Meropenem
Synonym(s):(1R,5S,6S)-2-[(3S,5S)-5-(dimethylaminocarbonyl)pyrrolidin-3-ylthio]-6-[(R)-1-hydroxyethyl]-1-methylcarbapen-2-em-3-carboxylic acid trihydrate;Meropenem trihydrate
- CAS NO.:96036-03-2
- Empirical Formula: C17H25N3O5S
- Molecular Weight: 383.46
- MDL number: MFCD00864966
- EINECS: 641-424-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:30
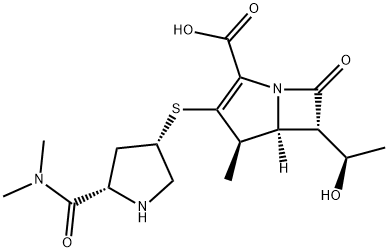
What is Meropenem?
Toxicity
In mice and rats, large intravenous doses of meropenem (2200-4000 mg/kg) have been associated with ataxia, dyspnea, convulsions, and mortalities.
Description
Meropenem is a new carbapenem antibiotic introduced to market for the i.v. treatment of a wide variety of hospital infections such as lower respiratory tract, urinary tract, intraabdominal, gynecological and polymicrobial infections. Meropenem has a broad spectrum of antibacterial activity against most clinically important Gram-positive and Gramnegative aerobic and anaerobic bacteria with especially high potency against multiresistant Enterobacteriaceae and Pseudornonas aeruginosa. Compared with imipenem, the only other available carbapenem antibiotic, meropenem has the advantage of being dehydropeptidase 1 (DHP-1) stable and therefore does not need to be administered in conjunction with the DHP-1 inhibitor cilastatin. Meropenem is also being evaluated for treatment of resistant pseudomonal infections in cystic fibrosis patients.
Chemical properties
1KG;
Originator
Sumitomo (Japan)
The Uses of Meropenem
Meropenem, is an ultra-broad spectrum injectable antibiotic used to treat a wide variety of infections, including meningitis and pneumonia.
The Uses of Meropenem
antineoplastic, PDGF receptor blocker, immunomodulator
Indications
For use as single agent therapy for the treatment of the following infections when caused by susceptible isolates of the designated microorganisms: complicated skin and skin structure infections due to Staphylococcus aureus (b-lactamase and non-b-lactamase producing, methicillin-susceptible isolates only), Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus agalactiae, viridans group streptococci, Enterococcus faecalis (excluding vancomycin-resistant isolates), Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli, Proteus mirabilis, Bacteroides fragilis and Peptostreptococcus species; complicated appendicitis and peritonitis caused by viridans group streptococci, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Bacteroides fragilis, B. thetaiotaomicron, and Peptostreptococcus species. Also for use in the treatment of bacterial meningitis caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae (b-lactamase and non-b-lactamase-producing isolates), and Neisseria meningitidis.
Background
Meropenem is a broad-spectrum carbapenem antibiotic. It is active against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Meropenem exerts its action by penetrating bacterial cells readily and interfering with the synthesis of vital cell wall components, which leads to cell death.
In August 2017, a combination antibacterial therapy under the market name vabomere was approved for treatment of adult patients with complicated urinary tract infections (cUTI). Vabomere consists of meropenem and Vaborbactam and is intravenously admininstered. The treatment aims to resolve infection-related symptoms and achieve negative urine culture, where the infections are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria.
What are the applications of Application
Meropenem is an antibiotic of the carbapenem subclass that has a high affinity for cell wall-synthesizing enzymes
Definition
ChEBI: Meropenem is a carbapenemcarboxylic acid in which the azetidine and pyrroline rings carry 1-hydroxymethyl and in which the azetidine and pyrroline rings carry 1-hydroxymethyl and 5-(dimethylcarbamoyl)pyrrolidin-3-ylthio substituents respectively. It has a role as an antibacterial drug, an antibacterial agent and a drug allergen. It is a carbapenemcarboxylic acid, a pyrrolidinecarboxamide, an alpha,beta-unsaturated monocarboxylic acid and an organic sulfide.
Manufacturing Process
3.10 g of trans-1-(p-nitrobenzyloxycarbonyl)-4-hydroxy-L-proline and 1.10 g of triethylamine were dissolved in 40 ml of dried tetrahydrofuran, and a solution of 1.20 g of ethyl chloroformate in 10 ml of dried tetrahydrofuran was added dropwise thereto at -25-35°C. After stirring at the same temperature for 50 min, 10 ml of concentrated aqueous ammonia was added dropwise to the mixture at -25-40°C. The temperature was then gradually elevated to room temperature, and the reaction mixture was stirred for 1 hour, followed by concentration under reduced pressure. To the residue were added 20 ml of water and 50 ml of diethyl ether. After ice-cooling, the thus formed white crystals were separated by filtration, washed successively with cool water and cool diethyl ether, and dried under reduced pressure to yield trans-1-(pnitrobenzyloxycarbonyl)-4-hydroxy-L-prolineamide. Melting point: 163.3-164.0°C.
