Palbociclib
Synonym(s):6-Acetyl-8-cyclopentyl-5-methyl-2-[[5-(1-piperazinyl)-2-pyridinyl]amino]pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-7(8H)-one;Ibrance;
- CAS NO.:571190-30-2
- Empirical Formula: C24H29N7O2
- Molecular Weight: 447.53
- MDL number: MFCD11840850
- EINECS: 810-186-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-08-06 15:14:14
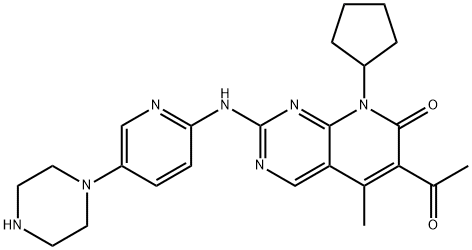
What is Palbociclib?
Absorption
Palbociclib presents a linear pharmacokinetic profile and its peak plasma concentration was observed 6-12 hours after oral administration. The oral bioavailability is reported to be of 46% with a steady-state reached after 8 days and a median accumulation ratio of 2.4.
The absorption of palbociclib is significantly reduced under fasting conditions and hence, food intake is recommended when this drug is administered.
Toxicity
The reported oral Ld50 is of 100 mg/kg. In cases of overdosage, only supportive measures are considered.
Palbociclib was showed to present clastogenic activities in in vitro and in vivo assays. As well, it has been reported to produce fetal harm due to its mechanism of action. Lastly, it was shown to increase the incidence of microglial cell tumors in the central nervous system at high doses.
Description
Palbociclib is a cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) 4 and CDK6 inhibitor approved by the FDA to treat hormone receptor-positive (HR+) human epidural growth factor 2-negative (HER2-) metastatic breast cancer. It is used in combination with letrazole as the first-line hormonal-based therapy in postmenopausal women, or with fulvestrant in women with disease progression following hormonal therapy. Palbociclib was discovered at Warner- Lambert and developed by Pfizer after their merger. Pfizer is also studying the effectiveness of palbociclib in a variety of other cancers at various stages in the clinic.
The Uses of Palbociclib
Palbociclib (also known as compound number PD-0332991) is an experimental drug for the treatment of breast cancer being developed by Pfizer. It is a selective inhibitor of the cyclin-dependent kinases CDK4 and CDK6.
Indications
Palbociclib is indicated in combination with letrozole as initial endocrine-based therapy for the treatment of human epidermal growth factor receptor type 2 (HER2)-negative and hormone receptor(HR)-positive tumors in adult patients with advanced/metastatic breast cancer. It is as well approved in combination with fulvestrant in patients with disease progression with prior endocrine therapy.
In the official labeling, the use of palbociclib should be accompanied with either an aromatase inhibition, no restricted to letrozole, as initial endocrine-based therapy in postmenopausal women or in man.
The breast cancer starts as a group of cancer cells that grow into and destroy the nearby breast tissue. This growth can spread into other parts of the body which is called metastasis. According to the location of the cancer cells, it can be categorized in ductal carcinoma and lobular carcinoma. However, other types of breast cancer include inflammatory breast cancer, Paget disease of the breast, triple negative breast cancer non-Hodgkin lymphoma and soft tissue sarcoma. In males, breast cancer is usually treated as the cases of postmenopausal women and almost all the cases are ductal carcinoma.
Background
Palbociclib is a piperazine pyridopyrimidine that acts in the cell cycle machinery. It is a second generation cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor selected from a group of pyridopyrimidine compounds due to its favorable physical and pharmaceutical properties.
Palbociclib was developed by Pfizer Inc after the discovery that identified the cyclin-dependent kinases as key regulators of cell growth. It was originally FDA approved on March 2015 for the treatment of HR-positive, HER2-negative advanced or metastatic breast cancer and its indications were updated in April 2019 to include male patients based on findings from postmarketing reports and electronic health records demonstrating safety and clinical efficacy.
Definition
ChEBI: A member of the class of pyridopyrimidines that is 2-{[5-(piperazin-1-yl)pyridin-2-yl]amino}pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-7-one bearing additional methyl, acetyl and cyclopentyl substituents at positions 5, 6 and 8 respectively. It is used in combina ion with letrozole for the treatment of metastatic breast cancer.
Indications
Palbociclib (Ibrane(R), Pfizer), a selective CDK4 and CDK6 inhibitor, received accelerated approval from FDA in 2015 for women with estrogen receptor-positive and HER2-negative breast cancer in combination with letrozole.
