Methylcyclohexane
Synonym(s):Hexahydrotoluene;Methylcyclohexane in dimethyl sulfoxide;Methylcyclohexane solution
- CAS NO.:108-87-2
- Empirical Formula: C7H14
- Molecular Weight: 98.19
- MDL number: MFCD00001497
- EINECS: 203-624-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
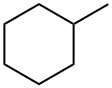
What is Methylcyclohexane?
Description
Methylcyclohexane, an alkene, is a colorless liquid with a faint benzene-like odor. The odor thre-shold is 630 ppm (this is above the OEL). Molecularweight = 98.21; Specific gravity (H2O:1)= 0.77; Boilingpoint = 101℃; Freezing/Melting point= - 127℃; Vaporpressure= 37 mmHg at 20℃; Flash point= - 3.9℃ (cc),- 5.9℃ (oc); Autoignition temperature = 258℃. Explosivelimits: LEL= 1.2%; UEL = 6.7%. Hazard Identification(based on NFPA-704 M Rating System): Health 2,Flammability 3, Reactivity 0. Insoluble in water.
Chemical properties
Methylcyclohexane, an alkene, is a colorless liquid with a faint benzene-like odor. The odor threshold is 630 ppm (this is above the OEL).
Physical properties
Clear colorless, very flammable liquid with a faint odor similar to benzene or cyclohexane. An odor threshold concentration of 150 ppbv was reported by Nagata and Takeuchi (1990).
The Uses of Methylcyclohexane
Methylcyclohexane is an environmentally friendly coating, mainly used as solvent for ink, rubber, paint, varnish, oil and grease extraction solvent, chromatographic analysis standard substance, also can be used in organic synthesis and analytical reagents.
The Uses of Methylcyclohexane
Solvent; starting material in the synthesis of toluene.
The Uses of Methylcyclohexane
Methylcyclohexane is used as a solvent and reagent in organic synthesis and polymer chemistry. It is a component of jet fuel and also used as correction fluid in certain consumer products. It acts as a starting material for toluene synthesis
Definition
ChEBI: Methylcyclohexane is a cycloalkane that is cyclohexane substituted by a single methyl group. It has a role as an aprotic solvent, a plant metabolite and a human metabolite. It is a cycloalkane and a volatile organic compound. It derives from a hydride of a cyclohexane.
What are the applications of Application
Methylcyclohexane is a methylated cyclohexane compound
Production Methods
Methylcyclohexane is separated by distillation from crude petroleum oils, and also produced by hydrogenation of toluene, reaction of benzene with methane, or acidic hydrocracking of polycyclic aromatics.
Synthesis Reference(s)
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 77, p. 5099, 1955 DOI: 10.1021/ja01624a044
The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 41, p. 1393, 1976 DOI: 10.1021/jo00870a022
General Description
A clear colorless liquid with a petroleum-like odor. Flash point 25°F. Less dense than water and insoluble in water. Vapors heavier than air.
Air & Water Reactions
Highly flammable. Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Saturated aliphatic hydrocarbons, such as Methylcyclohexane, may be incompatible with strong oxidizing agents like nitric acid. Charring of the hydrocarbon may occur followed by ignition of unreacted hydrocarbon and other nearby combustibles. In other settings, aliphatic saturated hydrocarbons are mostly unreactive. They are not affected by aqueous solutions of acids, alkalis, most oxidizing agents, and most reducing agents.
Hazard
Flammable, dangerous fire risk. Lowerexplosive limit 1.2% in air. Upper respiratory tractirritant, central nervous system impairment, liverand kidney damage.
Health Hazard
Harmful if inhaled or swallowed. Vapor or mist is irritating to the eyes, mucous membrane and upper respiratory tract and skin. Narcotic effects and dermititis.
Fire Hazard
Special Hazards of Combustion Products: Vapor may travel considerable distance to a source of ignition and flashback containing explosion may occur during fire conditions. Forms explosive mixtures in air.
