Propylthiouracil
Synonym(s):2,3-Dihydro-6-propyl-2-thioxo-4(1H)-pyrimidinone;4-Hydroxy-2-mercapto-6-propylpyrimidine;4-Propyl-2-thiouracil;6-Propyl-2-thiouracil
- CAS NO.:51-52-5
- Empirical Formula: C7H10N2OS
- Molecular Weight: 170.23
- MDL number: MFCD00006041
- EINECS: 200-103-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:30
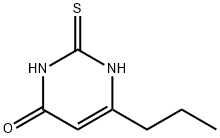
What is Propylthiouracil?
Absorption
Well absorbed following oral administration.
Toxicity
Oral, rat: LD50 = 1250 mg/kg.
Description
Propylthiouracil (PTU) is a thioamide antithyroid agent. It inhibits thyroid peroxidase activity in rat and monkey thyroid microsomes (IC50s = 0.081 and 4.1 μM, respectively). PTU (30 mg/kg) increases thyroid weight and serum thyroid stimulating hormone levels and decreases serum 3,5,3''-triiodothyronine and thyroxine levels in rats. Sensitivity to the bitter taste of PTU is genetically mediated and is associated with increased sensitivity to other sweet and bitter compounds. Formulations containing propylthiouracil have been used in the treatment of Graves'' disease and hyperthyroidism.
Chemical properties
White Crystalline Powder
Chemical properties
White crystalline solid or powder. Odorless. Bitter taste.
The Uses of Propylthiouracil
Antihyperthyroid. Has been used to promote fattening. This substance is reasonably anticipated to be a human carcinogen
The Uses of Propylthiouracil
antibacterial
The Uses of Propylthiouracil
Antihyperthyroid. Has been used to promote fattening. This substance is reasonably anticipated to be a human carcinogen.
Indications
Used to manage hyperthyroidism which is due to an overactive thyroid gland (Grave's disease).
Background
A thiourea antithyroid agent. Propythiouracil inhibits the synthesis of thyroxine and inhibits the peripheral conversion of throxine to tri-iodothyronine. It is used in the treatment of hyperthyroidism. (From Martindale, The Extra Pharmacopeoia, 30th ed, p534)
What are the applications of Application
6-Propyl-2-thiouracil is an inhibitor of DIO1
Definition
ChEBI: A pyrimidinethione consisting of uracil in which the 2-oxo group is substituted by a thio group and the hydrogen at position 6 is substituted by a propyl group.
General Description
Odorless white crystalline powder of starch-like appearance. Bitter taste. Saturated solution is neutral or slightly acid to litmus.
General Description
Propylthiouracil, 6-propyl-2-thiouracil (Propacil), is a stable, white, crystalline powderwith a bitter taste. It is slightly soluble in water but readilysoluble in alkaline solutions (salt formation).
Air & Water Reactions
Sensitive to light. May be sensitive to prolonged exposure to air. Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Propylthiouracil is incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong acids and strong bases. Forms complexes with divalent metals. Reacts with sulfhydryl-oxidizing agents . When reduced will produce hydrogen sulfide.
Hazard
Possible carcinogen.
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for Propylthiouracil are not available; however Propylthiouracil is probably combustible.
Biochem/physiol Actions
6-Propyl-2-thiouracil (6-PTU), a potential inhibitor of D1 iodothyronine deiodinase, is involved in the deiodination of iodothyronines. It is an uncompetitive inhibitor of iodothyronine substrates.
Mechanism of action
This drug has a pronounced thyrostatic effect and causes reduced thyroxine synthesis in the thyroid gland. It inhibits the process of iodination of thyroglobulin, reduces formation of the active form of iodine in the thyroid gland, and blocks the peroxidase system. Propylthiouracil is used for hyperthyrosis, thyrotoxic crises, and on thyrodectomia. Synonyms of this drug are propycil and tireostat.
Pharmacokinetics
Propylthiouracil is a thiourea antithyroid agent. Grave's disease is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism. It is an autoimmune disease where an individual's own antibodies attach to thyroid stimulating hormone receptors within cells of the thyroid gland and then trigger overproduction of thyroid hormone. The two thyroid hormones manufactured by the thyroid gland, thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), are formed by combining iodine and a protein called thyroglobulin with the assistance of an enzyme called peroxidase. PTU inhibits iodine and peroxidase from their normal interactions with thyroglobulin to form T4 and T3. This action decreases thyroid hormone production. PTU also interferes with the conversion of T4 to T3, and, since T3 is more potent than T4, this also reduces the activity of thyroid hormones. The actions and use of propylthiouracil are similar to those of methimazole.
