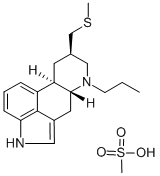
Pergolide
- CAS NO.:66104-22-1
- Empirical Formula: C19H26N2S
- Molecular Weight: 314.49
- MDL number: MFCD00867357
- EINECS: 200-110-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-24 15:44:27
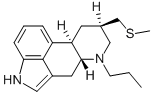
What is Pergolide?
Absorption
Significant amount may be absorbed (evidence on bioavailability still lacking).
Toxicity
Oral, rat LD50: 15 mg/kg. Symptoms of overdose include nausea, vomiting, convulsions, decreased blood pressure, and CNS stimulation.
Originator
Celance, Eli Lilly
The Uses of Pergolide
dopamine receptor agonist, anti-Parkinson's agent
Background
Pergolide is a long-acting dopamine agonist approved in 1982 for the treatment of Parkinson’s Disease. It is an ergot derivative that acts on the dopamine D2 and D3, alpha2- and alpha1-adrenergic, and 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) receptors. It was indicated as adjunct therapy with levodopa/carbidopa in the symptomatic treatment of parkinsonian syndrome. It was later found that pergolide increased the risk of cardiac valvulopathy. The drug was withdrawn from the US market in March 2007 and from the Canadian market in August 2007. While the use of pergolide in humans is still approved in only some countries, pergolide is mainly used for veterinary purposes.
Indications
Indicated as adjunctive treatment to levodopa/carbidopa in the management of the signs and symptoms of Parkinson's disease. It was withdrawn from the US and Canadian markets in 2007 due to an increased risk of cardiac valvulopathy.
Definition
ChEBI: Pergolide is a diamine that is ergoline in which the beta-hydrogen at position 8 is replaced by a (methylthio)methyl group and the hydrogen attached to the piperidine nitrogen (position 6) is replaced by a propyl group. A dopamine D2 receptor agonist which also has D1 and D2 agonist properties, it is used as the mesylate salt in the management of Parkinson's disease, although it was withdrawn from the U.S. and Canadian markets in 2007 due to an increased risk of cardiac valve dysfunction. It has a role as an antiparkinson drug and a dopamine agonist. It is a diamine, an organic heterotetracyclic compound and a methyl sulfide. It is a conjugate base of a pergolide(1+).
Manufacturing Process
Dimethyl disulfide (73.6 ml, 0.79 mol) and tri-n-butylphosphine (79.6 ml, 0.32 mol) were added to a solution of 9,10-dihydrolysergol in (8.1 g, 0.032 mol) in the 150 ml of anhydrous DMF and were stirred at room temperature for 6 hours under a nitrogen atmosphere. Dimethyl disulfide of the reaction mixture was removed under vacuo. A solution of the residue in ethyl acetate was extracted with 3.7% HCl (aq.). The aqueous layer was basified with ammonium hydroxide to a pH of 10 and then extracted with ethyl acetate. Removal of ethyl acetate followed by a silica gel column purification eluting with 10% MeOH/CH2Cl2 gave5.5.g of D-6-methyl-8β(methylthiomethyl)ergoline (60%).
A solution of D-6-methyl-8β-(methylthiomethyl)ergoline (0.4 g, 0.0014 mol) and NaI (0.63 g, 0.0042 mol) in 10 ml of propionic anhydride was refluxed for 40 hours. The reaction mixture was guenched with a 10% Na2CO3 solution and extracted by ethyl acetate. The combined organic layers were washed with a saturated brine solution, dried with magnesium sulfate and concentrated to produce oil. The oil was purified by silica gel column, eluting with 10% MeOH/CH2Cl2 to give 0.33 g of D-1,6-dipropionyl-8β(methylthiomethyl)ergoline.
LiAlH4 (0.6 g, 0.0156 mol) was slowly added to a solution of D-1,6dipropionyl-8β-(methylthiomethyl)ergoline in the 20 ml anhydrous THF at 0°C under nitrogene atmosphere. The mixture was stirred at 0°C for 30 min and then at room temperature for 4 hours. The reaction was cooled to 0°C and 0.6 ml of water was slowly added. The mixture was stirred at 0°C for 10 min and 1.8 ml of 15% NaOH (aq.) and 2.5 ml of water were added respectively. The mixture was stirred for 30 min at room temperature and then filtered. Excess of the solvent was removed under reduced pressure to give 150 mg of 8β-((methylthio)methyl)-6-propyl-ergoline or pergolide (yield: 68%). Ergoline,8-((methylthio)methyl)-6-propyl-, monomethanesulfonate, (8β)- may be prepared by mixing of components in solution.
brand name
Permax (Valeant).