Flammability and Explosibility
Highly flammable
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by ingestion. Mildly toxic by inhalation and skin contact. This material does not cause irritation to the eyes and nose, and, even at the level of 500 ppm, exhbits only a very faint odor. Therefore, it cannot be said to have any warning properties. It is believed to be about three times as toxic as hexane, and has caused death by tetanic spasm in animals. In sublethal concentrations, it causes narcosis and anesthesia. Dangerous fire hazard and moderate explosion hazard when exposed to heat, flame, or oxidzers. To fight fire, use foam, CO2, dry chemical. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and fumes.
Potential Exposure
Methylcyclohexane is used as a solvent for cellulose derivatives particularly with other solvents; and as an organic intermediate in organic synthesis. A component of jet fuel.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and inducevomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.
Source
Schauer et al. (1999) reported methylcyclohexane in a diesel-powered medium-duty truck
exhaust at an emission rate of 620 μg/km.
Schauer et al. (2001) measured organic compound emission rates for volatile organic
compounds, gas-phase semi-volatile organic compounds, and particle-phase organic compounds
from the residential (fireplace) combustion of pine, oak, and eucalyptus. The gas-phase emission
rate of methylcyclohexane was 8.6 mg/kg of pine burned. Emission rates of methylcyclohexane
were not measured during the combustion of oak and eucalyptus.
California Phase II reformulated gasoline contained methylcyclohexane at a concentration of
7.87 mg/kg. Gas-phase tailpipe emission rates from gasoline-powered automobiles with and
without catalytic converters were 1.86 and 274 mg/km, respectively (Schauer et al., 2002).
Environmental Fate
Biological. May be oxidized by microbes to 4-methylcyclohexanol, which may oxidize to give
4-methylcycloheptanone (Dugan, 1972).
Photolytic. Based on a photooxidation rate constant 1.04 x 10-11 cm3/molecule?sec for the
reaction of cyclohexane and OH radicals in the atmosphere at 298 K, the estimated lifetime of
methylcyclohexane is 13 h (Altshuller, 1991).
Chemical/Physical. Complete combustion in air produces carbon dioxide and water vapor.
Methycyclohexane will not hydrolyze in water because it does not contain a hydrolyzable
functional group.
Complete combustion in air yields carbon dioxide and water. Incomplete combustion also yields
carbon monoxide.
storage
Color Code—Red: Flammability Hazard: Store ina flammable liquid storage area or approved cabinet awayfrom ignition sources and corrosive and reactive materials.Methylcyclohexane must be stored to avoid contact withstrong oxidizers, (such as chlorine, bromine, chlorine oxide,nitrates and permanganates), since violent reactions occur.Before entering confined space where this chemical may bepresent, check to make sure that an explosive concentrationdoes not exist. Store in tightly closed containers in a cool,well-ventilated area away from heat. Sources of ignition,such as smoking and open flames, are prohibited wheremethylcyclohexane is handled, used, or stored. Metalcontainers involving the transfer of 5 gallons or more ofmethylcyclohexane should be grounded and bonded. Drumsmust be equipped with self-closing valves, pressure vacuumbungs, and flame arresters. Use only nonsparking tools andequipment, especially when opening and closing containersof methylcyclohexane
Shipping
UN2296 Methylcyclohexane, Hazard Class: 3; Labels: 3-Flammable liquid.
Purification Methods
Passage through a column of activated silica gel gives material transparent down to 220nm. It can also be purified by passage through a column of activated basic alumina, or by azeotropic distillation with MeOH, followed by washing out the MeOH with H2O, drying and distilling. Methylcyclohexane can be dried with CaSO4, CaH2 or sodium. It has also been purified by shaking with a mixture of conc H2SO4 and HNO3 in the cold, washing with H2O, drying with CaSO4 and fractionally distilling it from potassium. Percolation through a Celite column impregnated with 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine (DNPH), phosphoric acid and H2O (prepared by grinding 0.5g DNPH with 6mL 85% H3PO4, then mixing with 4mL of distilled H2O and 10g of Celite) removes carbonyl-containing impurities. [Cowan et al. J Chem Soc 1865 1939, Beilstein 5 III 65, 5 IV 94.]
Incompatibilities
Vapor may form explosive mixture with air. Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides. Attacks some plastics, rubber and coatings
Waste Disposal
Dissolve or mix the material with a combustible solvent and burn in a chemical incinerator equipped with an afterburner and scrubber. All federal, state, and local environmental regulations must be observed.