Clinical Use
Propylthiouracil is useful in the treatment of hyperthyroidism.There is a delay in appearance of its effects because propylthiouracildoes not interfere with the activity of thyroid hormonesalready formed and stored in the thyroid gland. Thislag period may vary from several days to weeks, dependingon the condition of the patient. The need for three equallyspaced doses during a 24-hour period is often stressed, butevidence now indicates that a single daily dose is as effectiveas multiple daily doses in the treatment of most hyperthyroidpatients.
Safety Profile
Confirmed carcinogen with experimental carcinogenic, neoplastigenic, and tumorigenic data. Poison by intraperitoneal route. Moderately toxic by ingestion. Human systemic effects: agranulocytosis, hepatitis, jaundice. Human teratogenic effects by ingestion: developmental abnormalities of the endocrine system and changes in newborn viability. Human and experimental teratogenic and reproductive effects. Human mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of SO, and NO,. See also MERCAPTANS.
Synthesis
Propylthiouracil, 6-propyl-2-thio-2,4-(1H,3H)-pyrimidindione (25.2.2), is synthesized by condensating ethyl butyroacetate with thiourea in the presence of sodium ethoxide.

Potential Exposure
Medication (antihyperthyroid; thyroid inhibitor) with human and veterinary applications.
Carcinogenicity
Propylthiouracil is reasonably anticipated to be a human carcinogenbased on sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity from studies in experimental animals.
Metabolism
Not Available
Metabolism
Propylthiouracil undergoes rapid first-pass metabolism in the liver, and is mainly excreted in the urine as the glucuronic acid conjugate, with very little excreted as unchanged drug.
Shipping
UN3249 Medicine, solid, toxic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials.
Purification Methods
Purify propacil by recrystallisation from H2O (soluble in 900 parts at 20o, and 100 parts at 100o). UV, MeOH: max 277nm. [Anderson et al. J Am Chem Soc 67 2197 1945, Vanderhaegue Bull Soc Chim Belg 59 689 1950, Beilstein 24 III/IV 1333.]
Incompatibilities
This chemical is probably combustible; it’s dust may form explosive mixture with air. Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanga- nates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); con- tact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides. Forms complexes with divalent metals. Reacts with sulfhydryl-oxidizing agents . Sensitive to light and may be sensitive to air.
Waste Disposal
It is inappropriate and possi- bly dangerous to the environment to dispose of expired or waste pharmaceuticals by flushing them down the toilet or discarding to trash. Household quantities of expired or waste pharmaceuticals may be mixed with wet cat litter or coffee grounds, double-bagged in plastic, discard in trash. Larger quantities shall carefully take into consideration applicable DEA, EPA, and FDA regulations. If possible return the pharmaceutical to the manufacturer for proper disposal being careful to properly label and securely pack- age the material. Alternatively, the waste pharmaceutical shall be labeled, securely packaged and transported by a state licensed medical waste contractor to dispose by burial in a licensed hazardous or toxic waste landfill or incinerator.
Properties of Propylthiouracil
| Melting point: | 218-220 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 1.1880 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5960 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 300 °C |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | 1.1g/l |
| form | neat |
| pka | pKa 7.8; 8.3 (Uncertain) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White |
| PH | 6-7.5 (5g/l, H2O, 20℃)(slurry) |
| Water Solubility | 1.1 g/L |
| Merck | 14,7869 |
| BRN | 130039 |
| Stability: | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong acids, strong bases. Light sensitive. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 51-52-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 2B (Vol. Sup 7, 79) 2001 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Tegretol(51-52-5) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Propylthiouracil (51-52-5) |
Safety information for Propylthiouracil
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H351:Carcinogenicity |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for Propylthiouracil
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 6-Propyl-2-thiouracil CAS 51-52-5View Details
6-Propyl-2-thiouracil CAS 51-52-5View Details
51-52-5 -
 4-Propyl-2-thiouracil, 98% CAS 51-52-5View Details
4-Propyl-2-thiouracil, 98% CAS 51-52-5View Details
51-52-5 -
 Propylthiouracil 99% (HPLC) CAS 51-52-5View Details
Propylthiouracil 99% (HPLC) CAS 51-52-5View Details
51-52-5 -
 Propylthiouracil CAS 51-52-5View Details
Propylthiouracil CAS 51-52-5View Details
51-52-5 -
 Propylthiouracil CAS 51-52-5View Details
Propylthiouracil CAS 51-52-5View Details
51-52-5 -
 6-Propyl-2-thiouracil CAS 51-52-5View Details
6-Propyl-2-thiouracil CAS 51-52-5View Details
51-52-5 -
 Propylthiouracil CAS 51-52-5View Details
Propylthiouracil CAS 51-52-5View Details
51-52-5 -
 4-Propyl-2-thiouracil CAS 51-52-5View Details
4-Propyl-2-thiouracil CAS 51-52-5View Details
51-52-5