Nickel oxide
Synonym(s):NI516011;NI516030
- CAS NO.:1314-06-3
- Empirical Formula: Ni2O3
- Molecular Weight: 165.385
- MDL number: MFCD00011143
- EINECS: 215-217-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:57
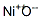
What is Nickel oxide?
Description
Nickel oxide (Ni2O3) is an important metal oxide used as a plating agent, surface treatment agent, and photocatalyst. Ni2O3 is also used as an electrode material in the manufacture of fuel cells and as a catalytic material in the production of electrolytic cells.
Chemical properties
solid
The Uses of Nickel oxide
Nickel oxide (NiO) is produced from nickel minerals to form nickel oxide when heated to 400°C, which is then reduced at a temperature of 600°C, resulting in the formation of nickel oxide. It is used as electrodes in fuel cells.
The Uses of Nickel oxide
Storage batteries.
The Uses of Nickel oxide
Nickel oxide is used in the ceramic industry for making frit, ferrites, and coloring porcelain. The oxide in sinter form is used in the production of nickel-steel alloys. It supplies oxygen to the melt for removal of carbon as carbon dioxide. Some other important uses of nickel oxide include preparation of many nickel salts, specialty chemicals, and nickel catalysts. It also is used as an electrode in fuel cells.
The Uses of Nickel oxide
Hazard
Confirmed carcinogen.
Industrial uses
Nickel produces a bluish-violet in potash glasses and a violet tending toward brown in soda glasses. Nickel rates as one of the more powerful colorants, since 1 part in 50,000 produces a recognizable tint. Nickel oxide is sometimes used to decolorize potash glass. Nickel oxide and nickel silicate have an advantage over manganese dioxide for decolorizing purposes in that they are not as sensitive in changing oxidizing and reducing environments.
Safety Profile
Confirmed human carcinogen. Poison by subcutaneous route. Mutation data reported. Hazardous reaction with hydrogen peroxide. Presence of the oxide increases the sensitivity of nitroalkanes (e.g., nitromethane, nitroethane, 1 -nitropropane) to heat. See also NICKEL COMPOUNDS and PEROXIDES.
Properties of Nickel oxide
| Melting point: | decomposes at ~600℃ [CRC10] |
| Density | 4.83 |
| solubility | insoluble in H2O; soluble in hot acid solutions |
| form | gray-black cubic crystals |
| color | gray-black cubic crystals, crystalline |
| Water Solubility | insoluble H2O; very slightly soluble cold acid; dissolves in hot HCl releasing Cl2; dissolves in hot H2SO4 or HNO3 evolving O2 [MER06] |
| Stability: | Stable. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 1314-06-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Nickel(III) oxide (1314-06-3) |
Safety information for Nickel oxide
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. |
Computed Descriptors for Nickel oxide
Nickel oxide manufacturer
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Nickel oxide CASView Details
Nickel oxide CASView Details -
 Nickel oxide CASView Details
Nickel oxide CASView Details -
 Nickel oxide CASView Details
Nickel oxide CASView Details -
 Nickel oxide CASView Details
Nickel oxide CASView Details -
 Nickel oxide CASView Details
Nickel oxide CASView Details -
 Nickel oxide CASView Details
Nickel oxide CASView Details -
 Nickel oxide CASView Details
Nickel oxide CASView Details -
 Nickel oxide CASView Details
Nickel oxide CASView Details