Properties of Methylcyclohexane
| Melting point: | -126 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 101 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 0.77 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| vapor density | 3.4 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 37 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 25 °F |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | Miscible with acetone, benzene, ether, carbon tetrachloride, ethanol, insoluble in water. |
| form | Liquid |
| color | Colorless |
| explosive limit | 1.1-6.7%(V) |
| Odor Threshold | 0.15ppm |
| Water Solubility | 0.1 g/L (20 ºC) |
| λmax | λ: 207 nm Amax: 1.00 λ: 221 nm Amax: 0.40 λ: 232 nm Amax: 0.15 λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.05 λ: 300-400 nm Amax: 0.01 |
| Merck | 14,6047 |
| BRN | 505972 |
| Henry's Law Constant | 0.0678 at 25.0 °C (Ramachandran et al., 1996) |
| Exposure limits | NIOSH REL: TWA 400 ppm (1,600 mg/m3), IDLH 1,200 ppm; OSHA PEL:
TWA 500 ppm (2,000 mg/m3); ACGIH TLV: TWA 400 ppm (adopted). |
| Dielectric constant | 2.1(25℃) |
| Stability: | Stable. Very flammable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 108-87-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Cyclohexane, methyl-(108-87-2) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Methylcyclohexane (108-87-2) |
Safety information for Methylcyclohexane
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H225:Flammable liquids H304:Aspiration hazard H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H336:Specific target organ toxicity,single exposure; Narcotic effects H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P233:Keep container tightly closed. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P331:Do NOT induce vomiting. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. |
Computed Descriptors for Methylcyclohexane
Methylcyclohexane manufacturer
New Products
1-Amino-1-cyclohexanecarboxylic acid Cycloleucine 6-Bromo-3-iodo-1-methyl-1H-indazole 3-(2,4-Dimethoxybenzyl)dihydropyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione 7-Bromo-1H-indazole ELECTROLYTIC IRON POWDER 2-Methyl-2-phenylpropyl acetate 1-Aminocyclobutanecarboxylic acid 1-(2-Ethoxyethyl)-2-(piperidin-4-yl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole hydrochloride Decanonitrile tert-butyl 4-(1H-benzo[d]iMidazol-2-yl)piperidine-1-carboxylate 4-Ethylbenzylamine Methyl 5-bromo-2-chloro-3-nitrobenzoate N-(5-Amino-2-methylphenyl)acetamide 2-Chloro-3-nitropyridine 5-Bromo-2,3-dimethoxypyridine methyl 6-chloro-2-(chloromethyl)nicotinate 2-methoxy-4-methyl-5-nitro pyridine 2-iodo-5-bromo pyridine 2-amino-4-methyl-5-nitro pyridine 5-Fluoro-2-Oxindole methyl L-alaninate hydrochloride diethyl L-glutamate hydrochloride Ethyl tosylcarbamateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Methylcyclohexane CAS 108-87-2View Details
Methylcyclohexane CAS 108-87-2View Details
108-87-2 -
 Methylcyclohexane CAS 108-87-2View Details
Methylcyclohexane CAS 108-87-2View Details
108-87-2 -
 Methyl Cyclohexane extrapure CAS 108-87-2View Details
Methyl Cyclohexane extrapure CAS 108-87-2View Details
108-87-2 -
 Methylcyclohexane CAS 108-87-2View Details
Methylcyclohexane CAS 108-87-2View Details
108-87-2 -
 Methyl cyclohexane, puriss, 99% CAS 108-87-2View Details
Methyl cyclohexane, puriss, 99% CAS 108-87-2View Details
108-87-2 -
 Methylcyclohexane CASView Details
Methylcyclohexane CASView Details -
 Methyl cyclohexane 99% CAS 108-87-2View Details
Methyl cyclohexane 99% CAS 108-87-2View Details
108-87-2 -
 Liquid Methylcyclo Hexane CAS 108-87-2View Details
Liquid Methylcyclo Hexane CAS 108-87-2View Details
108-87-2