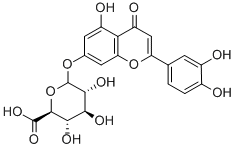
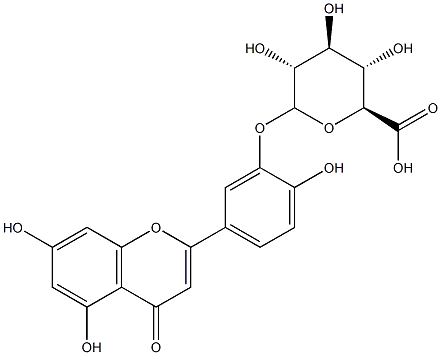
Luteolin
Synonym(s):3ʹ,4ʹ,5,7-Tetrahydroxyflavone;3′,4′,5,7-Tetrahydroxyflavone;Luteolin - CAS 491-70-3 - Calbiochem
- CAS NO.:491-70-3
- Empirical Formula: C15H10O6
- Molecular Weight: 286.24
- MDL number: MFCD00017309
- EINECS: 207-741-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-23 13:58:55
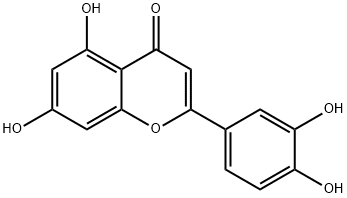
What is Luteolin?
Description
Luteolin is a flavone derived from Honeysuckle(Lonicera japonica Thunb). Luteolin is widely distributed in nature. It can be isolated from a variety of natural herbs, vegetables, and fruits. At present, luteolin is found mainly in honeysuckle, chrysanthemum, Schizonepeta, Ajuga, artichokes, Scutellaria, and Callicarpa nudiflora natural herbs. Dietary sources include celery, broccoli, green pepper, parsley, thyme, dandelion, perilla, chamomile tea, carrots, olive oil, peppermint, rosemary, navel oranges, and oregano. It can also be found in the seeds of the palm Aiphanes aculeata.
Description
Luteolin is a flavonoid found in many plants, including celery, thyme, green peppers, and chamomile tea. It was first reported by A. G. Perkin and colleagues in 1896. It plays several helpful roles in the human body. D. Hwang and co-workers recently showed that luteolin acts as an anti-inflammatory agent in the body by targeting the enzyme TBK1.
Chemical properties
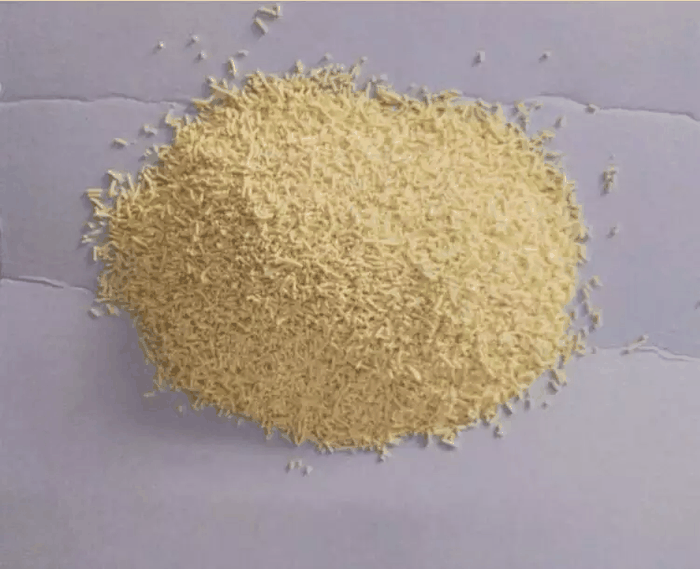
Yellow Needles
Physical properties
Appearance: yellow needle crystal. Solubility: slightly soluble in water and soluble in alkaline solution (monohydrate). Density, 1.654 g/cm3. Melting point, 330 °C. Boiling point, 616.1 °C (760 mmHg). Flash point, 239.5 °C. Vapor pressure, 9.03E-16 mmHg (25 °C). Acidity, weak acid.
