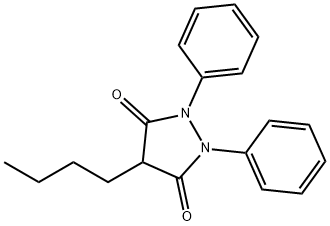
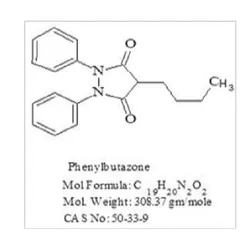
Phenylbutazone
Synonym(s):4-Butyl-1,2-diphenyl-3,5-pyrazolidinedione;Phenylbutazone
- CAS NO.:50-33-9
- Empirical Formula: C19H20N2O2
- Molecular Weight: 308.37
- MDL number: MFCD00005500
- EINECS: 200-029-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-16 16:15:04
What is Phenylbutazone?
Toxicity
Oral, LD50 = 238 mg/kg (mouse); Oral, LD50 = 781 mg/kg (rabbit); Oral, LD50 = 245 mg/kg (rat); Oral, LD50 = 375 mg/kg (rat)
Description
Phenylbutazone, one of the earliest NSAIDs introduced, is now indicated for the symptomatic relief of rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, gout, and acute superficial thrombophlebitis. The gastrointestinal and bone marrow toxicity observed in its early use have been greatly reduced by lower dosage (300 mg/d). Nevertheless, it is used primarily where other drugs have failed and then only for short-term therapy. The drug has a long serum half-life of about 100 h. It is a moderately active cyclooxygenase inhibitor and it suppresses both spontaneous and chemotactic motility of neutrophils. In addition to the serious gastrointestinal and hematological adverse effects, sodium and water retention, rash, vertigo, and dermatitis are observed.
Chemical properties
Off-Whtie Solid
Originator
Butazolidin, Geigy ,US,1952
The Uses of Phenylbutazone
Phenylbutazone, a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, is an efficient reducing cofactor for the peroxidase activity of COX. Phenylbutazone-dependent inactivation of COX and prostacyclin synthase is markedly increased in the presence of 100 μM hydrogen peroxide with half-maximal effects at Phenylbutazone concentrations of 100 and 25 μM for COX and prostacyclin synthase, respectively.
The Uses of Phenylbutazone
A non-steroidal anti-inflammatory compound. An inhibitor of cyclooxygenase that is also a substrate for peroxidation by cyclooxygenase
The Uses of Phenylbutazone
For the treatment of backache and ankylosing spondylitis
The Uses of Phenylbutazone
An inhibitor of Cox.
Indications
For the treatment of backache and ankylosing spondylitis
Background
A drug that has anti-inflammatory, antipyretic, and analgesic activities. It is especially effective in the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis. It also is useful in rheumatoid arthritis and Reiter's syndrome (investigational indication). Although phenylbutazone is effective in gouty arthritis, risk/benefit considerations indicate that this drug should not be employed for this disease. (From AMA Drug Evaluations Annual, 1994, p1822)
What are the applications of Application
Phenylbutazone is an inhibitor of Cox
Definition
ChEBI: Phenylbutazone is a member of the class of pyrazolidines that is 1,2-diphenylpyrazolidine-3,5-dione carrying a butyl group at the 4-position. It has a role as a non-narcotic analgesic, a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug, an antirheumatic drug, a peripheral nervous system drug, a metabolite and an EC 1.1.1.184 [carbonyl reductase (NADPH)] inhibitor.
Manufacturing Process
7.6 parts of sodium are dissolved in 190 parts by volume of absolute alcohol; 65 parts of diethyl-n-butyl malonate and 65 parts of hydrazobenzene are added. The alcohol is slowly distilled off and the reaction mixture heated for 12 hours at a bath temperature of 150°C and finally in vacuo, until no more alcohol comes off.
