Nickle chloride
Synonym(s):Nickel chloride;Nickel dichloride;Nickel(II) chloride;Nickel(2+) chloride;Nickelous chloride
- CAS NO.:7718-54-9
- Empirical Formula: Cl2Ni
- Molecular Weight: 129.6
- MDL number: MFCD00011142
- EINECS: 231-743-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:14
What is Nickle chloride?
Description
Nickel chloride, NiCl2, is a water-soluble salt used in a variety of industries. It is typically produced and used either as an anhydrous salt or as a hydrate: nickel chloride hexahydrate as well as nickel chloride dihydrate. Nickel chloride is very rarely found in nature, and is produced via extraction from nickelcontaining ores via treatment with hydrochloric acid.
Chemical properties
Brown scales, deliquescent
Chemical properties
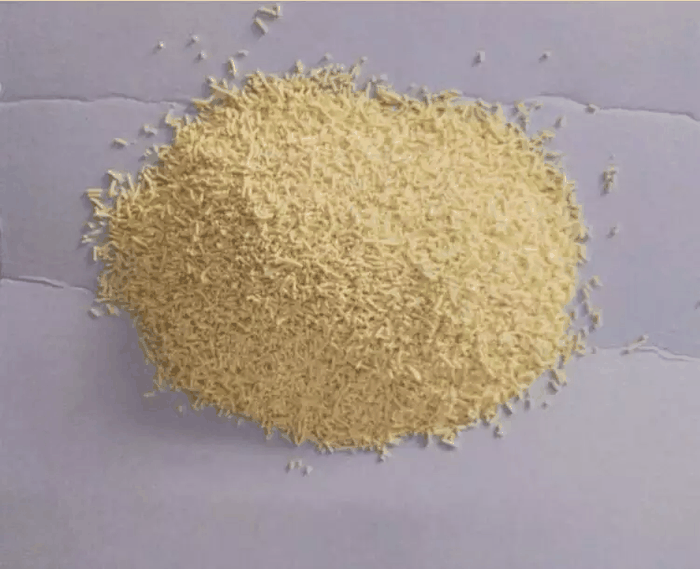
Nickel chloride appears as green or brown scales, or sparkling golden-yellow powder.
Physical properties
The anhydrous salt forms yellow crystal scales; deliquesces; density 3.55 g/cm3; melts at 1,001°C; sublimes at 973°C; highly soluble in water, 64 g/100mL at 20°C; soluble in alcohol.
The hexahydrate forms green monoclinic crystals; deliquesces; extremely soluble in water, 254 g/100mL at 20°C, and about 600 g/100 ml at 100°C; also very soluble in alcohol.
The Uses of Nickle chloride
Nickel chloride solutions are used for electroplating nickel onto other metal items.It also is used to prepare various nickel salts and nickel catalysts; and in industrial gas masks to protect from ammonia.
The Uses of Nickle chloride
Nickel chloride (NiCl2) is used for electroplating nickel onto the surfaces of other metals and as a chemical reagent in laboratories.
The Uses of Nickle chloride
Nickel chloride is used for nickel plating cast zinc, as an agent in electrolytic refining of nickel, as a chemical intermediate for nickel catalysts and complex nickel salts, as an absorber of ammonia gas in industrial gas masks, as a catalyst in diarylamine and silicon tetrachloride production, as an agent in electrodeless plating of nickel, as an agent in tin–nickel alloy plating, and as a fungicide for control of rust and rustlike disease. However, workers exposed to different forms of nickel have an elevated risk of lung cancer. Besides, Ni and its compounds (particularly insoluble compounds of nickel) have been reported to be potent carcinogens and toxic agents in humans and experimental animals. Therefore, Ni compounds are considered to be an industrial/occupational health hazard.
What are the applications of Application
Nickel(II) chloride is a useful halogenated metal used for synthesis
What are the applications of Application
Nickel(II) chloride anhydrous is used in semiconducting metal-containing polymer synthesis reactions
Definition
ChEBI: A compound of nickel and chloride in which the ratio of nickel (in the +2 oxidation state) to chloride is 1:2.
Nickel chloride is a yellow deliquescent solid with a boiling point of 973°C(1690°F). Nickel chloride is soluble in water and alcohol. Nickel chloride(hydrated),NiCI2·H20, is a gray deliquescent solid that is also soluble in water and alcohol.It is used in nickel plating.
Definition
hexahydrate: A crystalline compoundthat has six moles of waterper mole of compound.
Production Methods
Nickel chloride (hexahydrate) is obtained by reacting metal nickel powder or nickel oxide with hot, dilute hydrochloric acid.
Preparation
Nickel(II) chloride can be obtained by reaction of the elements either in a flow system at high temperatures or by reaction in ethanol at 20°. It is readily prepared in the laboratory by dehydration of the hexahydrate with thionyl chloride.