History
At present, luteolin does not have the application of the proprietary medicine, but as
one of the main active ingredients of medicinal plants, there is a long history of
application. In northern and southern dynasties, honeysuckle with sweet taste, nontoxic, can treat swelling, lose weight, and prolong life under long-term use. In Tang dynasty, honeysuckle was used for treatment of abdominal distension, hot toxic blood dysentery, and water dysentery. It was showed that the clinical application of honeysuckle had made significant progress.
During the Song and Yuan dynasties, honeysuckle was widely used for the treatment of diseases such as sore and ulcer. To the Ming dynasty, there were many treatises about honeysuckle. For example, it is said in Compendium of Materia Medica: honeysuckle cure all rheumatism QI and all sorts of swollen poison, ulcer,scab, and heat dissipation detoxify. The prescription has also expanded its scope of application. Up to the Qing dynasty, the application of honeysuckle can not only inherit the theory of the predecessors but also put forward some original ideas and innovation in some respects.
In recent years, through the in-depth study of pharmacological effects, it is found that luteolin has significant effects on antitumor, cardioprotection, neuroprotection,respiratory system, immune regulation, anti-inflammatory, spasmolysis, expectorant, anti-allergic, enzyme activities, antioxidant, diuretic, and other aspects.
The Uses of Luteolin
Luteolin has been used:
- to induce and elucidate the apoptotic pathway in renal cell carcinoma 786-O cells
- as an additive in M9 minimal medium to induce nodF gene expression
- as a reference standard to qualitatively and quantitatively analyse luteolin using reverse phase-high performance liquid chromatography with diode array detector (RP-HPLC-DAD)
- as a reaction supplement for β-galactosidase assay
- to elucidate the anti-inflammatory efficacy of luteolin in pseudorabies virus infected RAW264.7 cell line by measuring the anti-inflammatory mediators production and also cell viability and cytotoxicity assay
What are the applications of Application
Luteolin is an inhibitor of LPS-induced TNF-α, IL-6 and inducible nitric oxide production and blocker of NF-κB and AP-1 activation.
Indications
Luteolin compound prescription is mainly used for relieving cough, eliminating phlegm, diminishing inflammation, treating cardiovascular diseases, and treating amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), hepatitis, etc.
Definition
ChEBI: Luteolin is a tetrahydroxyflavone in which the four hydroxy groups are located at positions 3', 4', 5 and 7. It is thought to play an important role in the human body as an antioxidant, a free radical scavenger, an anti-inflammatory agent and an immune system modulator as well as being active against several cancers. It has a role as an EC 2.3.1.85 (fatty acid synthase) inhibitor, an antineoplastic agent, a vascular endothelial growth factor receptor antagonist, a plant metabolite, a nephroprotective agent, an angiogenesis inhibitor, a c-Jun N-terminal kinase inhibitor, an anti-inflammatory agent, an apoptosis inducer, a radical scavenger and an immunomodulator. It is a 3'-hydroxyflavonoid and a tetrahydroxyflavone. It is a conjugate acid of a luteolin-7-olate.
General Description
Luteolin is a naturally occurring flavone, readily present in vegetables. It may possess many biological properties like anti-tumor activity against condition of skin papilloma. Luteolin is one of the most potent flavanoid inhibitors of soybean and reticulocyte 15-lipoxygenases, with an IC50 of 0.6 μM. Luteolin has also been found to inhibit the release of TNFα from neutrophils, and to inhibit matrix metalloproteinases.
Biological Activity
Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and free radical scavenger. Inhibits LPS-induced TNF- α , IL-6 and inducible nitric oxide production and blocks NF- κ B and AP-1 activation. Antiproliferative; inhibits proliferation of Lewis lung carcinoma cells in vivo .
Biochem/physiol Actions
Hydroxylated flavone derivative, a strong antioxidant and radical scavenger. Suggested to play a role in prevention of cancer, possibly via the inhibition of fatty acid synthase activity.
Pharmacology
Luteolin can selectively inhibit the fatty acid synthase activity in prostate cancer and breast cancer cells, which is related to the inhibitory effect of luteolin on tumor cell growth and apoptosis. Luteolin can significantly reduce the incidence of colon cancer and the size of tumor caused by dimethylhydrazine, which may be related to the
regulation of lipid peroxidation, antioxidation, and antiproliferative effect.
The anti-inflammatory activity of luteolin is related to the inhibition of nitric oxide (NO) and other inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) generation and inhibition of protein tyrosine phosphorylation and nuclear transcription factor KB (NF-KB)-mediated gene expression.
