Pentadecafluorooctanoic acid
Synonym(s):PFOA;Perfluorooctanoic acid;Pentadecafluorooctanoic acid;Perfluorocaprylic acid;Perfluorocaprylic acid solution
- CAS NO.:335-67-1
- Empirical Formula: C8HF15O2
- Molecular Weight: 414.07
- MDL number: MFCD00004174
- EINECS: 206-397-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-06 13:21:43
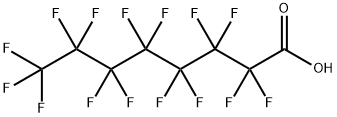
What is Pentadecafluorooctanoic acid?
Description
Concerns about the potential environmental and toxicological impacts of long-chain perfluoroalkyl sulfonates and carboxylic acids have led to: (1) the phaseout of production of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and related compounds and perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) by their major global manufacturer in 2000–02; (2) the conclusion of a stewardship agreement between the United States Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA) and eight leading global companies to reduce emissions and product content of PFOA and related chemicals by 95% by 2010 and to work toward their elimination by 2015; (3) a similar agreement between the Canadian environmental and health authorities and five companies to restrict perfluorinated carboxylic acids in products; (4) a European Union Marketing and Use Directive restricting the use of ‘PFOSs’ in the European Union; and (5) the inclusion of PFOS in the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants as an Annex B substance, i.e., restricted in its use; and other regulatory and voluntary initiatives intended to reduce environmental emissions of this family of compounds.
Description
Perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA), or pentadecafluorooctanoic acid, is a colorless liquid with a boiling range of 189–192 oC. Its chief use is as a surfactant in the emulsion polymerization of fluoropolymers such as poly(tetrafluoroethylene) (Teflon). It is invaluable in the production of microchips.
In 1947, the 3M Company began to manufacture PFOA via electrochemical fluorination. Octanoyl chloride is treated with hydrofluoric acid, which replaces all of the hydrogen atoms with fluorine; and the acyl fluoride product is then hydrolyzed to PFOA. PFOA also can be produced in a telomerization process, in which smaller fluorocarbons react to make larger ones.
The C–F bonds in PFOA make it quite chemically inert, which turns out to be a blessing and a curse. Its inertness makes it persistent in the environment; it has been detected, mostly at very low levels, in the blood of ≈98% of the US population. Because it is carcinogenic and exhibits other forms of toxicity, governments have restricted the concentrations permitted in drinking water and are threatening to ban it altogether. As PFOA and similar fluorinated compounds become more restricted, electronics companies are struggling to replace them in the?manufacture of ever-smaller semiconductor chips.
Chemical properties
Perfluorooctanoic acid is a white to off-white powder or colorless flakes. It is very soluble in water.It has a pH of 2.6. Perfluorooctanoic acid has the ability to react with bases, oxidizing agents, and reducing agents. Upon decomposition, PFOA can form carbon oxides and hydrogen fluoride. Additional information related to physical and chemical properties of PFOA are not currently available.

The Uses of Pentadecafluorooctanoic acid
Perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) is fluorinated surfactant used, primarily as its ammonium salt (APFO), as an aid in the chemical synthesis of fluoropolymers and fluoroelastomers. As such, it may be found in nonstick cookware and utensils, stain-repellant fabric treatments, and water-proofing treatments for garments. Although an effort is underway by the U.S. EPA to reduce use of and replace perfluoroalkyls with other substances, PFOA is still used in United States industry.
Perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA, C8, pentadecafluorooctanoic acid, perfluoro caprylic acid) is an eightcarbon compound in the perfluoroalkyl family of chemicals. Perfluorooctane sulfonate is used in a variety of applications, including nonstick cookware, waterproof clothing, leather products, cleaning products, and pesticides. Its main use was as a stain repellent on carpet, furniture, and other consumer products. In 2006, the U.S. Protection Agency along with eight major companies that utilized PFOA embarked on a program to reduce emissions and use of the chemical by 2015 (USEPA, 2012).
The Uses of Pentadecafluorooctanoic acid
PFOA is a completely fluorinated organic acid that is produced synthetically as its salts. The typical structure has a nonbranched chain of eight carbon atoms. The industrial production of perfluoroalkyl carboxylates started in the late 1940s. Two principal production processes are used to manufacture PFOA, viz. electrochemical fluorination and telomerization. PFOA can also appear as a result of degradation of some precursors, e.g., fluorotelomer alcohols. The ammonium salt of PFOA is primarily used as an emulsifier or ‘processing aid’ in industrial applications, for example, in the production of fluoropolymers such as polytetrafluoroethylene, but also produced for fluorosurfactant use. Typical uses include fluoropolymers in electronics, textiles, and nonstick cookware, and fluorosurfactants in aqueous filmforming foams used for fire fighting.
The Uses of Pentadecafluorooctanoic acid
Pentadecafluorooctanoic acid solution may be used as an ion-pairing reagent in the development of a chromatographic method for the separation and determination of underivatized proteinic amino acids using liquid chromatography with evaporative light scattering detection (LC-ELSD) and atmospheric pressure ionization-mass spectrometry (LC-API-MS), respectively.
Definition
ChEBI: A fluoroalkanoic acid that is perfluorinated octanoic acid.