Biochem/physiol Actions
PF-00080665 (Palbociclib; PD 0332991) is an orally active and highly specific inhibitor against cyclin-dependent kinase 4 & 6 (IC50 = 9, 11, 15 nM, respectively, using CDK4/cycD3, CDK4/cycD1, CDK6/cycD2; IC50 >10 μM against 36 other kinases) that potently suppresses Cdk4/6-dependent cellular Rb phosphorylation (IC50 = 66 nM/pSer780 & 63 nM/pSer795; MDA-MB-435). PF-00080665 exhibits selective antiproliferation activity against Rb-positive human breast/colon/lung/leukemia cancer cultures (IC50 = 40-400 nM; IC50 >3 μM/Rb-negative MDA-MB-468 & H2009) and displays in vivo efficacy against various advanced stage human tumor xenografts in mice (12.5-150 mg/kg/day p.o.).
Pharmacokinetics
Due to its mechanism of action, palbociclib inhibits cell growth and suppresses DNA replication in retinoblastoma tumor suppressor gene (RB) proficient cancer cells. As expected, these RB cells present a significant increase in the proportion of cells in G1 state and the presence of palbociclib produces effective dephosphorylation of RB, reduce proliferation and induce senescence causing cell-cycle arrest.
In vitro studies showed the potential for palbociclib to reduce cellular proliferation of estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer cell lines through the inhibition of the cell-cycle progression from G1 to S phase. In this study, it was demonstrated that the sensitivity of the cells significantly increased with the expression of RB1 and CCND1 and low expression of CDKN2A. As well, palbociclib, combined with antiestrogens, enhanced in vivo antitumor activity in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer mouse models.
In clinical trials, palbociclib, in combination with letrozole, was shown to significantly increase the progression-free survival (PFS) in patients with metastatic breast cancer without prior endocrine treatment. In the results, the PFS increased from 4.5 to 9.5 months with an overall response rate (ORR) of 24.6%.
Clinical Use
Protein kinase inhibitor:
Treatment of hormone receptor (HR)-positive,
human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-
negative locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer
Synthesis
Numerous syntheses of palbociclib have been reported,149,150
and the commercial scale process published by scientists at
Pfizer is described herein. The amino-pyridylpiperazine
fragment 212 was prepared in two steps. Commercial
piperazine 209 was added to 5-bromo-2-nitropyridine (210)
to give nitro-pyridine 211 in 93% yield.
Hydrogenation of the nitro group using catalytic palladium
on carbon provided the amino-pyridylpiperazine 212 in 96%
yield.
As such, cyclopentylamine
(214) was added to 5-bromo-2,4-dichloropyrimidine (213) to
give 5-bromo-2-chloro-6-cyclopentylaminopyrimidine (215) in
84% yield. Heck reaction with crotonic acid followed by
treating the resulting product with acetic anhydride formed the
mixed anhydride under elevated temperatures, and this resulted
in cyclization to give pyrimidinone 214 in 81% yield.
Bromination using N-bromosuccinimide (NBS) provided
coupling partner 217 in 88% yield. Next, aminopyridine 212
was treated with cyclohexylmagnesium chloride and then
reacted with 217 to give the SNAr product 218 in 88%
yield. A second Heck reaction between bromide 218 and
butyl vinyl ether (219) using palladium acetate/bis(2-
diphenylphosphinophenyl)ether (DPEPhos) as the catalyst
provided enol ether 220 in 84% yield. Exposure of 220 to
acidic conditions removed the Boc group from the piperazine
while converting the enol ether to the corresponding ketone,
providing palbociclib (XXVII) in 90% yield.

Enzyme inhibitor
This orally active, non-ATP-competitive cyclin kinase-directed inhibitor (FW = 483.99 g/mol (mono-HCl); CASs = 827022-32-2 (mono- hydrochloride, 571190-30-2 (free base); Solubility: 10 mg/mL DMSO; 30 mg/mL Water; Formulation: Dissolved in sodium lactate buffer (50 mM, ® pH 4.0) ), also known as PD-0332991, Ibrance, and 6-acetyl-8-cyclopentyl- 5-methyl-2- (5- (piperazin-1-yl) pyridin-2-ylamino) pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin- 7 (8H) -one hydrochloride, targets Cdk-4 (Cyclin D1) and Cdk-6 (Cyclin D2), enzymes that participate in the so-called CDK4/6-retinoblastoma signaling pathway governing the cell-cycle restriction point. Palbociclib induces rapid G1 cell-cycle arrest in primary human myeloma cells. This agent also shows significant efficacy in a broad spectrum of human tumor xenografts in vivo, resulting in complete regression in some tumors with no evidence of acquired resistance or ability to circumvent the growth inhibitory properties of this agent. Ibrance received FDA approval in 2015 for combined use with letrozole to treat postmenopausal women with estrogen receptor- positive, (HER2) -negative advanced breast cancer as an initial endocrine- based therapy for metastatic disease. Cyclin Target Selectivity: Cdk1 (weak, if any), Cdk2 (weak, if any), Cdk3 (weak, if any), Cdk4 (IC50 = 11 nM), Cdk5 (weak, if any), Cdk6 (IC50 = 16 nM), Cdk7 (weak, if any), Cdk8 (weak, if any), Cdk9 (weak, if any), Cdk10 (weak, if any).