Luteolin can enhance the transfer of synapses in the hippocampus dentate gyrus, causing long-term potentiation. Moreover, in chronic hypoperfusion injury caused by vascular occlusion, luteolin can still protect synapses, causing long-term potentiation, and reduce the escape latency in the Morris water maze test in rats.
Luteolin can reduce the degree of hepatic fibrosis, hydroxyproline level in liver tissues (HYP), malondialdehyde (MDA) content, and mRNA expression of procollagen type I and inhibit hepatic stellate cell (HSC) proliferation and collagen synthesis in vitro. Luteolin can also improve the histological changes of pulmonary fibrosis induced by bleomycin, reduce the lung weight index, significantly reduce the increase in MDA and HYP, and inhibit the level of mRNA of transforming
growth factor beta 1 (TGF-β1) in lung tissue. Luteolin in vitro can inhibit the proliferation of human embryonic lung fibroblast cells and promote apoptosis .
Anticancer Research
It is a flavone with yellow crystalline appearance. Dietary sources of luteolin includeoregano, celery, orange, broccoli, rosemary, green pepper, peppermint, parsley,olive oil, thyme, carrot, dandelion, chamomile tea, and perilla. It is found to obstructepithelial-mesenchymal transition (Singh et al. 2016b). It is inhibiting the cancercell proliferation, angiogenesis, and metastasis. In addition, it suppresses thepathways like PI3K/AKT, NF-κB, and X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein(XIAP) which enhances the cell growth and function. It also induces apoptosis andtumor suppressor p53. Hence, luteolin can be used as a potential antineoplasticagent in different cancers (Lin et al. 2008).
Clinical Use
The natural extract containing luteolin has been used in clinical treatment of many diseases. Lamiophlomis rotata Kudo capsule is made from traditional Chinese medicine Lamiophlomis rotata Kudo, which consists of the medicinal components such as flavonoids, saponins, sterols, amino acids, and many trace elements. Among these components, luteolin content is not less than 0.80 mg/g. This capsule is mainly used for a variety of surgical incision pain, postoperative bleeding, fracture, sprain of muscles, rheumatic pain, dysmenorrhea, uterine bleeding, gingival swelling, and bleeding.
Storage
Store at +4°C
Properties of Luteolin
| Melting point: | ~330 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 348.61°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.2981 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.4413 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Methanol (Slightly, Heated) |
| form | powder |
| pka | 6.50±0.40(Predicted) |
| color | yellow |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in aqueous alkaline solutions (1.4 mg/ml), ethanol (~5 mg/ml), dimethyl sulfoxide (7 mg/ml), 1eq. Sodium hydroxide (5 mM), dimethylformamide (~20 mg/ml), water (1 mg/ml) at 25°C and methanol. |
| Merck | 14,5614 |
| BRN | 292084 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 491-70-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Luteolin (491-70-3) |
Safety information for Luteolin
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P304+P340:IF INHALED: Remove victim to fresh air and Keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P405:Store locked up. |
Computed Descriptors for Luteolin
| InChIKey | IQPNAANSBPBGFQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Luteolin 98%View Details
Luteolin 98%View Details -
 3',4',5,7-Tetrahydroxyflavone CAS 491-70-3View Details
3',4',5,7-Tetrahydroxyflavone CAS 491-70-3View Details
491-70-3 -
 Luteolin CAS 491-70-3View Details
Luteolin CAS 491-70-3View Details
491-70-3 -
 3',4',5,7-Tetrahydroxyflavone CAS 491-70-3View Details
3',4',5,7-Tetrahydroxyflavone CAS 491-70-3View Details
491-70-3 -
 Luteolin CAS 491-70-3View Details
Luteolin CAS 491-70-3View Details
491-70-3 -
 Luteolin 98% (HPLC) CAS 491-70-3View Details
Luteolin 98% (HPLC) CAS 491-70-3View Details
491-70-3 -
 Luteolin 99% (HPLC) CAS 491-70-3View Details
Luteolin 99% (HPLC) CAS 491-70-3View Details
491-70-3 -
 Luteolin 95% CAS 491-70-3View Details
Luteolin 95% CAS 491-70-3View Details
491-70-3
