a-ketocyclopropane 102 which is prepared as summarized in the scheme. Conversion of 1-(bromomethyl)-2-fluorobenzene (99) to the corresponding Grignard reagent through reaction with magnesium followed by condensation with nitrile 100 resulted in ketone 101 in 72% yield. Chlorination of ketone 101 with CuCl2 resulted in the key prasugrel coupling component 102 in 92% yield. The piperidine coupling partner was prepared by treating thiolactone 103 with TBDMSCl and triethylamine to give thiophene 104 in 91% yield. Treatment of piperidine 104 with a-chloroketone 102 resulted in enol silane 105 in 65% yield. Reaction of silylenol ether 105 with acetic anhydride in the presence of triethylamine and catalytic DMAP resulted in the preparation of prasugrel (XVII) in 60% yield.

Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Anticoagulants: enhanced anticoagulant effect with
coumarins and phenindione.
Metabolism
Prasugrel is a prodrug and is rapidly metabolised in the liver by various cytochrome P450 enzymes to an active metabolite and inactive metabolites. The active metabolite is further metabolised to 2 inactive compounds which are excreted in the urine and faeces; about 68% of a dose is excreted in urine and about 27% in faeces.
Metabolism
Prasugrel is not detected in plasma following oral administration. It is rapidly hydrolyzed in the intestine to thiolactone by human carboxylesterase (hCE) 2. This intermediate is further metabolized to its active metabolite, R-138727, in a single step by cytochrome P450 enzymes in the liver (primarily CYP3A4 and CYP2B6 and to a lesser extent by CYP2C9 and CYP2C19). The active metabolite is further metabolized by S-methylation or cysteine conjugation to two inactive metabolites.
Unlike clopidogrel, transformation of prasugrel to its active metabolite does not appear to be affected by cytochrome P450 polymorphisms.
Storage
Store at +4°C
Properties of Prasugrel
| Melting point: | 120.0 to 124.0 °C |
| Boiling point: | 493.5±45.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.347 |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO: >5mg/mL (warmed at 60 °C) |
| form | powder |
| pka | 3.65±0.20(Predicted) |
| color | white to beige |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 150322-43-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Prasugrel
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Prasugrel
| InChIKey | DTGLZDAWLRGWQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Prasugrel manufacturer
ALS India Life Sciences Pvt. Ltd
Kavya Pharma
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 150322-43-3 prasugrel base 98%View Details
150322-43-3 prasugrel base 98%View Details
150322-43-3 -
 Prasugrel 98% CAS 150322-43-3View Details
Prasugrel 98% CAS 150322-43-3View Details
150322-43-3 -
 Prasugrel CAS 150322-43-3View Details
Prasugrel CAS 150322-43-3View Details
150322-43-3 -
 Prasugrel 98% (HPLC) CAS 150322-43-3View Details
Prasugrel 98% (HPLC) CAS 150322-43-3View Details
150322-43-3 -
 Prasugrel for system suitability CAS 150322-43-3View Details
Prasugrel for system suitability CAS 150322-43-3View Details
150322-43-3 -
 Prasugrel CAS 150322-43-3View Details
Prasugrel CAS 150322-43-3View Details
150322-43-3 -
 150322-43-3 Prasugrel 95.00%View Details
150322-43-3 Prasugrel 95.00%View Details
150322-43-3 -
 Prasugrel ip/bp/usp cas 150322-43-3View Details
Prasugrel ip/bp/usp cas 150322-43-3View Details
150322-43-3