A solution of 1.89 g of methanesulfonyl chloride in 10 ml of dried
tetrahydrofuran was added dropwise to a suspension of 2.32 g of trans-1-(pnitrobenzyloxycarbonyl)-4-hydroxy-L-prolineamide and 1.67 g of triethylamine
in 40 ml of dried tetrahydrofuran at room temperature. After stirring for 1
hour, the reaction mixture was concentrated under reduced pressure, and to
the residue were added 30 ml of water and 30 ml of diethyl ether. After
cooling, the resulting white crystals were separated by filtration, washed
successively with cool water and cool diethyl ether and dried under reduced
pressure to obtain trans-1-(p-nitrobenzyloxycarbonyl)-4-methanesulfonyloxyL-prolineamide. Melting point: 149.5-151°C.
A solution of 642 mg of thioacetic acid in 14 ml of dried dimethylformamide
was added to a suspension of 374 mg of 50% sodium hydride in 13 ml of
dried dimethylformamide in a nitrogen stream, followed by stirring at room
temperature for 25 minutes. To the mixture were added 975 mg of sodium
iodide and then a solution of 2.52 g of trans-1-(p-nitrobenzyloxycarbonyl)-4-
methanesulfonyloxy-L-prolineamide in 12 ml of dried dimethylformamide, and
the resulting mixture was heated to 70°C for 6 hours while stirring. The
reaction mixture was poured into a cool aqueous solution of sodium chloride
and extracted with benzene. The extract was washed successively with a 10%
aqueous solution of sodium sulfate and a sodium chloride aqueous solution,
dried over sodium sulfate and distilled off to remove the solvent. The resulting
crude crystals were washed with a warm mixed solvent of tetrahydrofuran and
benzene to obtain (2S,4S)-1-(p-nitrobenzyloxycarbonyl)- 2-carbamoyl-4-
acetylthio-L-prolineamide. Melting point: 168.5-169.5°C.
950 mg of (2S,4S)-1-(p-nitrobenzyloxycarbonyl)-2-carbamoyl-4-
acetylthiopyrrolidine was dissolved in 95 ml of methanol, and 2.59 ml of a 1 N
aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide was added thereto at room temperature
in an argon stream, followed by stirring at that temperature for 15 min. The
reaction mixture was neutralized with 2.59 ml of a 1 N aqueous solution of
hydrochloric acid and distilled off under reduced pressure to remove the
methanol. The thus precipitated crystals were filtered and washed with water
to obtain (2S,4S)-1-(p-nitrobenzyloxycarbonyl)-2-carbamoyl-4-
mercaptopyrrolidine. Melting point: 158-162°C.
To 1.33 g (20 mM) of activated zinc was added 20 ml of dried
tetrahydrofuran, and 8.8 ml of a 15% n-hexane solution of diethylaluminium
chloride was added thereto in a nitrogen stream under ice-cooling. A solution
prepared by dissolving 1.49 g (5.2 mM) of (3R,4R)-4-acetoxy-3-[(R)-1-(tbutyldimethylsilyloxy)ethyl]-2-azetidinone and 3.73 g (15.3 mM) of benzyl-αbromopropionate in 13.3 ml of dried tetrahydrofuran was added dropwise to
the mixture over a period of 30 to 40 min, followed by stirring for 1 hours.
Under ice-cooling, 2.8 ml of pyridine, 13.2 ml of water, 26.5 ml of ethyl
acetate and 13.2 ml of a 1 N hydrochloric acid aqueous solution were
successively added thereto, and the resulting mixture was filtered using
Celite. The filtrate was washed with water, and the organic layer was dried
over sodium sulfate and distilled off to remove the solvent. The resulting oily
residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to obtain an
isomeric mixture of 4-(1-benzyloxycarbonyl)ethyl-3-[(R)-1-(tbutyldimethylsilyloxy)ethyl]-2-azetidinone.
The isomeric mixture was separated into each compound by Lober column
chromatography using silica gel and 1.5% isopropanol/n-hexane as an eluent
to obtain the compound (1a) and the compound (1b) as oily substances.
200 mg of 4-(1-benzyloxycarbonyl)ethyl-3-[(R)-1-(t-butyl-dimethylsilyloxy)
ethyl]-2-azetidinone (1a) was dissolved in 2 ml of dried dimethylformamide.
