Pizotifen
Synonym(s):Pizotifen;Pizotyline; 4-(9,10-Dihydro-4H-benzo[4,5]cyclohepta[1,2-b]thien-4-ylidene)-1-methylpiperidine
- CAS NO.:15574-96-6
- Empirical Formula: C19H21NS
- Molecular Weight: 295.44
- MDL number: MFCD00864192
- EINECS: 239-632-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-17 08:48:38
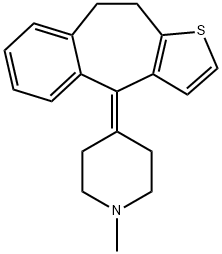
What is Pizotifen?
Absorption
The absorption half-life of pizotifen following oral administration is 0.5 to 0.8 hours in an adult male with nearly complete absorption rate of 80%. Maximum blood levels are reached 5 hours post-administration and the absolute bioavailability is 78% .
Toxicity
The oral Lowest published toxic dose (TDLo) is 12.86 mg/kg in man . Oral LD50 ranges from 410 to 1500 mg/kg in rat . Oral LD50 in mouse and rabbit is 880 mg/kg and 700 mg/kg, respectively . The LD50 following intravenous administration in rat was 17 mg/kg .
In adults, the symptoms of overdosage include sedation, drowsiness (preceding excitement, convulsions, and postictal depression), dizziness, hypotension, dryness of the mouth, confusion, tachycardia, ataxia, nausea, vomiting, dyspnea, cyanosis, convulsions, coma, respiratory paralysis and CNS depression . Antihistamine toxicity of pizotifen in children may involve excitation, hallucinations, ataxia, incoordination, convulsions, fixed dilated pupils, flushed faces, and fever, leading to coma and cardiorespiratory collapse . The use of activated charcoal is recommended in the management of overdose. For drug recent uptake, induction of emesis or gastric lavage and diuresis should be performed . Supportive measures should be initiated to maintain effective respiration while closely monitoring vital signs. While severe hypotension must be corrected, the use of adrenaline may produce paradoxical effects .
As pizotifen has the potential to cause tachycardia, an ECG should be performed and attention directed at the QRS and QT intervals . Excitatory states or convulsions induced by pizotifen may be treated with short-acting barbiturates or benzodiazepines. However analeptics should be avoided .
Chemical properties
White to Off-White Solid
Originator
Sandomigran ,Sandoz ,Italy ,1972
The Uses of Pizotifen
Serotonin antagonist structurally related to Cyproheptadine. Antimigraine; appetite stimulant.
The Uses of Pizotifen
benzocycloheptane based drug
Background
Pizotifen belongs to the class of antamines and is related to cyproheptadine. It is a potent serotonin and tryptamine antagonist that has been used for migraine prevention for many years. It exhibits weak anticholinergic, antihistamine, and antikinin actions in addition to sedative and appetite-stimulating properties . Some patients receiving pizotifen treatment developed tolerance with the prolonged use of the drug . Numerous studies have revealed the potential antidepressant effects of pizotifen, which are independent of its antimigraine action . While it is suggested that pizotifen may act similarly to the classic tricyclic antidepressants , its full mechanism of antidepressant action is not fully elucidated. Pizotifen hydrochloride is an active ingredient in Sandomigran, which is used for the prophylactic management of migraines. Sandomigran is available in a number of countries but is not approved by the FDA nor EMA.
Indications
Indicated for the prophylactic management of migraines .
What are the applications of Application
Pizotifen is a serotonin antagonist acting at the 5-HT1, 5-HT2A and 5HT2C receptors
Definition
ChEBI: A benzocycloheptathiophene that is 9,10-dihydro-4H-benzo[4,5]cyclohepta[1,2-b]thiophene 4-ylidene)-1-methylpiperidine which is joined from the 4 position to the 4 position of an N-methylpiperidine moiety b a double bond. It is a sedating antihistamine, with strong serotonin antagonist and weak antimuscarinic activity. It is generally used as the malate salt for the treatment of migraine and the prevention of headache attacks during cluster periods.
Indications
Pizotifen, a potent antihistamine and antiserotonin agent usually prescribed for migraine prophylaxis, has had reported success in patients with polycythemia vera.
