Moricizine
- CAS NO.:31883-05-3
- Empirical Formula: C22H25N3O4S
- Molecular Weight: 427.52
- MDL number: MFCD00336543
- EINECS: 250-854-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-10-23 13:36:13
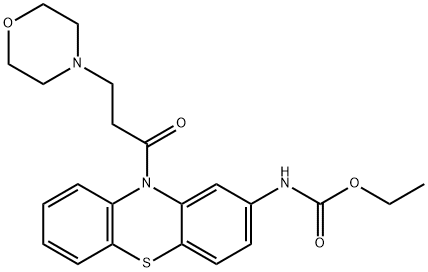
What is Moricizine?
Absorption
Well absorbed, absorption is complete within 2 to 3 hours. Significant first-pass metabolism results in an absolute bioavailability of approximately 38%. Administration within 30 minutes after a meal slows the rate, but does not affect the extent of absorption, although peak plasma concentrations are reduced.
Toxicity
Symptoms of overdose include vomiting, unconsciousness, and severe low blood pressure.
Originator
Ethmozine,Bristol-Myers Squibb
The Uses of Moricizine
Moricizine, is Phenothiazine (P318040) derivative, which It was used as an Antiarrhythmic agent. It is also shown that moracizine is effective in suppressing premature ventricular contractions, couplets, and nonsustained ventricular tachycardia.
The Uses of Moricizine
Cardiac depressant (anti-arrhythmic).
Background
An antiarrhythmia agent used primarily for ventricular rhythm disturbances.
Indications
Used to treat irregular heartbeats (arrhythmias) and maintain a normal heart rate.
Definition
ChEBI: A phenothiazine substituted on the nitrogen by a 3-(morpholin-4-yl)propanoyl group, and at position 2 by an (ethoxycarbonyl)amino group.
Manufacturing Process
To a solution of 10 g (0.035 mole) of ethyl phenthiazine-2-carbamate in 30 ml
of anhydrous toluene is added dropwise 5.3 g (0.042 mole) of 3-
chloropropionyl chloride, and the mixture is refluxed at 110-120°C for 4
hours, followed by clarifying the mixture with activated carbon and cooling it
to room temperature. A precipitate of ethyl 10-(3-chloropropionyl)-
phenthiazine-2-carbamate is removed by filtration. The yield is 10.2 g (77.5%
of the theoretical amount), M.P. 169-170°C.
10.2 g of ethyl 10-(3-chloropropionyl)-phenthiazine-2-carbamate ester is
dissolved in 50 ml of toluene, 4.72 g of morpholine is added thereto, and the
mixture is refluxed at 110-120°C for a period of 3 hours. A precipitate of
morpholine hydrochloride is removed by filtration, and the filtrate is washed
with water in order to remove excess morpholine, followed by acidulating with
dilute hydrochloric acid to adjust the pH of the filtrate is adjusted at 3. The
acidic aqueous layer is separated, clarified by treatment with activated carbon
and made alkaline until the pH equals 8-9. This procedure yields the free base
of ethyl 10-(β-morpholylpropionyl)-phenthiazine-2-carbamate, M.P. 156-
157°C.
The free base thus obtained is extracted with toluene, the extract is dried over
magnesium sulphate and to the anhydrous toluene solution is added an
anhydrous ethereal solution of hydrogen chloride until the precipitation of the
target compound is complete. This procedure yields 9.53 g (76.2% of the
theoretical amount) of ethyl 10-(β-morpholylpropionyl)-phenthiazine-2-
carbamate hydrochloride. After recrystallization from dichloroethane, the
target compound melts at 189°C. (decomp.).
brand name
Ethmozine (Roberts Pharmaceutical).
Therapeutic Function
Antiarrhythmic
General Description
Moricizine, ethyl 10-(3-morpholinopropionyl)phenothiazine-2-carbamate (Ethmozine), is aphenothiazine derivative used for the treatment of malignantventricular arrhythmias. It is categorized as a class ICantiarrhythmic agent, blocking the Na+ channel with 1:1stochiometry. The drug has higher affinity for the inactivatedstate than the activated or resting states. It appearsto bind to a site on the external side of the Na channelmembrane. It has been used to suppress life-threateningventricular arrhythmias.
Pharmacokinetics
Moricizine is used to treat irregular heartbeats (arrhythmias) and to maintain a normal heart rate. It acts on the heart muscle to improve the heart's rhythm. Moricizine has potent local anesthetic activity and membrane stabilizing effect. Decreases excitability, conduction velocity, and automaticity as a result of slowed atrioventricular (AV) nodal and His-Purkinje conduction. Decreases the action potential duration (APD) in Purkinje fibers; also decreases the effective refractory period (ERP) but to a lesser extent than the APD, so the ERP/APD ratio is increased. Decreases the maxiumum rate of Phase 0 depolarization (V max ), but does not affect action potential amplitude or maximum diastolic potential. Does not affect atrial, AV nodal, or left ventricular refractory periods and has minimal effect on ventricular repolarization (evidenced by the overall decrease in JT interval). Has no effect on sinoatrial (SA) nodal or intra-atrial conduction and only minimal effect on sinus cycle length and sinus node recovery time. In the Vaughan Williams classification of antiarrhythmics, moricizine is considered to be a class I agent. It has properties of class IA, IB, and IC agents but does not clearly belong to any of the three subclasses. It has less effect on the slope of phase 0 and a greater effect on action potential duration and effective refractory period than class IC agents.
Clinical Use
Moricizine (Ethmozine) is an antiarrhythmic used to
treat documented life-threatening arrhythmias.
Moricizine is indicated for the treatment of documented
ventricular arrhythmias, particularly sustained ventricular
tachycardia. Moricizine was evaluated in the CAST
II clinical trial for the prevention of postinfarction ventricular
premature complexes. It was ineffective and
found to be proarrhythmic. Patients in the moricizine
arm of the trial exhibited a greater incidence of sudden
cardiac death than did controls.
Side Effects
The principal adverse gastrointestinal effect of moricizine is nausea (7%). Abdominal discomfort has also been reported. Dizziness (11%) is the most frequently reported CNS-related adverse effect. Such reactions increase in frequency with prolonged drug administration. As with other antiarrhythmic drugs, moricizine has proarrhythmic activity, which may manifest as new ventricular ectopic beats or a worsening of preexisting ventricular arrhythmias. These effects are most common in patients with depressed left ventricular function and a history of congestive heart failure. Cardiovascular effects requiring drug withdrawal include conduction defects, sinus pauses, junctional rhythm, and A-V block.
Drug interactions
Clinically significant interactions with moricizine do not appear to exist.
Metabolism
Hepatic and extensive, to at least 26 metabolites, none accounting for as much as 1% of the administered dose. Two metabolites may be pharmacologically active but are present in extremely small quantities. Moricizine induces its own metabolism (it induces hepatic cytochrome P-450 activity).
Precautions
Patients with preexisting second- or third-degree A-V block, cardiogenic shock, or drug hypersensitivity should not be treated with moricizine.
Properties of Moricizine
| Melting point: | 156-157° |
| Boiling point: | 625.0±55.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.315±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | -20°C Freezer, Under inert atmosphere |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), Methanol (Very Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 6.4(at 25℃) |
| color | Pale Orange to Light Orange |
Safety information for Moricizine
Computed Descriptors for Moricizine
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1