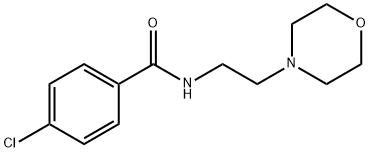
Moclobemide
Synonym(s):4-Chloro-N-[2-(4-morpholinyl)ethyl]benzamide;Aurorix;Moclamine
- CAS NO.:71320-77-9
- Empirical Formula: C13H17ClN2O2
- Molecular Weight: 268.74
- MDL number: MFCD00865388
- EINECS: 629-727-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
What is Moclobemide?
Absorption
Well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract (> 95%). The presence of food reduces the rate but not the extent of absorption. Hepatic first-pass metabolism reduces bioavailability to about 56% following administration of one dose, but increases to 90% with steady-state dosing as a result of saturation of the first pass effect. Peak plasma concentrations are reached within 0.3 - 1 hours following oral administration with a terminal half-life of 1.6h .
Toxicity
LD50 (mouse) is 730mg/kg and LD50 (rat) is 1,300mg/kg. Signs of toxicity include hypertension, drowsiness, dizziness, confusion, tremors, headache, agitation, muscle rigidity and seizures . The effects of moclobemide alone in overdose are negligible, even with high volume ingestion. However, moclobemide overdose with a serotonergic agent (even in small, therapeutic doses) can cause severe serotonin toxicity. The elimination half-life is prolonged by two to four times in overdose, compared with that found in healthy volunteers given therapeutic doses .
Description
Moclobemide is the first of a new generation of non-hydrazine, reversible MAO-A inhibitors useful in the treatment of depression. Moclobemide is a selective inhibitor of MAO-A, allowing tyramine to be metabolized by MAO-B. In controlled studies, moclobemide was clinically superior to desipramine and showed no cholinergic or cardiovascular side-effects. A metabolite is currently under investigation for treatment of Parkinson’s disease,.
Description
Moclobemide (Item No. 24361) is an analytical reference standard categorized as an antidepressant. This product is intended for research and forensic applications.
Chemical properties
White to Off-White Solid
Originator
Hoffmann-LaRoche (Switzerland)
The Uses of Moclobemide
A reversible monoamine oxidase inhibitor
The Uses of Moclobemide
Antidepressant;Mono amine oxidase inhibitor (Type A)
The Uses of Moclobemide
A reversible monoamine oxidase inhibitor.
Background
A reversible monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) selective for isoform A (RIMA) used to treat major depressive disorder. Most meta-analyses and most studies indicate that in the acute management of depression, moclobemide is more efficacious than placebo medication and similarly efficacious as tricyclic antidepressants (TCA) or selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). Due to negligible anticholinergic and antihistaminic actions, moclobemide has been better tolerated than tri- or heterocyclic antidepressants .
Indications
For the treatment of major depressive disorder and bipolar disorder .
What are the applications of Application
Moclobemide is a reversible monoamine oxidase inhibitor
Definition
ChEBI: A member of the class of benzamides that is benzamide substituted by a chloro group at position 4 and a 2-(morpholin-4-yl)ethyl group at the nitrogen atom. It acts as a reversible monoamine oxidase inhibitor and is used in the treatment of depression.
brand name
Aurorix
Biochem/physiol Actions
Moclobemide is a reversible monoamine oxidase A inhibitor (MAOI); antidepressant. Elimination half-life in humans = 1 -3 hrs; absolute oral bioavailability. Unlike other MAO inhibitors, does not significantly increase blood pressure in humans upon combination with tyramine.
Mechanism of action
Moclobemide is an RIMA that preferentially inhibits MAO-A (~80%) and, to a lesser extent, MAO-B (20–30%
inhibition), thereby increasing the concentration of 5-HT, NE, and other catecholamines in the synaptic cleft
and in storage sites. During chronic therapy with the MAOIs, adaptive changes at the noradrenergic and
serotonergic receptors occur (“downregulation”) as a result of neurotransmitter hypersensitivity because of
prolonged concentrations of NE and 5-HT at the postsynaptic receptor. This mechanism is likely the basis for its antidepressant activity. Inhibition
of MAO-A by moclobemide is short-acting (maximum, 24 hours) and reversible. This is in contrast to
phenelzine, which is nonselective, long-acting, and irreversible in its binding to MAO-A and MAO-B.