126 mg of triethylamine was added to the resulting solution, and then 151 mg
of t-butyldimethylsilyl chloride was added thereto, followed by stirring at room
temperature overnight. The reaction mixture was diluted with ethyl acetate,
washed with water, dried over sodium sulfate and purified by silica gel
chromatography to obtain 4-(1-benzyloxycarbonyl)ethyl-3-[(R)-1-(tbutyldimethylsilyloxy)ethyl]-1-(t-butyldimethylsilyl)-2-azetidinone (2a).
184 mg of (2a) was dissolved in 4 ml of methanol, and the resulting solution
was stirred together with 20 mg of 10% palladium-on-carbon at an
atmospheric pressure of hydrogen for 2 hours. The catalyst was removed by
filtration, and the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure to obtain
4-(1-carboxy)ethyl-3-[(R)-1-(t-butyldimethylsilyloxy)ethyl]-1-(tbutyldimethylsilyl)-2-azetidinone (3a).
(4R,5R,6S,8R)-p-Nitrobenzyl-4-methyl-6-(1-hydroxyethyl)-1-azabicyclo
[3.2.0]-hept-3,7-dione-2-carboxylate was obtained from 170 mg of 4-(1-
carboxy)ethyl-3-[(R)-1-(t-butyldimethylsilyloxy)ethyl]-1-(t-butyldimethylsilyl)-
2-azetidinone (3a) according to the method described in Japanese Patent
Application OPI No. 26887/83, pages 64-65.
(a) 53 mg of (4R,5R,6S,8R)-p-nitrobenzyl-4-methyl-6-(1-hydroxyethyl)-1-
azabicyclo[3,2,0 ]-hept-3,7-dione-2-carboxylate was dissolved in 5 ml of dry
acetonitrile, and 57 mg of diisopropylethylamine and then 43 mg of diphenyl
chlorophosphate were added thereto. After stirring for 2.5 hours, 57 mg of
[2S,4S]-1-p-nitrobenzyloxycarbonyl-2-dimethylaminocarbonyl-4-
mercaptopyrrolidine was added to the mixture, followed by stirring for 1 hour.
The reaction solution was diluted with ethyl acetate, washed with water, dried
over magnesium sulfate and the solvent was distilled off. The residue was
purified by silica gel thin layer chromatography to obtain 35 mg of
(4R,5S,6S,8R,2'S,4'S)-p-nitrobenzyl-3-[4-(1-p-nitrobenzyloxycarbonyl-2-
dimethylaminecarbonyl)pyrrolidinylthio]-4-methyl-6-(1-hydroxyethyl)-1-
azabicyclo[3,2,0]-hept-2-ene-7-one-2-carboxylate.
(b) 25 mg of (4R,5S,6S,8R,2'S,4'S)-p-nitrobenzyl-3-[4-(1-pnitrobenzyloxycarbonyl-2-dimethylaminecarbonyl)pyrrolidinylthio]-4-methyl-6-
(1-hydroxyethyl)-1-azabicyclo[3,2,0]hept-2-ene-7-one-2-carboxylate was
dissolved in a mixture of 1.9 ml of tetrahydrofuran and 0.3 ml of ethanol, and
the mixture was hydrogenated in a morpholinopropanesulfonic acid buffer
solution (pH = 7.0, 1.9 ml) under atmospheric pressure of hydrogen for 3
hours at room temperature in the presence of 30 mg of 10% palladiumcarbon, which had been activated in hydrogen atmosphere for 1 hour followed
by washing with water. After filtering off the catalyst, tetrahydrofuran and
ethanol were distilled off under reduced pressure, and the residual solution
was washed with ethyl acetate. The aqueous layer was again distilled under
reduced pressure to remove organic solvents, and the residual solution was
subjected to polymer chromatography (CHP-20P) to obtain
(4R,5S,6S,8R,2'S,4'S)-3-[4-(2-dimethylaminecarbonyl)pyrrolidinylthio]-4-
methyl-6-(1-hydroxyethyl)-1-azabicyclo[3,2,0]hept-2-ene-7-one-2-carboxylic acid from the fraction eluted with water.
brand name
Merrem I.V. (AstraZeneca).
Therapeutic Function
Antibiotic
Pharmacokinetics
Meropenem is a broad-spectrum carbapenem antibiotic. It is active against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Meropenem exerts its action by penetrating bacterial cells readily and interfering with the synthesis of vital cell wall components, which leads to cell death.
