Phenyl salicylate
Synonym(s):Phenyl salicylate;Salol
- CAS NO.:118-55-8
- Empirical Formula: C13H10O3
- Molecular Weight: 214.22
- MDL number: MFCD00002213
- EINECS: 204-259-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:50:40
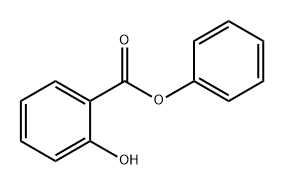
What is Phenyl salicylate?
Absorption
Rapidly absorbed. Refer to Aspirin for detailed salicylate absorption information.
Toxicity
Oral LD50 in the rat is 3000 mg/kg
Adverse effects can be divided into several categories , :
Eyes: irritation
Skin: skin irritation
Cardiovascular: rapid pulse, flushing
Central Nervous System —blurred vision, dizziness
Respiratory —shortness of breath or troubled breathing , irritation of respiratory system
Genitourinary —difficult micturition, acute urinary retention
Gastrointestinal —dry mouth, nausea/vomiting
Overdosage may be managed by inducing emesis or gastric lavage. Slow intravenous administration of physostigmine in doses of 1 to 4 mg (0.5 to 1 mg in children) repeated as needed in 1-2 h to relieve severe antimuscarinic symptoms. Administration of small doses of diazepam to control excitement and seizures may be warranted. Artificial respiration with oxygen can be used if needed for respiratory depression. Adequate hydration is important, as well as symptomatic treatment, provided as necessary .
Description
Phenyl salicylate, also referred to as salol, is a member of the hydroxybenzoic acid family of organic compounds. Its chemical formula is C13H10O3. It is manufactured through the chemical reaction between phenol and salicylic acid. Phenyl salicylate is a good antiseptic that is used in the production of toothpaste. It has several medical properties, including its ability to act as an analgesic, anti-septic with antibacterial properties, and antipyretic to reduce fever. Additionally, it can be utilized for treating lower urinary tract inflammation. Although it is no longer widely used in human medicine, it is still employed in veterinary medicine.
Chemical properties
Phenyl salicylate is a white crystalline solid that has a balsamic type odor. It readily dissolves in ether, benzene, and chloroform, and can be dissolved in ethanol, but is almost insoluble in water and glycerol.
The Uses of Phenyl salicylate
Phenyl salicylate is used as an analgesic and antipyretic. It is also used in the manufacture of polymer plastics, lacquers, waxes, polishes, adhesives, and sunscreen products(suntan oils and cremes). As light absorber to prevent discoloration of plastics. It is also a fragrance ingredient, but has limited use. in veterinary use as an external disinfectant and intestinal antiseptic agent.
Indications
Pain and fever .
Background
Phenyl salicylate is a 2-hydroxybenzoic acid phenyl ester. It is utilized in some manufacturing processes of polymers, lacquers, adhesives, waxes, as well as polishes. It is an active ingredient in some pharmaceutical products as a mild analgesic for pain relief by releasing salicylate (found in Aspirin ). Phenyl salicylate may also be found in some antiseptic agents . It is synthesized by heating salicylic acid with phenol , .
Phenyl salicylate is used as a food additive in the USA .
This compound belongs to the class of organic compounds known as depsides and depsidones. These are polycyclic compounds that is either a polyphenolic compound composed of two or more monocyclic aromatic units linked by an ester bond (depside), or a compound containing the depsidone structure (depsidone) .
Definition
ChEBI: Phenyl salicylate is a benzoate ester that is the phenyl ester of salicylic acid. Also known as salol, it can be formed by heating salicylic acid with phenol and is used in the manufacture of some polymers, lacquers, adhesives, waxes and polishes. It has a role as an ultraviolet filter. It is a benzoate ester, a member of phenols and a member of salicylates. It derives from a salicylic acid.
Preparation
Phenyl salicylate was synthesized by esterification of salicylic acid and phenol in the presence of catalyst sulfuric acid. The esterification liquid is neutralized, washed with water and distilled to obtain the finished product. It also can preparation by the action of phosphorus oxychloride on a mixture of phenol and salicylic acid (Merck Index, 1968).
Taste threshold values
Sweet, mildly medicinal taste at concentrations near 50 ppm.
Toxicity evaluation
The acute oral LD50 value in rats was reported as 3 g/kg and the acute dermal LD50 value in rabbits exceeded 5 g/kg (Levenstein, 1975). The probable LD in man is 50-500 mg/kg. The toxic effects of phenyl salicylate are similar to those of phenol but do not include a corrosive action on the alimentary canal (Dittmer, 1959).
General Description
Phenyl salicylate is a phenyl ester of salicylic acid and is used as a medicine under the name ′salol′ as an internal antiseptic. It finds its application in paints, waxes, and varnishes as it is found to absorb UV radiation in the range of 290-325 nm. It also shows its presence in cosmetics and sunscreens as a UV filter.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Incompatible with bromine water, ferric salts, camphor, phenol, chloral hydrate, monobrominated camphor, thymol, or urethane in trituration. .
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for Phenyl salicylate are not available, however Phenyl salicylate is probably combustible.