Manufacturing Process
(A) Preparation of Thenylidene-(2)-Phthalide: 24.2 g of thienyl-(2)-acetic acid, 52.0 g of phthalic acid anhydride, 4.0 g of anhydrous sodium acetate and 125 ml of 1-methylpyrrolidone-(2) are heated while stirring in an open flask for 3 hours to 205° to 208°C, while nitrogen is passed through. It is then cooled and the viscous reaction mixture poured into 1 liter of water. The precipitated substance is filtered off, washed with water and then dissolved in 200 ml of chloroform. After filtering off some undissolved substance, shaking is effected twice with 100 ml of 2 N sodium carbonate solution and then with water, drying is then carried out over sodium sulfate and the volume is reduced by evaporation. The crude phthalide is repeatedly recrystallized from ethanol, while treating with animal charcoal. It melts at 114° to 115°C.
(B) Preparation of o-[2-Thienyl-(2')-Ethyl]Benzoic Acid: 24.0 g of thenylidene(2)-phthalide, 8.8 g of red pulverized phosphorus, 240 ml of hydrochloric acid (d = 1.7) and 240 ml of glacial acetic acid are heated to boiling under nitrogen and while stirring vigorously. 70 ml toluene are then added and 6.0 g of red phosphorus added in small portions over a period of 1 hour. It is then poured into 3 liters of ice water, stirred with 300 ml of chloroform and the phosphorus removed by filtration.
The chloroform phase is then removed, the aqueous phase extracted twice more with 200 ml of chloroform and the united extracts shaken out 4 times,each time with 200 ml of 2 N sodium hydroxide solution. The alkaline solution is then rendered acid to Congo red reagent, using hydrochloric acid and extracted 3 times with chloroform. After drying over sodium sulfate and evaporating the solvent, the residue is chromatographed on aluminum oxide (Activity Stage V). The substance eluted with benzene and benzene/chloroform (1:1) is recrystallized from chloroform/hexane (1:1); MP 107° to 109°C.
(C) Preparation of 9,10-Dihydro-4H-Benzo[4,5]Cyclohepta[1,2-b]Thiophen(4)-One: 200 ml of 85% phosphoric acid and 112 g of phosphorus pentoxide are heated to 135°C. 7.0 g of o-[2-thienyl-(2')-ethyl]benzoic acid are then introduced while stirring thoroughly over a period of 30 min. Stirring is then continued for another hour at 135°C and the reaction mixture is then stirred into 1 liter of ice water. Extraction is then effected 3 times, using 250 ml ether portions, the ethereal extract is washed with 2 N sodium carbonate solution, dried over sodium sulfate and reduced in volume by evaporation. The residue is boiled up with 55 ml of ethanol, the solution freed of resin by decanting and then stirred at room temperature for 6 hours with animal charcoal. It is then filtered off, reduced in volume in a vacuum and the residue distilled. BP 120° to 124°C/0.005 mm, nD24.5 = 1.6559.
(D) Preparation of 4-[1'-Methyl-Piperidyl-(4')]-9,10-Dihydro-4HBenzo[4,5]Cyclohepta[1,2b]Thiophen-(4)-ol: 0.94 g of magnesium filings which have been activated with iodine are covered with a layer of absolute tetrahydrofuran and etched with a few drops of ethylene bromide. A solution of 5.0 g of 1-methyl-4-chloropiperidine in 5 ml of tetrahydrofuran is then added dropwise and boiling then effected for a further hour under reflux. After cooling to room temperature, the solution of 4.5 g of 9,10-dihydro-4Hbenzo[4,5]cyclohepta[1,2-b]thiophen-(4)-one in 5 ml of tetrahydrofuran is added dropwise.
Stirring is carried out first for 3 hours at room temperature and then for 2 hours at boiling temperature, it is then cooled and poured into 300 ml of icecold 20% ammonium chloride solution. It is then shaken out with methylene chloride, the methylene chloride solution washed with water and shaken 3 times with 30 ml portions of aqueous 2 N tartaric acid solution. The tartaric acid extract is rendered alkaline while cooling thoroughly and then extracted twice with methylene chloride. After washing with water, drying over potassium carbonate and reducing in volume by evaporation, the residue is recrystallized from ethanol. MP 197° to 199°C.
(E) Preparation of 4-[1'-Methyl-Piperidylidene-(4')]-9,10-Dihydro-4HBenzo[4,5]Cyclohepta[1,2-b]Thiophene Hydrochloride: 2 g of 4-[1'-methylpiperidyl-(4')]-9,10-dihydro4H-benzo[4,5]cyclohepta[1,2-b]thiophen-(4)-ol, 60 ml of glacial acetic acid and 20 ml of concentrated hydrochloric acid are boiled for 30 minutes under reflux. After evaporating in a vacuum, the residue is triturated with 3 ml of acetone, the precipitated hydrochloride is then filtered off and it is recrystallized from isopropanol/ether. MP 261° to 263°C (decomposition).
brand name
Sandomigran (Novartis).