Clinical Use
Meropenem is a synthetic carbapenem possessing a complex side chain at C-3. It also has a chiral methyl group at C-4. This methyl group conveys intrinsic resistance to hydrolysis by dehydropeptidase-1. As a consequence, it can be administered as a single agent for the treatment of severe bacterial infections.
in vitro
the meropenem mics for penicillin-resistant streptococcus pneumoniae were higher than for the penicillin-susceptible strains but the organisms remained susceptible. clinical susceptibility in vitro to meropenem was defined by mics of ≤4 mg/l, intermediate susceptibility by mics of 8 mg/l and mics of ≥16 mg/l define resistance; equivalent figures for zones of growth inhibition were ≥14 (susceptible), 12-13 (intermediate) and ≤11 (resistant) mm [1].meropenem was 2- to 4-fold more active than imipenem against gram-negative organisms and its spectrum of antimicrobial activity was wider than those of all other drugs tested.meropenem inhibited all anaerobic bacteria at less than or equal to 8 mg/l and 0.25 mg/l inhibited 50% of strains. meropenem mics were not significantly influenced by high inocula and the drug was generally bactericidal [2]. meropenem bound most strongly to penicillin-binding protein 2 of escherichia coli and pseudomonas aeruginosa, and to penicillin-binding proteins 1 of staphylococcus aureus [3].meropenem had one identified metabolite, a β-lactam ring-opened form which is devoid of microbiological activity [4].
in vivo
in rabbits, meropenem significantly increased the plamsa total clearance of valproate to about 1.5 times compared to the control (6.09 ml/min/kg vs. 4.28 ml/min/kg). meropenem significantly increased the urinary excretion of valproate- glucuronide in rabbits [5].
Metabolism
Primarily excreted unchanged. There is one metabolite which is microbiologically inactive.
References
[1] edwards j r. meropenem: a microbiological overview [j]. journal of antimicrobial chemotherapy, 1995, 36 (suppl a): 1-17.
[2] jones r n, barry a l, tbornsberry c. in-vitro studies of meropenem [j]. journal of antimicrobial chemotherapy, 1989, 24 (suppl a): 9-29.
[3] yang y, bhachech n, bush k. biochemical comparison of imipenem, meropenem and biapenem: permeability, binding to penicillin-binding proteins, and stability to hydrolysis by β-lactamases [j]. journal of antimicrobial chemotherapy, 1995, 35 (1): 75-84.
[4] drusano g l, hutchison m. the pharmacokinetics of meropenem [j]. scandinavian journal of infectious diseases.supplementum, 1994, 96: 11-16.
Properties of Meropenem
| Boiling point: | 627.4±55.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.42±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Store in freezer, under -20°C |
| solubility | insoluble in EtOH; ≥19.15 mg/mL in DMSO; ≥9.88 mg/mL in H2O with ultrasonic |
| form | solid |
| pka | 4.27±0.60(Predicted) |
| color | White to off-white |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C17H25N3O5S/c1-7-12-11(8(2)21)16(23)20(12)13(17(24)25)14(7)26-9-5-10(18-6-9)15(22)19(3)4/h7-12,18,21H,5-6H2,1-4H3,(H,24,25)/t7-,8-,9+,10+,11-,12-/m1/s1 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 96036-03-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Meropenem (96036-03-2) |
Safety information for Meropenem
Computed Descriptors for Meropenem
| InChIKey | DMJNNHOOLUXYBV-PQTSNVLCSA-N |
| SMILES | N12[C@@]([H])([C@@H]([C@H](O)C)C1=O)[C@@H](C)C(S[C@H]1C[C@@H](C(N(C)C)=O)NC1)=C2C(O)=O |
Meropenem manufacturer
Honour Lab Limited
Aspen Biopharma Labs Pvt Ltd
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
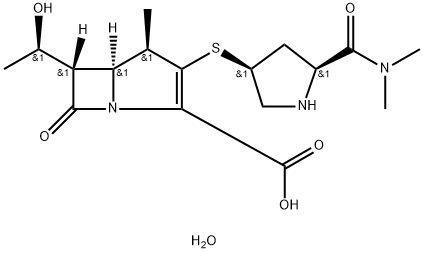

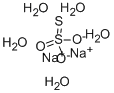
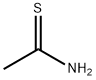
You may like
-
 96036-03-2 Meropenem 98%View Details
96036-03-2 Meropenem 98%View Details
96036-03-2 -
 96036-03-2 99%View Details
96036-03-2 99%View Details
96036-03-2 -
 Meropenem 95% CAS 96036-03-2View Details
Meropenem 95% CAS 96036-03-2View Details
96036-03-2 -
 Meropenem 98% (HPLC) CAS 96036-03-2View Details
Meropenem 98% (HPLC) CAS 96036-03-2View Details
96036-03-2 -
 96036-03-2 Meropenem 98%View Details
96036-03-2 Meropenem 98%View Details
96036-03-2 -
 Meropenem 98%View Details
Meropenem 98%View Details
96036-03-2 -
 Meropenem 95.00% CAS 96036-03-2View Details
Meropenem 95.00% CAS 96036-03-2View Details
96036-03-2 -
 Meropenem >98% (HPLC) CAS 96036-03-2View Details
Meropenem >98% (HPLC) CAS 96036-03-2View Details
96036-03-2