The pharmacokinetics for moclobemide are linear only up to 200 mg; at higher doses, nonlinear
pharmacokinetics are observed. Although well absorbed from the GI tract, the presence of food reduces
the rate but not the extent of absorption of moclobemide. Small quantities of moclobemide are distributed into
human breast milk. Moclobemide undergoes a complex metabolism, initially involving morpholine carbon and
nitrogen oxidation, deamination, and aromatic hydroxylation. The N-oxide and ring-opened metabolites retain
some in vitro MAO-A inhibition. Moclobemide is a weak inhibitor of CYP2D6 in vitro. It is extensively
metabolized in the liver by oxidation and is eliminated primarily into the urine as conjugates. Less than 1% of
an administered dose of moclobemide is eliminated unmetabolized.
Because moclobemide is partially metabolized by the polymorphic isozymes CYP2C19 and CYP2D6, plasma
concentrations of moclobenmide may be affected in patients who are poor metabolizers. In patients who are
slow metabolizers, the AUC for moclobemide was 1.5 times greater than the AUC in patients who are extensive metabolizers and receiving the same dose. This increase is within the normal range of variation (up to twofold) typically seen in patients.
Pharmacokinetics
A selective, reversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase (MAO) which increases the . Besides its presence in sympathetic nerves, there is an abundant evidence that MAO-A is localized in noradrenergic neurons in the locus coeruleus and MAO-B is closely associated with serotonergic neurons of the raphe nucleus .
Clinical Use
Reversible MAOI:
Depression
Social phobia
Drug interactions
Drug interactions for the RIMAs include interaction with SSRI antidepressants, which can cause the 5-HT syndrome. The effect of stimulant drugs, such as methylphenidate and dextroamphetamine (used to treat ADHD), may be increased. Some over-the-counter cold and hay fever decongestants (i.e., sympathomimetic amines) can have increased stimulant effects. Selegiline, a selective MAO-B used for Parkinson's disease, should not be used concurrently with the RIMAs. Unlike the irreversible MAOIs, no significant interactions with foods occur, because the selective inhibition of MAO-A does not stop the metabolism of tyramine. The RIMAs must not be taken concurrently with a nonreversible MAOI.
Metabolism
Moclobemide is almost completely metabolized in the liver by Cytochrome P450 2C19 and 2D6. Moclobemide is a substrate of CYP2C19. Although it acts as an inhibitor of CYP1A2, CYP2C19, and CYP2D6 .
Metabolism
Moclobemide is extensively metabolised in the liver, partly by the cytochrome P450 isoenzymes CYP2C19 and CYP2D6. Metabolites of moclobemide and a small amount of unchanged drug are excreted in the urine
storage
Room temperature
References
[1] pisani l, barletta m, soto-otero r, nicolotti o, mendez-alvarez e, catto m, introcaso a, stefanachi a, cellamare s, altomare c, carotti a. discovery, biological evaluation, and structure-activity and -selectivity relationships of 6'-substituted (e)-2-(benzofuran-3(2h)-ylidene)-n-methylacetamides, a novel class of potent and selective monoamine oxidase inhibitors. j med chem. 2013 mar 28;56(6):2651-64.
[2] nair np, ahmed sk, kin nm. biochemistry and pharmacology of reversible inhibitors of mao-a agents: focus on moclobemide. j psychiatry neurosci. 1993 nov;18(5):214-25.
Properties of Moclobemide
| Melting point: | 137°C |
| Boiling point: | 447.7±40.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.206±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | room temp |
| solubility | DMSO: >20mg/mL |
| form | solid |
| pka | 14.26±0.46(Predicted) |
| color | white |
| Merck | 14,6226 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 71320-77-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Moclobemide(71320-77-9) |
Safety information for Moclobemide
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. |
Computed Descriptors for Moclobemide
Moclobemide manufacturer
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 4-(3-chloropropyl)morpholine phenylhydrazine hydrochloride (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran




You may like
-
 71320-77-9 Moclobemide 98%View Details
71320-77-9 Moclobemide 98%View Details
71320-77-9 -
 Moclobemide CAS 71320-77-9View Details
Moclobemide CAS 71320-77-9View Details
71320-77-9 -
 Moclobemide CAS 71320-77-9View Details
Moclobemide CAS 71320-77-9View Details
71320-77-9 -
 (9H-fluoren-9-yl)methyl (2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl) carbonate 82911-69-1 98.0%View Details
(9H-fluoren-9-yl)methyl (2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl) carbonate 82911-69-1 98.0%View Details
82911-69-1 -
 13057-17-5 95.0%View Details
13057-17-5 95.0%View Details
13057-17-5 -
 4-bromoaniline 106-40-1 99.0%View Details
4-bromoaniline 106-40-1 99.0%View Details
106-40-1 -
 5-bromo-2-chlorobenzoic acid 99.0%View Details
5-bromo-2-chlorobenzoic acid 99.0%View Details
21739-92-4 -
 15761-38-3 97.0%View Details
15761-38-3 97.0%View Details
15761-38-3