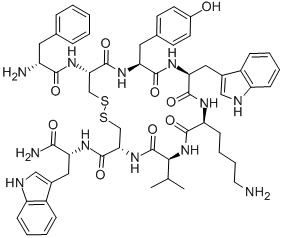
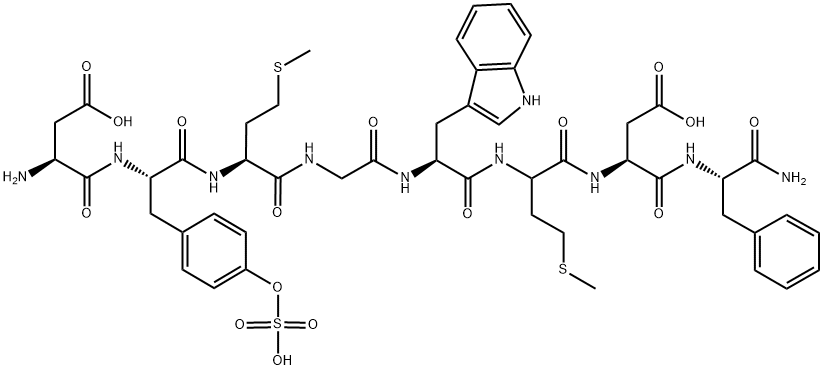
Pasireotide
- CAS NO.:396091-73-9
- Empirical Formula: C58H66N10O9
- Molecular Weight: 1047.23
- MDL number: MFCD08067735
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-06 11:03:33
What is Pasireotide?
Absorption
The peak plasma concentration of pasireotide occurs in 0.25-0.5 hours. After administration of single and multiple doses, there is dose-proportionoal increases in Cmax and AUC.
Toxicity
The most common toxic effects observed are hyperglycemia, cholelithiasis, diarrhea, nausea, headache, abdominal pain, fatigue, and diabetes mellitus.
Description
In April 2012, the European Commission approved pasireotide for the treatment of Cushing’s Disease (CD) in adult patients who have not responded to surgical interventionor forwhomsurgery is not anoption.Pasireotide was approved for the same indication by the US FDA in December of 2012. Pasireotide (also known as SOM230) is a cyclohexapeptide that acts as a somatostatin analogue to inhibit the release of ACTH. Somatostatins are cyclic peptides of 14 and 28 amino acids that play animportant role inregulating endocrineandexocrine release inmany tissues through an inhibitory mechanism. There are five known subtypes of somatostatin receptors (SSTRs). Natural somatostatins bind with high affinity to all five subtypes, however, their therapeutic use is limited by rapid degradation in plasma. Pasireotide arose fromefforts to identify a somatostatinmimetic with long-lasting inhibitory effects. Starting with a 14-amino acid somatostatin peptide, a systematic alanine scan revealed residues that were essential for receptor sub-type binding, including key b-turn regions and adjacent residues. Placing the key structural elements as unnatural amino acids in a cyclohexapeptide backbone gave pasireotide.
Originator
Novartis (Switzerland)
The Uses of Pasireotide
Pasireotide can be used in biological study of long-term treatment of Cushing''s disease with pasireotide, 5-yr results from open-label extension study of Phase III trial.
Background
Pasireotide is a synthetic long-acting cyclic hexapeptide with somatostatin-like activity. It is marketed as a diaspartate salt called Signifor, which is used in the treatment of Cushing's disease.
Indications
For the treatment of Cushing’s disease, specifically for those patients whom pituitary surgery has not been curative or is not an option.
Definition
ChEBI: Pasireotide is a six-membered homodetic cyclic peptide composed from L-phenylglycyl, D-tryptophyl, L-lysyl, O-benzyl-L-tyrosyl, L-phenylalanyl and modified L-hydroxyproline residues joined in sequence. A somatostatin analogue with pharmacologic properties mimicking those of the natural hormone somatostatin; used (as its diaspartate salt) for treatment of Cushing's disease. It has a role as an antineoplastic agent. It is a homodetic cyclic peptide and a peptide hormone. It is a conjugate base of a pasireotide(2+).
brand name
Signifor
Pharmacokinetics
Signifor? is an analogue of somatostatin that promotes reduced levels of cortisol secretion in Cushing's disease patients.
