Niraparib
- CAS NO.:1038915-60-4
- Empirical Formula: C19H20N4O
- Molecular Weight: 320.39
- MDL number: MFCD17779309
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 20:33:22
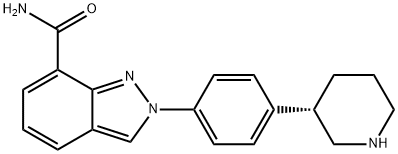
What is Niraparib?
Absorption
Following a single-dose administration of 300 mg niraparib, the mean (±SD) peak plasma concentration (Cmax) was 804 (±403) ng/mL. The exposure (Cmax and AUC) of niraparib increased in a dose-proportional manner with daily doses ranging from 30 mg (0.1 times the approved recommended dose) to 400 mg (1.3 times the approved recommended dose). The accumulation ratio of niraparib exposure following 21 days of repeated daily doses was approximately 2-fold for doses ranging from 30 to 400 mg. The Tmax is about three hours.
The absolute bioavailability of niraparib is approximately 73%. Food does not appear to affect drug exposure.
Toxicity
There is limited information available regarding the acute toxicity profile and overdosage of niraparib.
Description
(S)-2-(4-(piperidin-3-yl)phenyl)-2H-indazole-7-carboxamide is also known as MK-4827(Niraparib) tosylate is a selective inhibitor of PARP1/PARP2 (The poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase) with great activity in cancer cells with mutant BRCA-1 and BRCA-2. It has been recently approved by FDA for the maintenance treatment of adult patients with recurrent epithelial ovarian, fallopian tube, or primary peritoneal cancer who are in complete or partial response to platinum-based chemotherapy. In vitro studies have shown that niraparib-induced cytotoxicity may involve inhibition of PARP enzymatic activity and increased formation of PARP-DNA complexes resulting in DNA damage, apoptosis and cell death.
The Uses of Niraparib
Niraparib is a novel oral poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase (PARP) inhibitor efficacious in BRCA-1 and -2 mutant tumors.
Indications
Niraparib is indicated for the maintenance treatment of adult patients with advanced or recurrent epithelial ovarian, fallopian tube, or primary peritoneal cancer who are in complete or partial response to first-line platinum-based chemotherapy.
In Canada and the US, niraparib is also available in a combination product with abiraterone, which is indicated with prednisone for the treatment of adults with deleterious or suspected deleterious BRCA-mutated (BRCAm) metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC). In Canada, this combination product is also used with prednisolone and is reserved for patients who are asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic, and in whom chemotherapy is not clinically indicated.
Background
Niraparib is an orally active poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor. By blocking the enzymes responsible for DNA repair, niraparib induces cytotoxicity in cancer cells. Niraparib is selective towards PARP-1 and PARP-2. First approved by the FDA on March 27, 2017, niraparib is used to treat epithelial ovarian, fallopian tube, or primary peritoneal cancer. Niraparib was approved by the European Commission on November 16, 2017 and by Health Canada on June 27, 2019.
Definition
ChEBI: Niraparib is a 2-[4-(piperidin-3-yl)phenyl]-2H-indazole-7-carboxamide that has S-configuration. It is a potent inhibitor of PARP1 and PARP2 (IC50 of 3.8 and 2.1 nM, respectively) and approved as a first-line maintenance treatment for women with advanced ovarian cancer after responding to platinum-based chemotherapy. It has a role as an antineoplastic agent, an EC 2.4.2.30 (NAD(+) ADP-ribosyltransferase) inhibitor, a radiosensitizing agent and an apoptosis inducer.
Pharmacokinetics
Niraparib mediated cytotoxic effects in tumour cell lines with or without deficiencies in BRCA1/2. Decreased tumour growth was observed in both mouse xenograft models of human cancer cell lines with deficiencies in BRCA1/2 and human patient-derived xenograft tumour models with homologous recombination deficiency (HRD) that had either mutated or wild-type BRCA1/2.
In vitro studies suggest that niraparib inhibits dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin transporters, which may explain its off-target cardiovascular effects such as increased pulse rate and blood pressure.
Pharmacology
The synthesis and initial pharmacology of niraparib have been published. Niraparib has affinity for PARP 1 and 2 inhibition (IC50 = 3.8 and 2.1 nM, respectively) and inhibits the proliferation of cancer cells with mutant BRCA1 and BRCA2 with IC50 values in the 10–100 nM range in vitro. Niraparib demonstrated efficacy as a single agent in a xenograft model of BRCA1-deficient cancer. Niraparib has also been reported to act as a preclinical radiosensitiser and has entered into clinical oncology trials.
in vitro
mk-4827displayed excellent parp 1 and 2 inhibition with ic50 of 3.8 and 2.1 nm, respectively. in a whole cell assay, mk-4827 inhibited parp activity with ec50 of 4 nm. mk-4827 also inhibited proliferation of cancer cells with mutant brca-1 and brca-2 with cc50 in the 10-100 nm range[1].
in vivo
in a variety of human tumor xenografts of differing p53 status,mk-4827 showed high potential to improve the efficacy of radiotherapy,such as calu-6 (p53 null), a549 (p53 wild-type [wt]) and h-460 (p53 wt) lung cancers and triple negative mda-mb-231 human breast carcinoma [3].
Metabolism
Niraparib is primarily metabolized by carboxylesterases (CEs) to form M1, which is a major inactive metabolite. The M1 metabolite can subsequently undergo glucuronidation mediated by UDP-glucuronosyltransferases (UGTs) to form the M10 metabolite. In a mass balance study, M1 and M10 were the major circulating metabolites. The M1 metabolite can also undergo methylation, monooxygenation, and hydrogenation to form other minor metabolites.
References
https://newdrugapprovals.org/2016/12/22/niraparib-mk-4827/
https://www.fda.gov/drugs/informationondrugs/approveddrugs/ucm548487.htm
https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB11793
Sandhu, Shahneen K, et al. "The poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor niraparib (MK4827) in BRCA, mutation carriers and patients with sporadic cancer: a phase 1 dose-escalation trial." Lancet Oncology14.9 (2013):882.
Jones, P, et al. "Niraparib: A Poly (ADP-ribose) Polymerase (PARP) Inhibitor for the Treatment of Tumors with Defective Homologous Recombination. " Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 58.8(2015):3302-14.
Properties of Niraparib
| Melting point: | 187-189°C |
| Boiling point: | 463.6±45.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.34 |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C(protect from light) |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 15.36±0.30(Predicted) |
| color | Pale Yellow to Light Yellow |
Safety information for Niraparib
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H332:Acute toxicity,inhalation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Niraparib
Niraparib manufacturer
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![(S)-tert-butyl 2-(4-(4-chlorophenyl)-2,3,9-triMethyl-6H-thieno[3,2-f][1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a][1,4]diazepin-6-yl)acetate](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/1268524-70-4.gif)
You may like
-
 1038915-60-4 Niraparib 98%View Details
1038915-60-4 Niraparib 98%View Details
1038915-60-4 -
 1038915-60-4 98%View Details
1038915-60-4 98%View Details
1038915-60-4 -
 Veliparib Base 98%View Details
Veliparib Base 98%View Details
1038915-60-4 -
 Niraparib 99%View Details
Niraparib 99%View Details -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1