The product is dissolved in water, clarified with a little animal charcoal and 15% hydrochloric acid is slowly added until an acid reaction to Congo red paper is produced. 1,2-Diphenyl-3,5-dioxo-4-n-butyl-pyrazolidine separates as an oil, which rapidly become crystalline. It crystallizes from alcohol as colorless needles with a MP of 105°C.
brand name
Azolid (Sanofi Aventis); Butazolidin (Novartis);Algesin;Algirreudin;Algoverine;Alka butazolidin;Alkabutazone;Alka-phenylbutazone;Alka-sterazolidin;Anarthral;Apophenylbutazone;Apo-phenylbutazone;Arteopan;Arthirikin;Artibrin;Artrisin;Artrodesmol extra;Bizolin 20;Bizolin 700;Butacal;Butacol;Butadilat;Butadin;Butadyne;Butafenil;Butagros;Butakvertin;Butaparin;Butaphen;Buta-phen;Butarex;Butartiril;Butatril;Butazolidin alka;Butazolidina;Butial;Butinol;Butiwas;Buto beta;Butoroid cream;Butrex;Carudol;Celestalgon;Celestazone;Colfezone;Corbuvit;Dartranol;Debutazon;Delta-butazolidin;Delta-demoplas;Delta-myogit;Delta-tomanol;Deltawaukobuzon;Dephimixn;Dexa tomanol;Dexa-attritin;Dexa-escopyrin;Dexamed;Dexatrzona;Dibuzon;Direstop;Ditrone;Doctofril;Dolosin dexa;Dolpirina;Ectobutazone;Ethibute;Exraheudon;Exrheudon;F 650;Fenibutina;Flebosil;Glycyl;Hepabuzon;Inflazone;Intrabuzone;Mammyl;Megazone;Mepha-butazone;Mepropyrin;Mi 540;Naupax;Neuro-demoplas;Neuzoline m;Novobutazone;Oluprin;Oppazoen;Osadrinim;Parazolidin;Parzolidon;Pasirheuman;Penetradol;Phenbuff;Phenbutazone;Phenylarthrite;Phenylbetazone;Phenylon plus;Phlebolan;Pirabutil;Pirarreumol-b;Pirarreumol-p;Prebutex;Precirhemin;Prednirheumin;Proxyfezone;Proydynam;Pyrbutal;Ranocor;Reopin;Reumilene;Rheopyrin;Rheosolon;Rheumanoln;Rheumaphen;Rheumycalm;Salzone;Servizolidin;Sigma-elmedal;Sintobutina;Stabilat;Tevocodyn;Tibutazone;Ticinil calcio;Ticinil calico;Trabit;Zolapelin;Zolidinium.
Therapeutic Function
Antiinflammatory, Antiarthritic
World Health Organization (WHO)
Phenylbutazone, a pyrazolone derivative with anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic activity, was introduced in 1949 for the treatment of rheumatic disorders. Its use was subsequently associated with serious and sometimes fatal adverse reactions, notably cases of aplastic anaemia and agranulocytosis. Many national drug regulatory authorities consider that more recently introduced drugs offer a safer alternative for most, if not all, patients requiring anti-inflammatory agents. Phenylbutazone has thus been either withdrawn at the national level or retained with rigorously restricted indications for patients unresponsive to other therapy. These restrictions also apply, in general, to combination products containing phenylbutazone.
General Description
Odorless white or off-white crystalline powder. Tasteless at first, but slightly bitter aftertaste. pH (aqueous solution) 8.2.
Air & Water Reactions
Phenylbutazone is relatively stable at ambient temperatures. Aqueous decomposition of Phenylbutazone occurs by hydrolysis and oxidation. Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Phenylbutazone is incompatible with strong oxidizers, strong acids and strong bases. .
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for Phenylbutazone are not available; however, Phenylbutazone is probably combustible.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Phenylbutazone is a hepatotoxin and binds to plasma proteins. It is used to treat inflammation in horse. Phenylbutazone has potential to treat ankylosing spondylitis. It has therapeutic potential to treat myotonic dystrophy type 1 (DM1) by inducing muscle blind-like protein 1 (MBNL1) expression. It also favors the expression of muscle chloride channel in skeletal muscles.