Clinical Use
Pasireotide, also known as SOM230, is a cyclic, hexameric peptide developed by Novartis which exhibits somatostatin-like activity as an antisecretory agent used in the treatment of Cushing’s disease. Pasireotide activates a broad range of somatostatin receptors, and in particular displays a significantly higher binding affinity for somatostatin receptors 1, 3, and 5 than its competitor somatostatin-mimic octreotide in vitro, as well as a comparable binding affinity for somatostatin receptor 2. Pasireotide is more potent than somatostatin in inhibiting the secretion of human growth hormone (HGH), glucagon, and insulin.
Synthesis
The synthesis of pasireotide is relatively straightforward, given that the chemical entity is a cyclic peptide. The most likely scalable route closely mimics that described by the discovery authors involving a series of conventional couplings and deprotection steps to arrive at a linear peptide which then underwent sequential release from solid support, macrocyclization, and a global deprotection step.

Beginning from (2S,4R)-4-hydroxyproline methyl ester (110) in the scheme above, this pyrrolidine nitrogen was first Fmoc-protected in 85% yield followed by treatment with trisphosgene and N-Boc diaminoethane to provide the prolino carbamate shown in 49% yield over the two step sequence after a recrystallization with ethyl acetate.
Next, commercially available Fmoc-Tyr(Bzl)-O-CH2-Ph(3-OCH3)-O-CH2-SASRIN157 resin (112) was used as starting material in a manually operated reactor and carried through a standard protocol consisting of repetitive cycles of N|á deprotection (piperidine/DMF, 2:8), repeated washings with DMF, and coupling using DIC/HOBT in DMF (Schemes 2 and 3). The following amino acid derivatives were sequentially coupled: Fmoc-Lys(Boc)-OH, Fmoc-D-Trp(Boc)-OH, Fmoc-PhG-OH, proline derivative 111 above, and finally Fmoc-Phe-OH. Couplings were continued or repeated until complete disappearance of residual amino groups as monitored with a ninhydrin stain test. Before cleavage of the protected linear peptide from its resin support, the Fmoc group was removed. After washings with dichloromethane, the peptide resin was transferred into a column and the peptide fragment was cleaved from solid support upon subjection to 2% TFA in dichloromethane. The eluate was immediately neutralized with a saturated NaHCO3 solution which resulted in the side chain protected fragment 119 (the Scheme) was obtained in 93% homogeneity and cyclized without further purification. For cyclization, the linear fragment was dissolved in DMF, treated with DIPEA, and then 1.5 equiv of diphenylphosphoryl azide which resulted in the protected cyclized product obtained in good yield. For complete deprotection, the residue was dissolved at 0 ??C in aqueous TFA, and the mixture was stirred at this temperature for 30 min. The product was then precipitated with ether containing ca. 10 equiv of HCl, then filtered and washed with ether, and finally dried. The entire sequence produced pasireotide (XVIII) in 20% yield from resin-bound 112.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Antifungals: avoid with ketoconazole.
Ciclosporin: possibly reduces ciclosporin
concentration.
Metabolism
Metabolism is minimal.
Metabolism
Pasireotide is metabolically highly stable and in vitro
data show that pasireotide is not a substrate, inhibitor
or inducer of any major enzymes of CYP450. In healthy
volunteers, pasireotide is mainly found in the unchanged
form in plasma, urine and faeces.
Pasireotide is eliminated mainly by hepatic clearance
and is mostly found, unchanged, in the faeces (48%) and
urine.
Properties of Pasireotide
| Boiling point: | 1351.4±65.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.36±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Store at -20°C |
| solubility | Soluble in DMSO |
| form | Powder |
| pka | 11.86±0.46(Predicted) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 396091-73-9 |
Safety information for Pasireotide
Computed Descriptors for Pasireotide
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1