General Description
Nickel(II) chloride (NiCl2) is a nickel based halide that is prepared by burning nickel in chlorine. It is a water soluble compound that crystallizes to form a hexahydrate. It is majorly utilized in organic synthesis as a catalyst and a precursor.
Hazard
Confirmed carcinogen.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Safety Profile
Confirmed human carcinogen. Poison by ingestion, intravenous, intramuscular, and intraperitoneal routes. An experimental teratogen. Experimental reproductive effects. Mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of Cl-. See also NICICEL COMPOUNDS.
Potential Exposure
Nickel chloride is used in electroplating and ink manufacturing.
Environmental Fate
Nickel chloride is water soluble (642 g l-1 for anhydrous;
2540 g l-1 for hexahydrate) and would be expected to release
divalent nickel into the water. Since nickel chloride quickly
dissolves upon exposure to moist environments, and partially
due to the ubiquity of nickel in soil, water, and air, tracking the
course of the salt through the environment is difficult. This is
particularly due to nickel’s ability to complex with anionic
species other than chloride to form nickel oxide, sulfate, nitrate,
carbonate, or acetate, among others.
Industrial uses of nickel chloride result in nickel being
distributed mainly at soil surfaces and through surrounding
waterways and water tables. Once distributed to the soil, nickel
chloride produces nickel(II) ions to potentially form inorganic
crystalline minerals or precipitates, can complex or adsorb onto
organic and inorganic surfaces, can participate in cation
exchange, and can exist as free-ion or chelated metal complexes
in soil solution.
Shipping
UN3288 Toxic solids, inorganic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required.
Purification Methods
It crystallises from dilute HCl to form the green hexahydrate. At 70o this dehydrates to the tetrahydrate, and at higher temperatures it forms the anhydrous salt. It sublimes in yellow hexagonal scales in a stream of HCl. Store it in a desiccator as it is deliquescent. [Hart & Partington J Chem Soc 104 1943.]
Toxicity evaluation
The parent metal alters sodium balance and lipid metabolism; it induces metallothionein synthesis. Nickel chloride affects the T-cell portion of the immune system and suppresses the activity of natural killer cells. If given orally or by inhalation, nickel chloride has been reported to decrease iodine uptake by the thyroid gland. The lipid peroxidation properties of nickel can introduce potential malignancies in humans, as DNA strand gaps and breaks in DNA–protein cross-links can form. The downregulation of glycoprotein metabolism by nickel ions may produce nephrotoxicity in humans as well.
Incompatibilities
Strong acids, potassium, sulfur. Forms an impact-sensitive mixture with potassium.
Waste Disposal
Recycle or disposal in a chemical waste landfill is recommended.
Properties of Nickle chloride
| Melting point: | 1001 °C |
| Boiling point: | 987°C |
| Density | 3.55 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor pressure | 1.33 hPa (671 °C) |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | H2O: soluble |
| form | powder |
| color | Yellow to orange |
| Specific Gravity | 3.55 |
| PH | 4 (500g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| Water Solubility | slightly soluble |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| Merck | 14,6505 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 0.1 mg/m3 NIOSH: IDLH 10 mg/m3; TWA 0.015 mg/m3 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with peroxides. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7718-54-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Nickel dichloride(7718-54-9) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Nickel(II) chloride (7718-54-9) |
Safety information for Nickle chloride
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H317:Sensitisation, Skin H334:Sensitisation, respiratory H341:Germ cell mutagenicity H372:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. |
Computed Descriptors for Nickle chloride
| InChIKey | QMMRZOWCJAIUJA-UHFFFAOYSA-L |
Nickle chloride manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Nickel(II) chloride 98%View Details
Nickel(II) chloride 98%View Details -
 Nickel(II) chloride CAS 7718-54-9View Details
Nickel(II) chloride CAS 7718-54-9View Details
7718-54-9 -
 Nickel(II) chloride CAS 7718-54-9View Details
Nickel(II) chloride CAS 7718-54-9View Details
7718-54-9 -
 Nickel(II) chloride CAS 7718-54-9View Details
Nickel(II) chloride CAS 7718-54-9View Details
7718-54-9 -
 Nickel (II) chloride, Anhydrous CAS 7718-54-9View Details
Nickel (II) chloride, Anhydrous CAS 7718-54-9View Details
7718-54-9 -
 Nickel(II) chloride, anhydrous CAS 7718-54-9View Details
Nickel(II) chloride, anhydrous CAS 7718-54-9View Details
7718-54-9 -
 Nickel(II) chloride, anhydrous CAS 7718-54-9View Details
Nickel(II) chloride, anhydrous CAS 7718-54-9View Details
7718-54-9 -
 nickel chloride CASView Details
nickel chloride CASView Details