Pharmacokinetics
Phenylbutazone is a synthetic, pyrazolone derivative. It is a nonhormonal anti-inflammatory, antipyretic compound useful in the management of inflammatory conditions. The apparent analgesic effect is probably related mainly to the compound's anti-inflammatory properties and arise from its ability to reduce production of prostaglandin H and prostacyclin. Prostaglandins act on a variety of cells such as vascular smooth muscle cells causing constriction or dilation, on platelets causing aggregation or disaggregation and on spinal neurons causing pain. Prostacylcin causes vascular constriction platelet disaggregation
Clinical Use
Phenylbutazone is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug used for the acute treatment of ankylosing spondylitis, chronic polyarthritis, and gout. Because of severe side effects including disturbances of the hematopoietic system like agranulocytosis and aplastic anemia the use is limited to conditions in which other nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs do not show sufficient efficacy. Phenylbutazone is given as oral, rectal, intramuscular or topical formulation (up to 600 mg/d initial dose, up to 400 mg/d maintenance dose). The peak plasma concentration is reached 2 h after oral application. Phenylbutazone is bound to 98% to plasma protein. Oxyphenbutazone is formed as an active metabolite of phenylbutazone.
Safety Profile
Suspected human carcinogen producing leukemia. A human poison by parenteral route. An experimental poison by ingestion, intraperitoneal, subcutaneous, intravenous, and intramuscular routes. Human systemic effects by ingestion and possibly other routes: fever, blood pressure increase, other unspecified vascular effects, damage to kidney tubules and glomeruli, decreased urine volume, blood in the urine, reduction in the number of whte blood cells, and agranulocytosis. Experimental teratogenic and reproductive effects. Human mutation data reported. An eye irritant. An antiinflammatory agent. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx
Synthesis
Phenylbutazone, 4-butyl-1,2-diphenyl-3,5-pyrazolidinedione (3.2.6), is synthesized in a single stage by reacting hydrazobenzol with butylmalonic ester [68,69].

Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
One manufacturer lists the following as the indications for phenylbutazone: “For the relief of inflammatory conditions associated with the musculoskeletal system in dogs and horses.” (Package Insert; Butazolidin?—Coopers). It has been used primarily for the treatment of lameness in horses and, occasionally, as an analgesic/ antiinflammatory, antipyretic in dogs, cattle, and swine.
Metabolism
Not Available
Purification Methods
Crystallise the dione from EtOH. Its pK2 3 is 4.52 (in H2O), 4.89 (in 50% aqueous EtOH) and 5.25 (80% 2-methoxyethanol). It complexes with Hg2+, Cd2+ and Zn2+. It has UV with max at 239.5nm in MeOH+50% aqueous HClO4 and 264nm in aqueous 0.1N NaOH. [Beilstein 24 III/IV 1123.]
Properties of Phenylbutazone
| Melting point: | 106-108 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 448.76°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.1591 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.6140 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Practically insoluble in water, sparingly soluble in alcohol. It dissolves in alkaline solutions. |
| form | Powder |
| pka | 4.5(at 25℃) |
| color | White to almost white |
| Water Solubility | <0.1 g/100 mL at 23.5 ºC |
| Merck | 14,7277 |
| BRN | 290080 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong acids, strong bases. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 50-33-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 3 (Vol. 13, Sup 7) 1987 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Phenylbutazone(50-33-9) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Phenylbutazone (50-33-9) |
Safety information for Phenylbutazone
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H301:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Phenylbutazone
| InChIKey | VYMDGNCVAMGZFE-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Phenylbutazone manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Phenylbutazone 99% (HPLC) CAS 50-33-9View Details
Phenylbutazone 99% (HPLC) CAS 50-33-9View Details
50-33-9 -
 Phenylbutazone CAS NO. 50-33-9View Details
Phenylbutazone CAS NO. 50-33-9View Details
50-33-9 -
 Phenylbutazone API POWDERView Details
Phenylbutazone API POWDERView Details
50-33-9 -
 Phenylbutazone Ip Bp Usp, Packaging Size: 25 kg, Non prescriptionView Details
Phenylbutazone Ip Bp Usp, Packaging Size: 25 kg, Non prescriptionView Details
50-33-9 -
 Phenylbutazone USP API MANUFACTURER INDIAView Details
Phenylbutazone USP API MANUFACTURER INDIAView Details
50-33-9 -
 Phenylbutazone ApiView Details
Phenylbutazone ApiView Details
50-33-9 -
 Phenylbutazone ApiView Details
Phenylbutazone ApiView Details
50-33-9 -
 PhenylbutazoneView Details
PhenylbutazoneView Details
50-33-9