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Antibacterials: concentration possibly increased by
clarithromycin - avoid or reduce palbociclib dose;
concentration reduced by rifampicin - avoid.
Antidepressants: concentration possibly reduced by
St John’s wort - avoid.
Antiepileptics: concentration possibly reduced by
carbamazepine, fosphenytoin and phenytoin - avoid.
Antifungals: concentration possibly increased
by itraconazole, ketoconazole, posaconazole and
voriconazole - avoid or reduce palbociclib dose.
Antipsychotics: increased risk of agranulocytosis
with clozapine - avoid.
Antivirals: concentration possibly increased by
indinavir, lopinavir, ritonavir, saquinavir and
telaprevir - avoid or reduce palbociclib dose.
Cytotoxics: concentration possibly reduced by
enzalutamide - avoid.
Grapefruit juice: concentration possibly increased -
avoid
Metabolism
Palbociclib is mainly hepatically transformed. the metabolism is mainly performed by the activities of the cytochrome P450 isoenzyme 3A and the sulfotransferase 2A1. The metabolism of palbociclib is represented mainly by reactions of oxidation and sulfonation followed by acylation and glucuronidation as minor reactions. After its metabolism, palbociclib forms mainly inactive glucuronide and sulfamic acid conjugates. The major circulating metabolite, accounting for 1.5% of the dose in excreta is is the glucuronide conjugate.
Metabolism
Palbociclib undergoes extensive hepatic metabolism.
The main metabolic pathways for palbociclib involved
oxidation and sulphonation, with acylation and
glucuronidation contributing as minor pathways.
Unchanged drug accounts for 2.3% and 6.9% of
radioactivity in faeces and urine, respectively. In faeces,
the sulfamic acid conjugate of palbociclib was the major
drug-related component, accounting for 26% of the
administered dose.
References
1) El-Rayes?et al.?(2004),?Cyclooxygenase-2-dependent and –independent effects of celecoxib in pancreatic cancer cell lines; Mol. Cancer Ther.,?3?1427 2) Menu?et al.?(2008),?A novel therapeutic combination using PD 0332991 and bortezomib: study in 5T33MM myeloma model; Cancer Res.,?68?5519 3) Valenzuela?et al.?(2017),?Palbociclib-induced autophagy and senescence in gastric cancer cells; Exp. Cell Res.,?360?390 4) Palanisamy?et al.?(2016),?Palbociclib: A new hope in the treatment of breast cancer; J. Cancer Res. Ther.,?12?1220 5) Goel?et al.?(2017),?CDK4/6 inhibition triggers anti-tumour immunity; Nature?548?471 6)6) AbuHammad?et al.?(2019),?Regulation of PRMT5-MDM4 axis is critical in the response to CDK4/6 inhibitors in melanoma; Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA?116?179909
Properties of Palbociclib
| Melting point: | 200 ºC |
| Boiling point: | 711.5±70.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.313±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | room temp |
| solubility | Soluble in DMSO (up to 2 mg/ml with warming) |
| pka | 8.66±0.10(Predicted) |
| form | powder |
| color | white to beige |
| Stability: | Stable for 1 year from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions in DMSO may be stored at -20°C for up to 1 month. |
Safety information for Palbociclib
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H341:Germ cell mutagenicity H373:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H411:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Palbociclib
Palbociclib manufacturer
Triveni Interchem Private Limited (Group Of Triveni Chemicals)
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![6-broMo-2-chloro-8-cyclopentyl-5-Methylpyrido[2,3-d]pyriMidin-7(8H)-one](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/1016636-76-2.gif)


You may like
-
 PD-0332991 99% (HPLC) CAS 571190-30-2View Details
PD-0332991 99% (HPLC) CAS 571190-30-2View Details
571190-30-2 -
 Palbociclib Cas 571190 30 2, Strength: 100 mgView Details
Palbociclib Cas 571190 30 2, Strength: 100 mgView Details
571190-30-2 -
 Palbociclib (125mg)(Palborest 125)View Details
Palbociclib (125mg)(Palborest 125)View Details
571190-30-2 -
 Palbociclib (Ibrance) C24H29N7O2View Details
Palbociclib (Ibrance) C24H29N7O2View Details
571190-30-2 -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4