Therapeutic Function
Migraine therapy
Biochem/physiol Actions
Pizotifen is a serotonin antagonist acting mainly at the 5-HT1, 5-HT2A and 5HT2C receptors with some antihistamine activity. It is used for the prevention of vascular headache including migraine and cluster headache.
Pharmacokinetics
Various studies have shown pizotifen to be effective in the prophylaxis of migraines in reducing the frequency and severity of vascular headaches . Evidence from studies in vivo and in vitro demonstrate antagonistic actions towards serotonin and histamine. Pizotifen blocks the postsynaptic 5-HT2 receptors, as supported by antagonism of several direct agonists of 5-HT receptors . It is an antagonist at histamine H1 receptors, and is weakly anticholinergic . It also binds to α1- and α2-adrenergic receptors, and dopamine receptors . Pizotifen elicits a minimal effect as an epinephrine or bradykinin antagonist . Pizotifen exhibits weak sedative properties in mouse and monkey studies, as indicated by inhibition of locomotion and potentiation of barbiturates, without changes in cardiac or respiratory rates . In dogs, intravenous administration of pizotifen cause rapid hypotension but was reversed to normal within 30 minutes . Pizotifen was shown to inhibit serotonin uptake in the isolated perfused cat spleen and, in vivo, inhibits serotonin-induced contractions in rat uterus and cat nictiating membrane . In contrast, pizotifen demonstrated a venoconstrictor activity in vivo when orally or intravenously administered to saphenous veins in conscious dogs . Pizotifen has the potential to stimulate the appetite and may cause weight gain upon treatment .
In a double-blind clinical study of patients with mild to moderate depression, treatment of pizotifen led to clinical improvement of the depressive symptoms. However, deterioration of the schizophrenic emotional symptoms was also observed in patients with depression and chronic schizophrenia . This indicates that pizotifen may potentially improve the symptoms of patients with depressions in conjunction with migraines .
Neuroprotective effect of pizotifen was investigated in vitro in a mouse cell model of Huntington's disease (HD). According to a chemical screen of a mouse HdhQ111/Q111 striatal cell model of HD, treatment of pizotifen was associated with increased ATP levels and decreased activation of caspase-3, leading to enhanced cell viability . Transient activation of ERK signalling pathway lasting for less than 3 hours was also observed. In the R6/2 transgenic mouse model of HD, rotarod performance of the mouse treated with pizotifen was seen, accompanied by an increase in DARPP-32 protein expression and restoration of striatal area . However these effects being reflected in vivo are not established.
Clinical Use
Prophylactic treatment of vascular headaches including migraine
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Adrenergic neurone blockers: pizotifen antagonises
hypotensive effect.
Metabolism
Pizotifen is extensively metabolized in the liver, where it primarily undergoes N-glucuronidation to form the main metabolite, N-glucuronide conjugate . N-glucuronide conjugate accounts for at least 50% of the plasma and 60-70% of the urinary-excreted radioactivity .
Metabolism
Pizotifen undergoes extensive metabolism.
Over half of a dose is excreted in the urine, chiefly as
metabolites; a significant proportion is excreted in the
faeces.
Properties of Pizotifen
| Melting point: | 140-142°C |
| Boiling point: | 436.7±45.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.164±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | room temp |
| solubility | DMSO: ≥8mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| pka | pKa 6.95 (Uncertain) |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Merck | 14,7515 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 15574-96-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Pizotyline(15574-96-6) |
Safety information for Pizotifen
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H361:Reproductive toxicity |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Pizotifen
New Products
4-Fluorophenylacetic acid 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate (6-METHYL-[1,3]DITHIOLO[4,5-b]QUINOXALIN-2-ONE INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![Benzo[b]thien-2-ylboronic acid](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/98437-23-1.gif)

You may like
-
 Pizotifen CAS 15574-96-6View Details
Pizotifen CAS 15574-96-6View Details
15574-96-6 -
 Pizotifen 95% CAS 15574-96-6View Details
Pizotifen 95% CAS 15574-96-6View Details
15574-96-6 -
 Pizotifen CAS 15574-96-6View Details
Pizotifen CAS 15574-96-6View Details
15574-96-6 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1