General Description
Perfluorooctanoic acid is a perfluoroalkyl acid commonly used in the preparation of fluoroacrylic esters, fluoropolymers and fluoroelastmers. It is found to be environmentally persistent and bioaccumulative with a long half-life.
Safety Profile
Poison by intraperitoneal route. Mutation data reported. Whenheated to decomposition it emits toxic vapors of Fí.
Environmental Fate
Perfluorooctanoic acid found in the environment may result from waste stream releases from manufacture of cosmetics, lubricants, paints, polishes, adhesives, fabric treatments, and fire-fighting compounds. It can partition to the vapor phase in the atmosphere, where it is degraded atmospherically with a half-life of 31 days. It is very resistant to hydrolysis, and immobile in soil. It will not likely evaporate from soil (depending on soil pH) or surface waters. It is not expected to be absorbed to sediments and suspended particles. Perfluorooctanoic acid is not expected to bioaccumulate in aquatic organisms (BCF =3.1–9.4) (NLM, 2013).
Purification Methods
Crystallise the acid from CCl4 and toluene, and distil it. It forms micelles in H2O and the solubility is 1% in H2O. The acid chloride has b 129-130o/744mm. The amide has m 138o. [Bernett & Zisman J Phys Chem 63 1911 1959, Bro & Sperati J Polym Sci 38 289 1959, Beilstein 2 IV 994.]
Toxicity evaluation
Studies with animals fed PFOA for a long period showed effects
on the stomach, liver, and thyroid hormones. Animal studies
also indicate that PFOA may cause cancer at relatively high
levels. PFOA has also been shown to be a developmental
toxicant, and to have effects on the immune system.
PFOA affects primarily the liver and can cause developmental
and reproductive toxic effects at relatively low dose
levels in experimental animals. It increases the tumor incidence
in rats, mainly in the liver. The carcinogenic effects in rats
appear to be due to indirect/nongenotoxic modes of action.
Epidemiological studies in PFOA-exposed workers do not
indicate an increased cancer risk. There is relatively consistent
evidence of modest positive associations between serum levels
of PFOA and cholesterol, uric acid, and liver enzyme levels.
The critical effects observed in rodents and monkeys are on
the liver and include hypertrophy, changes in liver enzyme
activity, and proliferation of peroxisomes.
In rodents the anionic form of PFOA induces hepatocellular
adenomas, Leydig cell adenomas, and pancreatic hyperplasia.
The genotoxic activity of PFOA is a matter of current debate and
controversy, with classifications as ‘devoid of significant genotoxicity’
as well as ‘weakly nonspecific genotoxic.’ PFOA does
not appear directly genotoxic; animal data indicate that it can
cause several types of tumors and neonatal death and may have
toxic effects on the immune, liver, and endocrine systems.
Properties of Pentadecafluorooctanoic acid
| Melting point: | 55-56 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 189 °C/736 mmHg (lit.) |
| Density | 1,7 g/cm3 |
| Flash point: | 189-192°C |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | 3.4g/l |
| form | Crystalline Powder |
| pka | 0.50±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | White |
| Specific Gravity | 1.7 |
| PH | 2.6 (1g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| Water Solubility | 3.4 g/L |
| BRN | 1809678 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with bases, oxidizing agents, reducing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 335-67-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Octanoic acid, pentadecafluoro-(335-67-1) |
| IARC | 2B (Vol. 110) 2017 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Perfluorooctanoic acid (335-67-1) |
Safety information for Pentadecafluorooctanoic acid
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H351:Carcinogenicity H362:Reproductive toxicity, effects on or via lactation H372:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P263:Avoid contact during pregnancy/while nursing. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Pentadecafluorooctanoic acid
| InChIKey | SNGREZUHAYWORS-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde Electrolytic Iron Powder 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 3-(Hydroxymethyl)benzoate N-Boc-2-chloroethylamine 1-Bromo-2-methoxy-3-nitrobenzene N-Methyl-3-cyclopenten-1-amine 2-Bromo-3-hydroxybenzaldehyde 1H-indazole-5-carboxamideRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Pentadecafluorooctanoic acid 98.00% CAS 335-67-1View Details
Pentadecafluorooctanoic acid 98.00% CAS 335-67-1View Details
335-67-1 -
 Perfluorooctanoic acid, 95% CAS 335-67-1View Details
Perfluorooctanoic acid, 95% CAS 335-67-1View Details
335-67-1 -
 7441-43-2 98%View Details
7441-43-2 98%View Details
7441-43-2 -
 1260741-78-3 6-Bromo-3-iodo-1-methyl-1H-indazole 98%View Details
1260741-78-3 6-Bromo-3-iodo-1-methyl-1H-indazole 98%View Details
1260741-78-3 -
 4-bromo-3,5-dimethylbenzenesulfonyl chloride 1581266-79-6 98%View Details
4-bromo-3,5-dimethylbenzenesulfonyl chloride 1581266-79-6 98%View Details
1581266-79-6 -
 2490430-37-8 98%View Details
2490430-37-8 98%View Details
2490430-37-8 -
 N-(5-Amino-2-methylphenyl)acetamide 5434-30-0 98%View Details
N-(5-Amino-2-methylphenyl)acetamide 5434-30-0 98%View Details
5434-30-0 -
 124371-59-1 98%View Details
124371-59-1 98%View Details
124371-59-1