Therapeutic Function
Dopamine agonist
Pharmacokinetics
Pergolide stimulates centrally-located dopaminergic receptors resulting in a number of pharmacologic effects. Five dopamine receptor types from two dopaminergic subfamilies have been identified. The dopaminergic D1 receptor subfamily consists of D1 and D5 subreceptors and are associated with dyskinesias. The dopaminergic D2 receptor subfamily consists of D2, D3 and D4 subreceptors and has been associated with improvement of symptoms of movement disorders. Thus, agonist activity specific for D2 subfamily receptors, primarily D2 and D3 receptor subtypes, are the primary targets of dopaminergic antiparkinsonian agents. It is thought that postsynaptic D2 stimulation is primarily responsible for the antiparkinsonian effect of dopamine agonists, while presynaptic D2 stimulation confers neuroprotective effects. This semisynthetic ergot derivative exhibits potent agonist activity on dopamine D2- and D3-receptors. It also exhibits agonist activity on dopamine D4, D1, and D5, 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT)1A, 5-HT1B, 5-HT1D, 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B, 5-HT2C, α2A-, α2B-, α2C-, α1A-, α1B-, and α1D-adrenergic receptors. Parkinsonian Syndrome manifests when approximately 80% of dopaminergic activity in the nigrostriatal pathway of the brain is lost. As this striatum is involved in modulating the intensity of coordinated muscle activity (e.g. movement, balance, walking), loss of activity may result in dystonia (acute muscle contraction), Parkinsonism (including symptoms of bradykinesia, tremor, rigidity, and flattened affect), akathesia (inner restlessness), tardive dyskinesia (involuntary muscle movements usually associated with long-term loss of dopaminergic activity), and neuroleptic malignant syndrome, which manifests when complete blockage of nigrostriatal dopamine occurs. High dopaminergic activity in the mesolimbic pathway of the brain causes hallucinations and delusions; these side effects of dopamine agonists are manifestations seen in patients with schizophrenia who have overractivity in this area of the brain. The hallucinogenic side effects of dopamine agonists may also be due to 5-HT2A agonism. The tuberoinfundibular pathway of the brain originates in the hypothalamus and terminates in the pituitary gland. In this pathway, dopamine inhibits lactotrophs in anterior pituitary from secreting prolactin. Increased dopaminergic activity in the tuberoinfundibular pathway inhibits prolactin secretion. Pergolide also causes transient increases in somatotropin (growth hormone) secretion and decreases in luteinizing hormone (LH) concentrations.
Clinical Use
Pergolide is a nonpeptide ergot derivative with higher potency and efficacy as a D1 agonist and equivalent D2 agonist activity when compared to bromocriptine. For Parkinson's disease, as well as for inhibition of lactation, pergolide is more potent than bromocriptine and may be effective in patients who have become tolerant to bromocriptine. After oral administration, pergolide undergoes hepatic metabolism to 10 metabolites, some of which are pharmacologically active. Elimination of the drug is primarily renal, with a half-life is approximately 27 hours.
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
The primary use for pergolide in veterinary medicine is in treatment of horses for pituitary pars intermedia dysfunction (PPID), commonly called equine Cushing’s disease.
Metabolism
Extensively hepatic.
Metabolism
Extensively hepatically metabolised. At least 10
metabolites have been detected in the urine and faeces.
Following oral administration of [14C]-radiolabelled
pergolide mesilate to healthy subjects, approximately
55% of the administered radioactivity can be recovered as
pergolide metabolites from the urine, 40% from the faeces
and 5% from expired CO2
, suggesting that a significant
fraction is absorbed.
Properties of Pergolide
| Melting point: | 207.5 °C |
| Boiling point: | 491.3±35.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.124±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Store in freezer, under -20°C |
| pka | 17.66±0.40(Predicted) |
| Merck | 14,7162 |
Safety information for Pergolide
Computed Descriptors for Pergolide
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 1-methylindoline-2,3-dione 98%View Details
1-methylindoline-2,3-dione 98%View Details
2058-74-4 -
 614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 -
 3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