Pharmacokinetics
Phenyl salicylate has several medical uses. It can be used as an analgesic to relieve pain, as an antiseptic with antibacterial effect as well as a kind of antipyretic for the treatment of fever. It is also used for the treatment of inflammation in the lower urinary tract. It is no longer commonly applied to human medical practice but is still used in veterinary medicine .
When it is combined with methenamine, benzoic acid, phenyl salicylate, methylene blue, and hyoscyamine sulfate, it is used to relieve the discomfort, pain, frequent urge to urinate, and cramps/spasms of the urinary tract caused by a urinary tract infection or a diagnostic procedure .
Pharmacology
Phenyl salicylate was found to have slight analgesic activity against pain stimuli in mice (Kameyama, 1961), but ip administration of 500 mg/kg showed no analgesic action against an electric shock applied to the tails of mice (McKenzie & Beechey, 1962). In vitro studies on cartilage and rat-liver mitochondria have shown that phenyl salicylates are more active than salicylates in uncoupling oxidative phosphorylation (Bostrom, Berntsen & Whitehouse, 1964).
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by ingestion. Experimental teratogenic and reproductive effects. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes. See also ESTERS
Metabolism
Hydrolyzed to salicylic acid . Salicylic acid elimination kinetics are dependent on drug concentration because of the limited capacity of two major biotransformation pathways: formation of salicyluric acid and of salicyl phenolic glucuronide.
Metabolism of this drug occurs mainly in the liver, like other salicylates .
Metabolism of salicylic acid occurs through glucuronide formation (to produce salicyluric acid), and salicyl phenolic glucuronide), conjugation with glycine (to produce salicyluric acid), and oxidation to form gentisic acid. The rate of formation of salicyl phenolic glucuronide and salicyluric acid are easily saturated at low salicylic acid concentrations and their formation can be described by Michaelis-Menten kinetics .
Metabolism
According to Baas (1890) from 44 to 96% of a dose (5-8 g) of phenyl salicylate is hydrolysed in man and none of it is found in the faeces. An increase in the ethereal sulphates of the urine after its ingestion is due, no doubt, to the phenol liberated (Williams, 1959). Phenyl salicylate is hydrolysed in the gut primarily to phenol and salicylic acid, which are rapidly absorbed and excreted (Fassett, 1963), but it was not hydrolysed by a partially purified preparation of acetylarylesterase from human plasma (Augustinsson & Ekedahl, 1962). Intestinal absorption and excretion of orally administered phenyl salicylate were studied in rabbits and dogs by analysis of blood and urine samples; oral administration of glucosamine hydrochloride increased the blood concentration of phenyl salicylate but had little effect on urinary excretion (Tanaka, Kojima & Matsubara, 1961).
Purification Methods
Fractionally crystallise salol from its melt, then crystallise it from *benzene. [Beilstein 10 IV 154.]
References
https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Phenyl_salicylate
http://www.wisegeek.com/what-are-the-medical-uses-of-phenyl-salicylate.htm
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phenyl_salicylate
https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/SG/en/product/sial/phr1152
Properties of Phenyl salicylate
| Melting point: | 41-43 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 172-173 °C/12 mmHg (lit.) |
| Density | 1.250g/cm3 |
| refractive index | 1.5090 (estimate) |
| FEMA | 3960 | PHENYL SALICYLATE |
| Flash point: | >230 °F |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | dioxane: 0.1 g/mL, clear, colorless |
| form | Fine Crystalline Powder |
| pka | 8.71±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | White |
| Odor | at 100.00 %. mild sweet fruity balsam |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in alcohol, ether, chloroform, turpentine, acetone and benzene. Sparingly soluble in chloroformbenzene. Insoluble in water. |
| JECFA Number | 736 |
| Merck | 14,7310 |
| BRN | 393969 |
| Dielectric constant | 6.3(50.0℃) |
| Stability: | Light sensitive. Incompatible with strong oxidants. Flammable. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 118-55-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Benzoic acid, 2-hydroxy-, phenyl ester(118-55-8) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Phenyl salicylate (118-55-8) |
Safety information for Phenyl salicylate
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H317:Sensitisation, Skin H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H411:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Phenyl salicylate
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 118-55-8 98%View Details
118-55-8 98%View Details
118-55-8 -
 Phenyl Salicylate CAS 118-55-8View Details
Phenyl Salicylate CAS 118-55-8View Details
118-55-8 -
 Phenyl salicylate CAS 118-55-8View Details
Phenyl salicylate CAS 118-55-8View Details
118-55-8 -
 Phenyl salicylate 99% (HPLC) CAS 118-55-8View Details
Phenyl salicylate 99% (HPLC) CAS 118-55-8View Details
118-55-8 -
 Phenyl Salicylate CAS 118-55-8View Details
Phenyl Salicylate CAS 118-55-8View Details
118-55-8 -
 Phenyl Salicylate (Salol) extrapure CAS 118-55-8View Details
Phenyl Salicylate (Salol) extrapure CAS 118-55-8View Details
118-55-8 -
 Mettler-Toledo Calibration substance ME 30034252, Phenyl salicylate CAS 118-55-8View Details
Mettler-Toledo Calibration substance ME 30034252, Phenyl salicylate CAS 118-55-8View Details
118-55-8 -
 Phenyl salicylate CAS 118-55-8View Details
Phenyl salicylate CAS 118-55-8View Details
118-55-8
