Necrostatin-1
Synonym(s):5-(1H-Indol-3-ylmethyl)-3-methyl-2-thioxo-4-Imidazolidinone;5-(Indol-3-ylmethyl)-3-methyl-2-thio-Hydantoin;MTH-DL-Tryptophan;Necrostatin-1 - CAS 4311-88-0 - Calbiochem
- CAS NO.:4311-88-0
- Empirical Formula: C13H13N3OS
- Molecular Weight: 259.33
- MDL number: MFCD00056916
- EINECS: 200-256-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 20:33:22
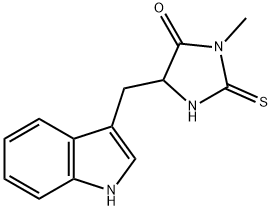
What is Necrostatin-1?
Description
Necrostatin-1 (4311-88-0) is an inhibitor of necroptosis (non-apoptotic cell death pathway; EC50 = 494 nM).1 It is an ATP-competitive death domain receptor-associated adaptor kinase (RIP1) inhibitor (EC50 = 182 nM).2 Necrostatin-1 displays a protective effect in a mouse model of ischemic brain injury1, inhibits myocardial cell death and reduces infarct size in various mouse heart models3 and inhibits glutamate-induced oxytosis in HT-22 cells4.
The Uses of Necrostatin-1
Necrostatin-1 is a specific RIP1 inhibitor and inhibits TNF-α-induced necroptosis with EC50 of 490 nM.
The Uses of Necrostatin-1
Necroptosis is a regulated caspase-independent cell death mechanism that results in morphological features resembling necrosis. Necrostatin-1 is an inhibitor of RIP1 kinase that prevents the death of TNF-α-treated FADD-deficient Jurkat cells. Necrostatin-1 has been used to investigate the pathological importance of necroptosis in ischemic brain injury and myocardial infarction.
What are the applications of Application
Necrostatin-1 is an inhibitor of the necroptosis cell death pathway
Definition
ChEBI: 5-(1H-indol-3-ylmethyl)-3-methyl-2-sulfanylidene-4-imidazolidinone is an organonitrogen compound and an organooxygen compound. It is functionally related to an alpha-amino acid.
Biological Activity
ATP-competitive death domain receptor-associated adaptor kinase (RIP1) allosteric inhibitor (EC 50 = 182 nM). Blocks non-apoptotic cell death via inhibition of a specific cellular pathway, necroptosis, which leads to necrosis (EC 50 = 494 nM). Reduces ischemic brain injury in a mouse model of stroke.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Necrostatin-1(Nec-1) might exhibit therapeutic benefit against patients with traumatic brain injury (TBI). In addition, it might also be used to treat other acute central nervous system (CNS) disorders that feature necroptosis as a mode of cell death. It is extensively used to study the effect of receptor-interacting protein kinase 1 (RIPK1) on cell death and inflammation in experimental disease models. Nec‐1 protects hippocampal (HT‐22) cells from glutamate‐induced oxytosis via increasing cellular glutathione (GSH) levels, decreasing reactive oxygen species production, inhibiting the nuclear translocation of apoptosis‐inducing factor and B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl‐2) /adenovirus E1B 19kDa‐interacting protein 3‐related pathways.
in vitro
previous study indicated that necrostatin-1 was a selective allosteric inhibitor of the death domain receptor–associated adaptor kinase rip1 in vitro. in this study, rip1 was found to be the primary cellular target responsible for the antinecroptosis activity of necrostatin-1. in addition, two other necrostatins, necrostatin-3 and necrostatin-5, were also shown to target the rip1 kinase step in the necroptosis pathway, but through different mechanism compared with that of necrostatin-1. the findings established necrostatins as the first-in-class inhibitors of rip1 kinase, the key upstream kinase involved in the activation of necroptosis [2].
in vivo
a previous study was designed to investigate the protective effects and mechanisms of nec-1 in concanavalin a-induced hepatitis in mice. it was found that in nec-1-treated mice the amelioration in liver functions and histopathological changes and the suppression of inflammatory cytokine production were observed. western blotting analyses showed that the expression of tnf-α, ifn-γ, il2, il6, and rip1 was significantly reduced in the nec-1-treated mice, which was further confirmed by immunofluorescence and immunohistochemistry. in addition, autophagosome formation was significantly reduced by nec-1 treatment. these results indicated that nec-1 could prevent concanavalin a -induced liver injury via rip1-related and autophagy-related pathways [3].
storage
Store at RT
References
1) Degterev, et al. (2005), Chemical inhibitor of nonapoptotic cell death with therapeutic potential for ischemic brain injury‘ Nature Chem. Biol., 1 112 2) Degterev et al. (2008) Identification of RIP1 kinase as a specific cellular target of necrostatins; Nature Chem. Biol., 4 313 3) Smith et.al. (2007), Necrostatin: a potentially novel cardioprotective agent?; Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther., 21 227 4) Xu et.al. (2007), Necrostatin-1 protects against glutamate-induced glutathione depletion and caspase-independent cell death in HT-22 cells; J. Neurochem., 103 2004
Properties of Necrostatin-1
| Melting point: | 151℃ |
| Boiling point: | 441.9±37.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.40±0.1 g/cm3 (20 ºC 760 Torr) |
| Flash point: | 93.3℃ |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | DMSO: >10 mg/mL |
| form | solid |
| pka | 9.46±0.40(Predicted) |
| color | Pale yellow |
| Sensitive | Light Sensitive |
| Stability: | Stable for 2 years from date of purchase as supplied.? Solutions in DMSO or ethanol may be stored at -20°C for up to 2 months. |
Safety information for Necrostatin-1
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H317:Sensitisation, Skin |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for Necrostatin-1
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Necrostatin-1 CAS 4311-88-0View Details
Necrostatin-1 CAS 4311-88-0View Details
4311-88-0 -
 Necrostatin-1 95% CAS 4311-88-0View Details
Necrostatin-1 95% CAS 4311-88-0View Details
4311-88-0 -
 Necrostatin-1 CAS 4311-88-0View Details
Necrostatin-1 CAS 4311-88-0View Details
4311-88-0 -
 Necrostatin-1 CAS 4311-88-0View Details
Necrostatin-1 CAS 4311-88-0View Details
4311-88-0 -
 Necrostatin-1 CASView Details
Necrostatin-1 CASView Details -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1